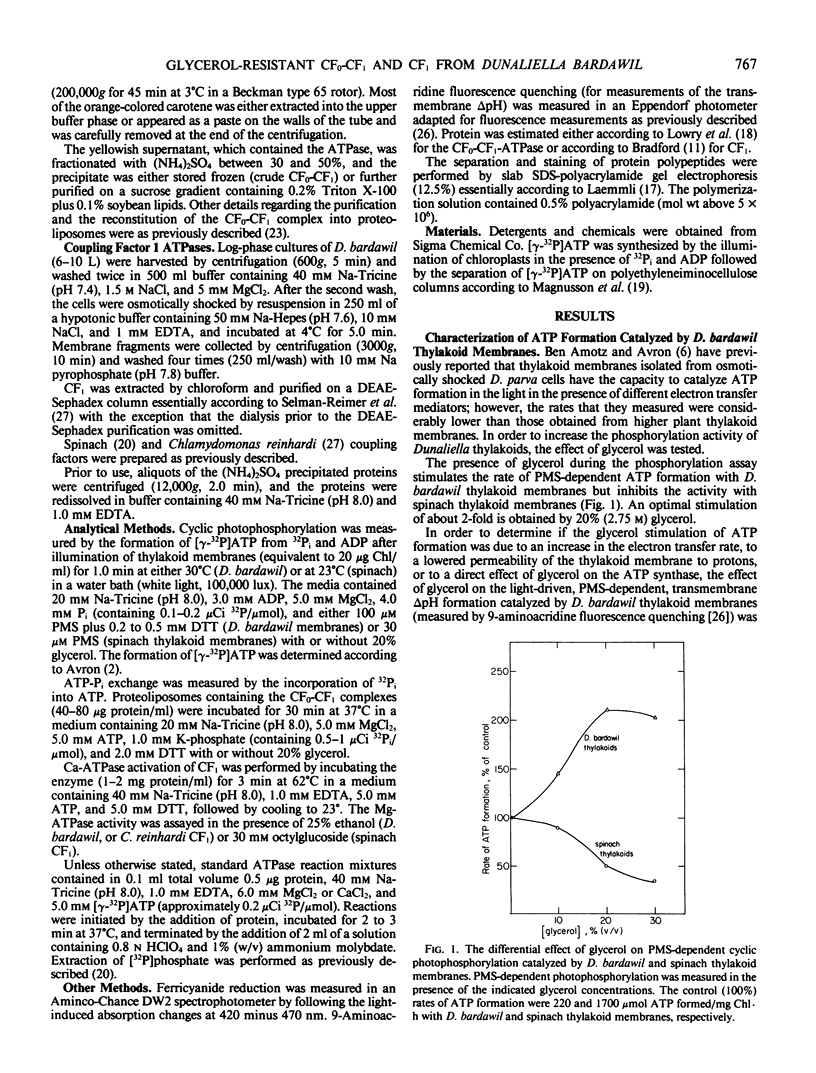
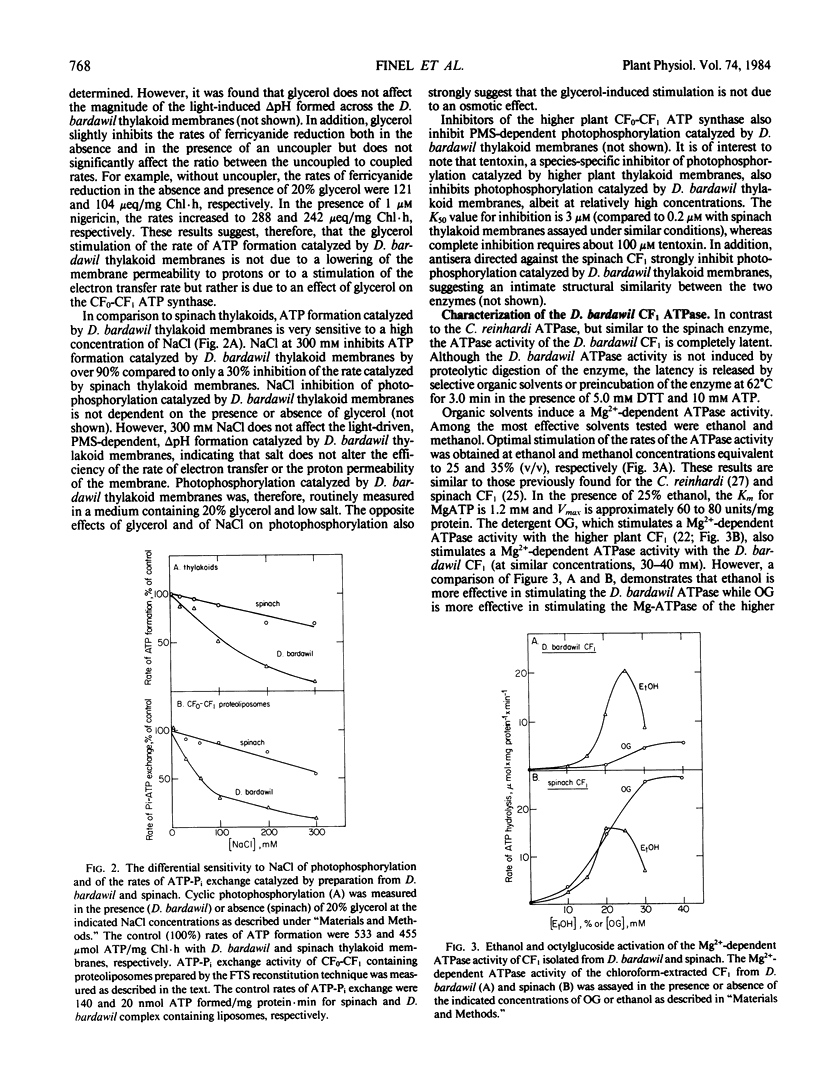
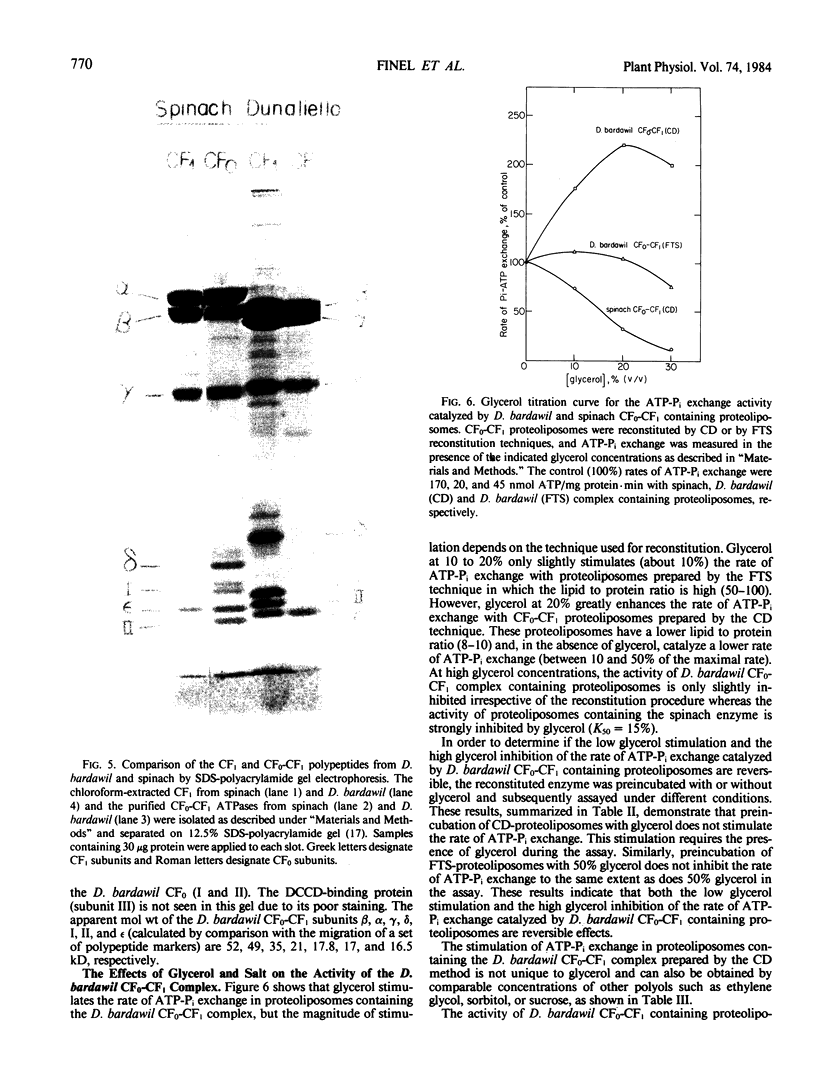
Abstract
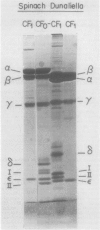
The isolation of the chloroplast ATP synthase complex (CF0-CF1) and of CF1 from Dunaliella bardawil is described. The subunit structure of the D. bardawil ATPase differs from that of the spinach in that the D. bardawil α subunit migrates ahead of the β subunit and ε-migrates ahead of subunit II of CF0 when separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The CF1 isolated from D. bardawil resembles the CF1 isolated from Chladmydomonas reinhardi in that a reversible, Mg2+-dependent ATPase is induced by selected organic solvents. Glycerol stimulates cyclic photophosphorylation catalyzed by D. bardawil thylakoid membranes but inhibits photophosphorylation catalyzed by spinach thylakoid membranes. Glycerol (20%) also stimulates the rate of ATP-Pi exchange catalyzed by D. bardawil CF0-CF1 proteoliposomes but inhibits the activity with the spinach enzyme. The ethanol-activated, Mg2+-ATPase of the D. bardawil CF1 is more resistant to glycerol inhibition than the octylglucoside-activated, Mg2+-ATPase of spinach CF1 or the ethanol-activated, Mg2+-dependent ATPase of the C. reinhardi CF1. Both cyclic photophosphorylation and ATP-Pi exchange catalyzed by D. bardawil CF0-CF1 are more sensitive to high concentrations of NaCl than is the spinach complex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVRON M. Photophosphorylation as a tool for the synthesis of specifically labeled nucleotides. Anal Biochem. 1961 Dec;2:535–543. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AVRON M. Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:257–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz A., Avron M. Photosynthetic Activities of the Halophilic Alga Dunaliella parva. Plant Physiol. 1972 Feb;49(2):240–243. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz A., Avron M. The Role of Glycerol in the Osmotic Regulation of the Halophilic Alga Dunaliella parva. Plant Physiol. 1973 May;51(5):875–878. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder A., Bachofen R. Isolation and characterization of a coupling factor I ATPase of the thermophilic blue-green alga (cyanobacterium) Mastigocladus laminosus. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):66–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka L. J., Brown A. D. The salt relations of marine and halophilic species of the unicellular green alga, Dunaliella. The role of glycerol as a compatible solute. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 1;96(1):37–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00590161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farron F., Racker E. Studies on the mechanism of the conversion of coupling factor 1 from chloroplasts to an active adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 15;9(19):3829–3836. doi: 10.1021/bi00821a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg M. The unusual membrane permeability of two halophilic unicellular organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):370–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson R. P., McCarty R. E. Light-induced exchange of nucleotides into coupling factor 1 in spinach chloroplast thylakoids. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7417–7422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Bassilian S. Activation of magnesium ion specific adenosinetriphosphatase in chloroplast coupling factor 1 by octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6144–6152. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Racker E. Purification and reconstitution of the N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive ATPase complex from spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2793–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E., Chien T. F., Kandrach A. A cholate-dilution procedure for the reconstitution of the Ca++ pump, 32Pi--ATP exchange, and oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):14–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai H., Shinohara K., Hisabori T., Shinohara K. Enhancement of adenosine triphosphatase activity of purified chloroplast coupling factor 1 in aqueous organic solvent. J Biochem. 1981 Jul;90(1):95–102. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Rottenberg H., Avron M. Determination of pH in chloroplasts. 2. Fluorescent amines as a probe for the determination of pH in chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):64–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selman-Reimer S., Merchant S., Selman B. R. Isolation, purification, and characterization of coupling factor 1 from Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 15;20(19):5476–5482. doi: 10.1021/bi00522a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]