Abstract
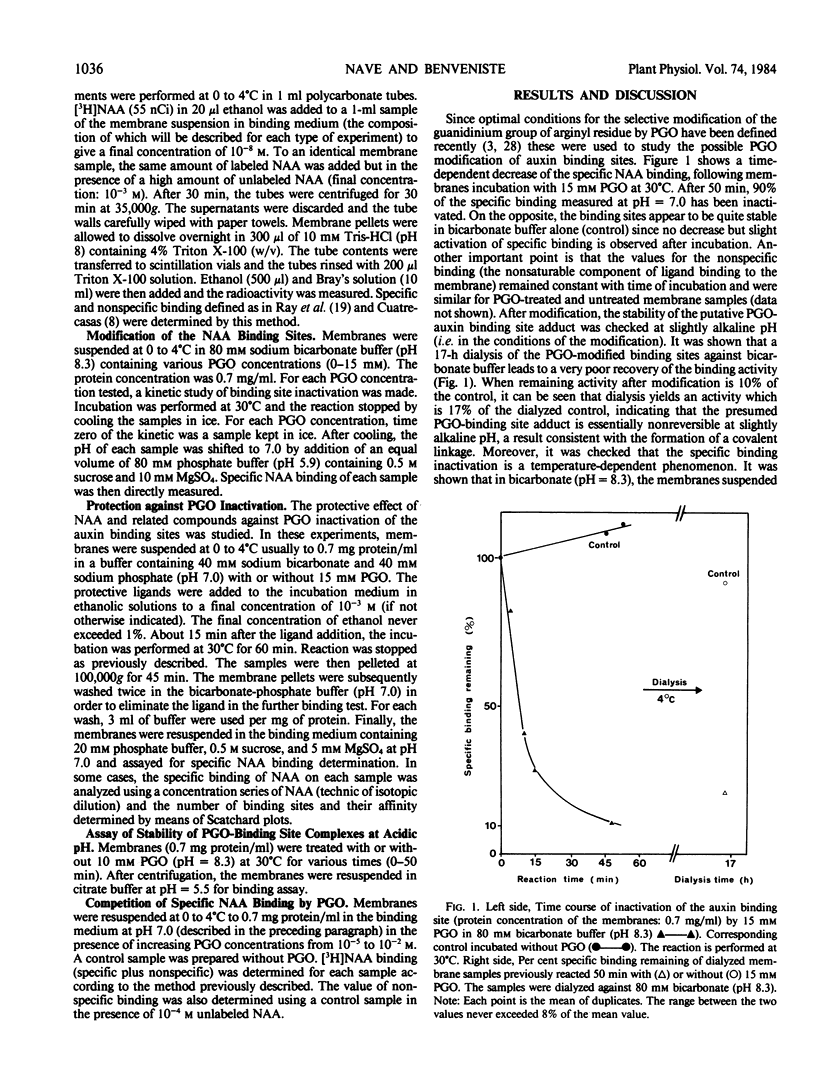
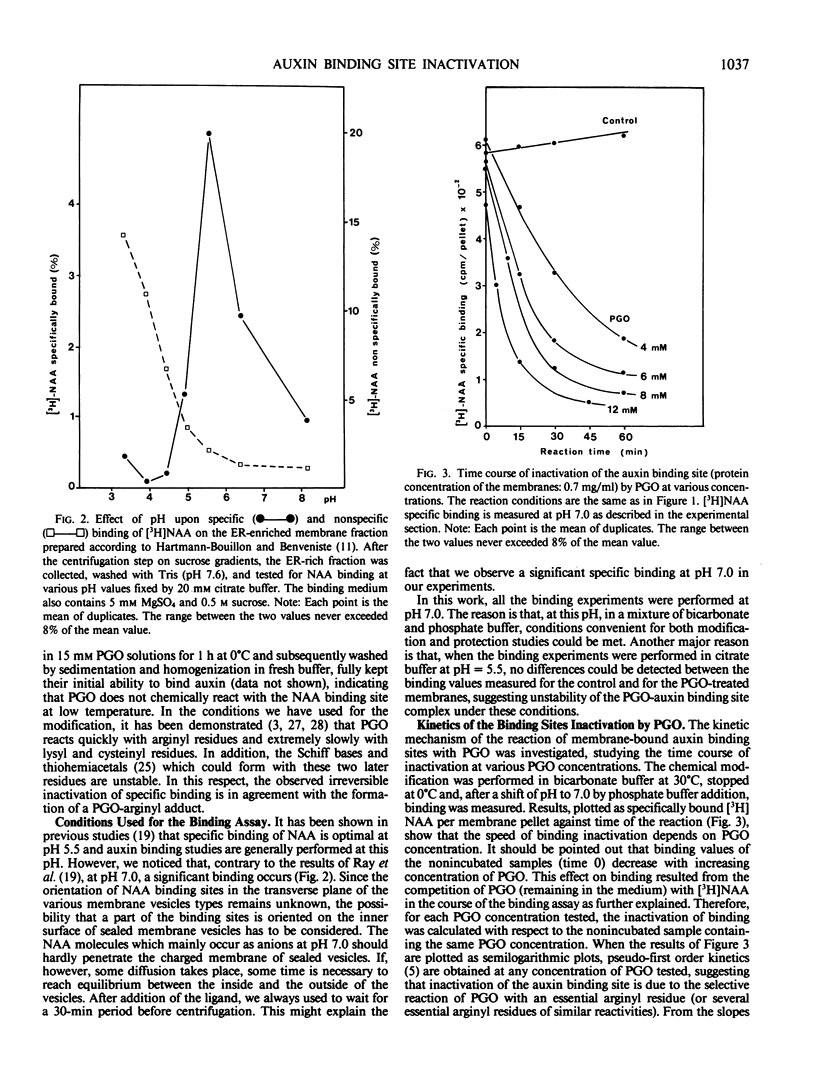
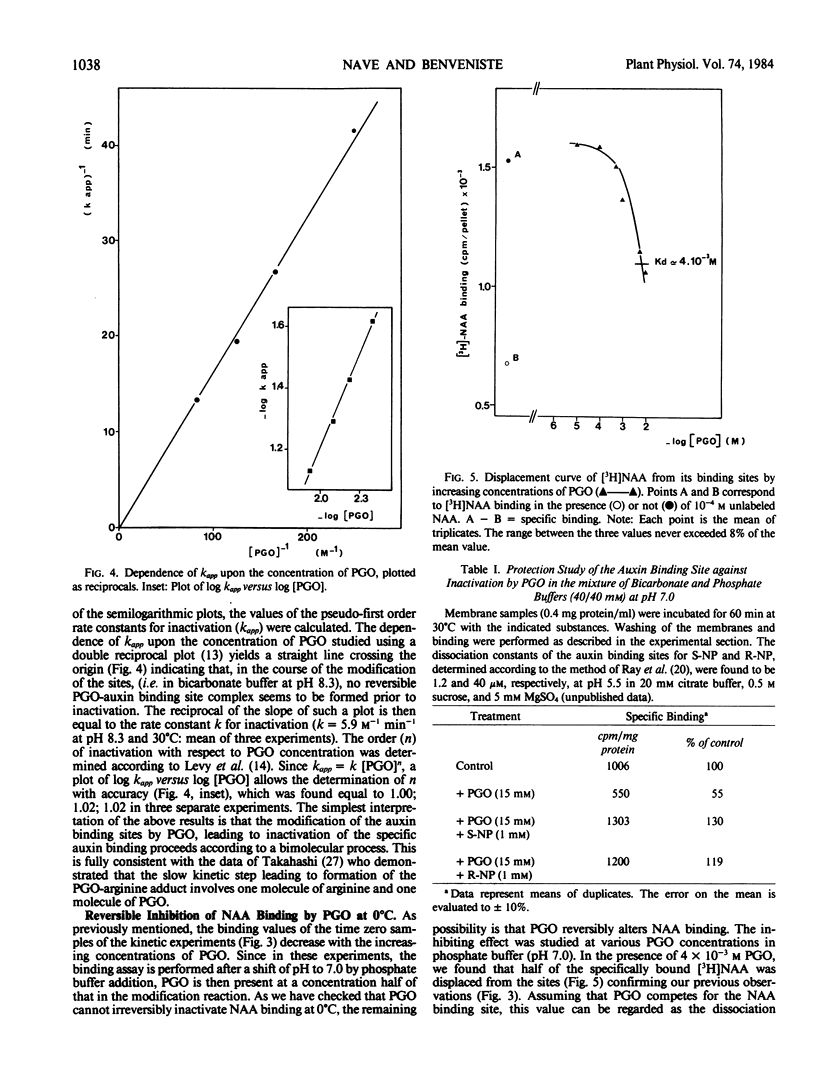
The specific binding of 1-[3H]naphthyl acetic acid (NAA) to membrane-bound binding sites from maize (Zea mays cv INRA 258) coleoptiles is inactivated by phenylglyoxal. The inactivation obeys pseudo first-order kinetics. The rate of inactivation is proportional to phenylglyoxal concentration. Under conditions at which significant binding occurs, NAA, R and S-1-naphthyl 2-propionic acids protect the auxin binding site against inactivation by phenylglyoxal. Scatchard analysis shows that the inhibition of binding corresponds to a decrease in the concentration of sites but not in the affinity. The results of the present chemical modification study indicate that at least one arginyl residue is involved in the positively charged recognition site of the carboxylate anion of NAA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. J., Buehner M., Chandrasekhar K., Ford G. C., Hackert M. L., Liljas A., Rossmann M. G., Smiley I. E., Allison W. S., Everse J. Structure-function relationships in lactate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1968–1972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung S. T., Fonda M. L. Kinetics of the inactivation of Escherichia coli glutamate apodecarboxylase by phenylglyoxal. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Dec;198(2):541–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung S. T., Fonda M. L. Reaction of phenylglyoxal with arginine. The effect of buffers and pH. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):940–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91918-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. W., Briggs W. R. Properties of a Solubilized Microsomal Auxin-binding Protein from Coleoptiles and Primary Leaves of Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):152–157. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):169–214. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITZ R., WILSON I. B. Esters of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3245–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY H. M., LEBER P. D., RYAN E. M. INACTIVATION OF MYOSIN BY 2,4-DINITROPHENOL AND PROTECTION BY ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE AND OTHER PHOSPHATE COMPOUNDS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3654–3659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L., Thész J. Origin of the selectivity of alpha-dicarbonyl reagents for arginyl residues of anion-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):387–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. C., Hatefi Y. Inhibition of D(--)-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase by butanedione, phenylglyoxal, and diethyl pyrocarbonate. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):459–463. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M. Auxin-binding Sites of Maize Coleoptiles Are Localized on Membranes of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):594–599. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M., Dohrmann U. Characterization of naphthaleneacetic Acid binding to receptor sites on cellular membranes of maize coleoptile tissue. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):357–364. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. M. Specificity of Auxin-binding Sites on Maize Coleoptile Membranes as Possible Receptor Sites for Auxin Action. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):585–591. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. F. Functional arginyl residues in carboxypeptidase A. Modification with butanedione. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3915–3923. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. F., McElvany K. D., Borders C. L., Jr Arginyl residues: anion recognition sites in enzymes. Science. 1977 Mar 4;195(4281):884–886. doi: 10.1126/science.190679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoun H., Beppu T., Arima K. An essential arginine residue at the substrate-binding site of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9319–9324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. The reaction of phenylglyoxal with arginine residues in proteins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6171–6179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K. The reactions of phenylglyoxal and related reagents with amino acids. J Biochem. 1977 Feb;81(2):395–402. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


