Abstract
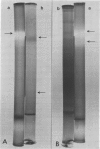
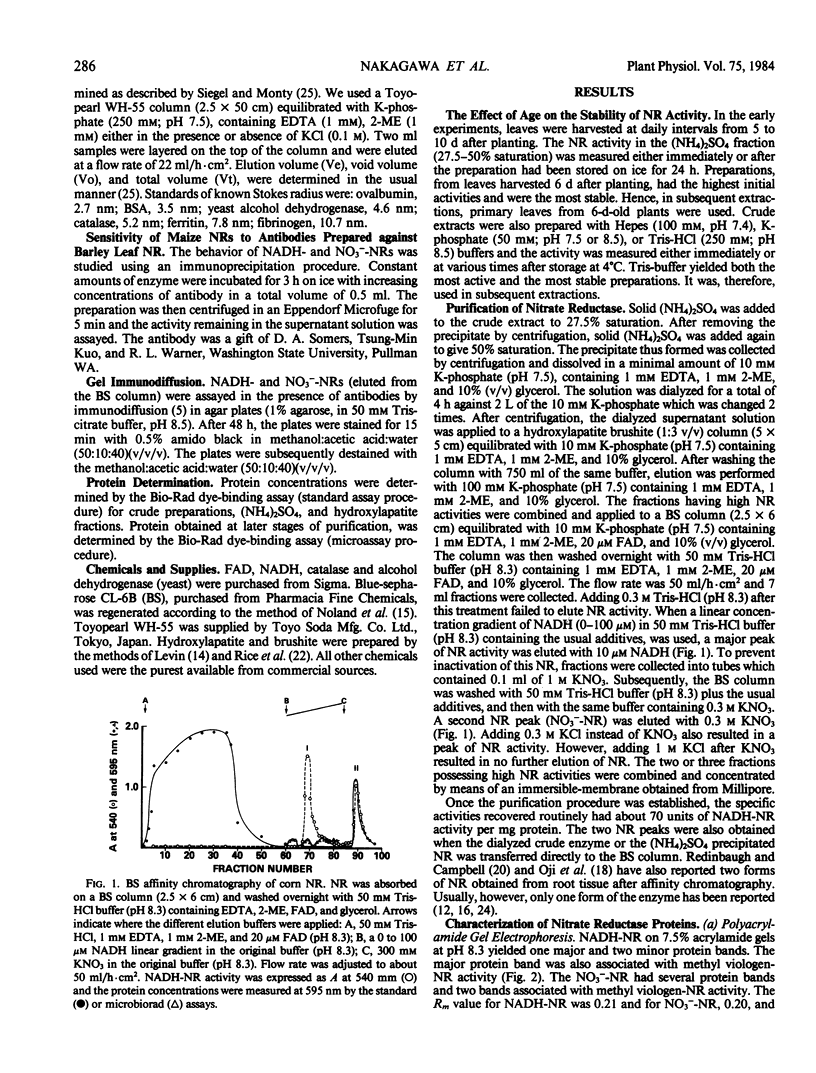
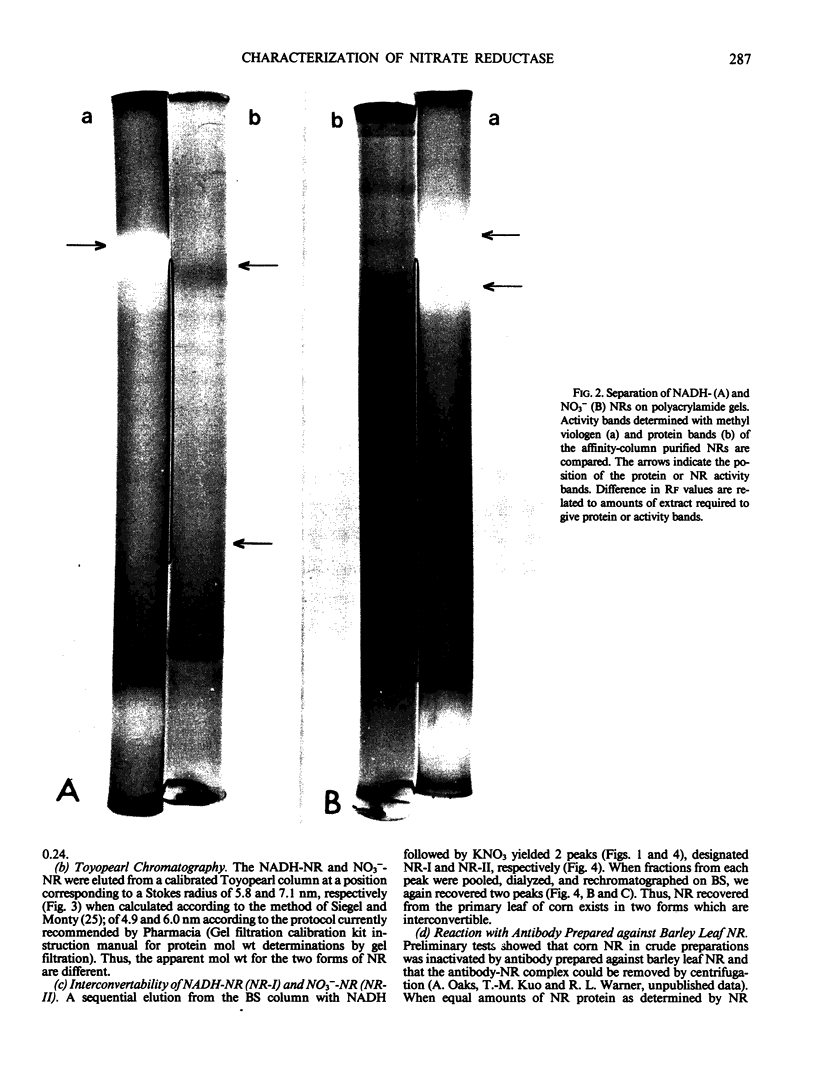
The primary leaves from corn seedlings grown for 6 days were harvested, frozen with liquid N2 and extracted in a Tris buffer (pH 8.5, 250 millimolar) containing 1 millimolar dithiothreitol, 10 millimolar cysteine, 1 millimolar EDTA, 20 micromolar flavin adenine dinucleotide and 10% (v/v) glycerol. Nitrate reductase (NR) in the crude extract was stable for several days at 0°C and for several months at −80°C. The enzyme was purified using (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, brushite-hydroxyl-apatite chromatography and blue-sepharose affinity chromatography. The enzyme was eluted from the blue-sepharose column with a linear gradient of NADH (0-100 micromolar) or with 0.3 molar KNO3. About 10% of the original activity was recovered with NADH (NADH-NR). It had a specific activity of about 60 to 70 units (micromoles NO2− per minute per milligram protein). A sequential elution with NADH followed by KNO3 (0.3 molar) or KCl (0.3 molar) yielded 2 peaks. Rechromatography of each peak gave two peaks again. These results indicate that we are dealing with two forms of the same enzyme rather than two different NR proteins. The two NRs had different molecular weights as judged by chromatography on Toyopearl. The NADH-NR was more sensitive than the NO3−-NR to antibody prepared against barley leaf NR. In Ouchterlony assays a single precipitin line, with completely fused boundaries, was observed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aslam M., Oaks A. Comparative studies on the induction and inactivation of nitrate reductase in corn roots and leaves. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):572–576. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. H., Smarrelli J. Purification and Kinetics of Higher Plant NADH:Nitrate Reductase. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):611–616. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero M. G., Jetschmann K., Völker W. The stereospecificity of nitrate reductase for hydrogen removal from reduced pyridine nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 12;482(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90349-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer Y. M., Krashin S., Riklis E. The use of affinity chromatography for the purification of nitrate reductase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 1;62(1):30–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard W. D., Solomonson L. P. Quaternary structure of assimilatory NADH:nitrate reductase from Chlorella. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10243–10250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noland B. J., Arebalo R. E., Hansbury E., Scallen T. J. Purification and properties of sterol carrier protein2. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4282–4289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks A., Wallace W., Stevens D. Synthesis and turnover of nitrate reductase in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1972 Dec;50(6):649–654. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.6.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinbaugh M. G., Campbell W. H. Purification and Characterization of NAD(P)H:Nitrate Reductase and NADH:Nitrate Reductase from Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):115–120. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redinbaugh M. G., Campbell W. H. Purification of Squash NADH:Nitrate Reductase by Zinc Chelate Affinity Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):205–207. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice H. V., Briggs W. R., Jackson-White C. J. Purification of oat and rye phytochrome. Plant Physiol. 1973 May;51(5):917–926. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.5.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader L. E., Ritenour G. L., Eilrich G. L., Hageman R. H. Some characteristics of nitrate reductase from higher plants. Plant Physiol. 1968 Jun;43(6):930–940. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrard J. H., Dalling M. J. In vitro stability of nitrate reductase from wheat leaves: I. Stability of highly purified enzyme and its component activities. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):346–353. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomonson L. P., Lorimer G. H., Hall R. L., Borchers R., Bailey J. L. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-nitrate reductase of Chlorella vulgaris. Purification, prosthetic groups, and molecular properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4120–4127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomonson L. P. Purification of NADH-Nitrate Reductase by Affinity Chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1975 Dec;56(6):853–855. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.6.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zielke H. R., Filner P. Synthesis and turnover of nitrate reductase induced by nitrate in cultured tobacco cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1772–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa M. A., Diez J., Vega J. M., Losada M. Purification and properties of assimilatory nitrate reductase [NAD(P)H] from Ankistrodesmus braunii. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]