Abstract
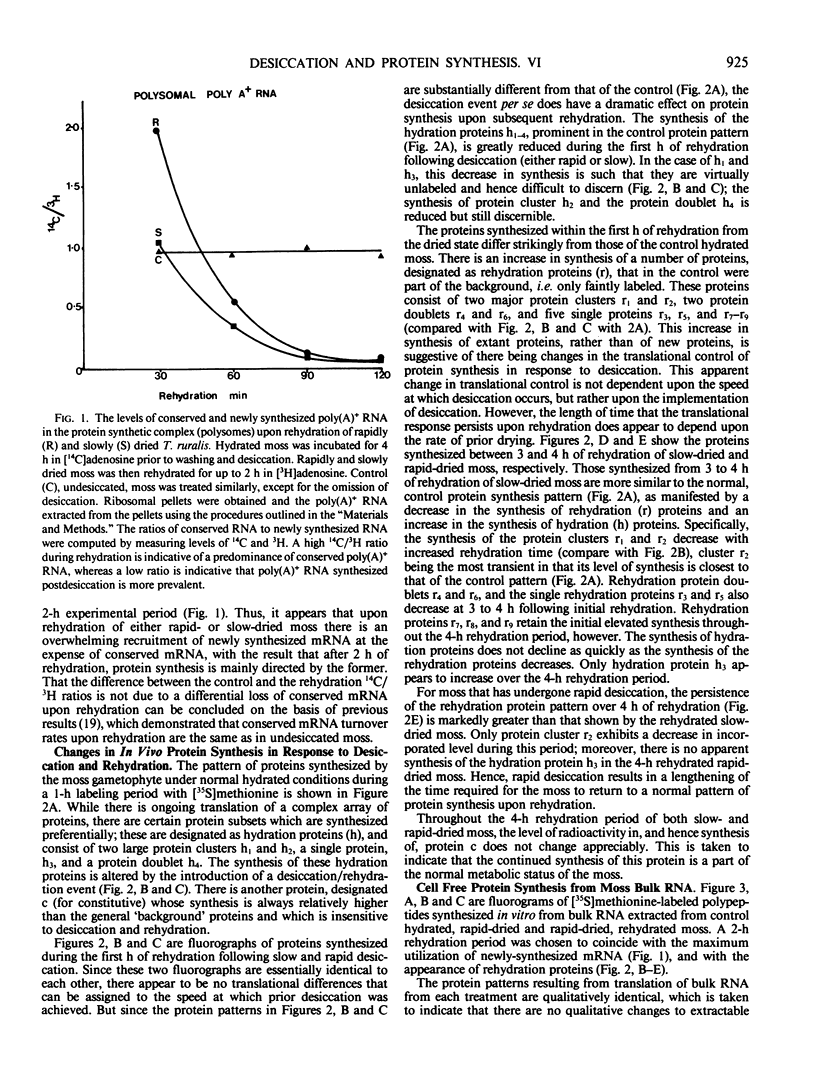
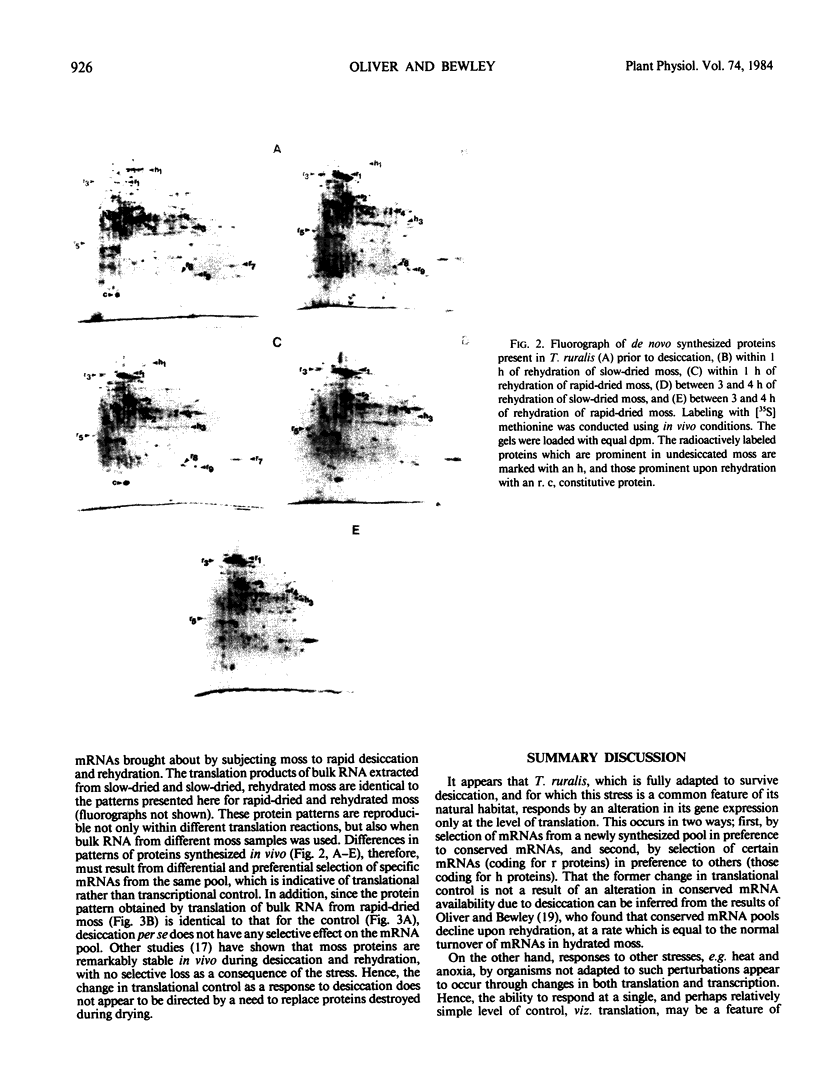
Upon rehydration of the moss Tortula ruralis following desiccation at a rapid or slow rate, there is increasing utilization of newly synthesized-poly(A)+ RNA for protein synthesis. Initially, poly(A)+ RNA conserved in the dry moss is associated with polysomes, but by 2 hours of rehydration there is an overwhelming recruitment of newly synthesized poly(A)+ RNA, at the expense of conserved messages. In rehydrated moss, there is a marked synthesis in vivo of new proteins, which are separable by two-dimensional electrophoresis, and identifiable by fluorography. These new proteins, termed rehydration proteins, are synthesized after both rapid and slow desiccation, but their synthesis persists longer after rapid desiccation. The protein patterns obtained following in vitro translation of bulk RNA from hydrated, desiccated, and rehydrated moss were qualitatively identical. Thus the differences in protein patterns observed in vivo must result from preferential selection of specific mRNAs from the same pool, which is indicative of control of protein synthesis at the translational level. The implications of these observations in relation to the response of the moss to drying in its natural environment are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baszczynski C. L., Walden D. B., Atkinson B. G. Regulation of gene expression in corn (Zea Mays L.) by heat shock. Can J Biochem. 1982 May;60(5):569–579. doi: 10.1139/o82-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley J. D., Gwódź E. A. Plant Desiccation and Protein Synthesis: II. On the Relationship between Endogenous Adenosine Triphosphate Levels and Protein-synthesizing Capacity. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jun;55(6):1110–1114. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.6.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner M. H., Chin M. B., Lane B. G. Wheat embryo ribonucleates. XII. Formal characterization of terminal and penultimate nucleoside residues at the 5'-ends of "capped" RNA from imbibing wheat embryos. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jul;56(7):729–733. doi: 10.1139/o78-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocquot B., Prat C., Mouches C., Pradet A. Effect of anoxia on energy charge and protein synthesis in rice embryo. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):636–640. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver M. J., Bewley J. D. Plant Desiccation and Protein Synthesis : V. Stability of Poly (A) and Poly (A) RNA during Desiccation and Their Synthesis upon Rehydration in the Desiccation-Tolerant Moss Tortula ruralis and the Intolerant Moss Cratoneuron filicinum. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):917–922. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver M. J., Bewley J. D. Plant Desiccation and Protein Synthesis. IV. RNA Synthesis, Stability, and Recruitment of RNA into Protein Synthesis during Desiccation and Rehydration of the Desiccation-Tolerant Moss, Tortula ruralis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):21–25. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]