Abstract
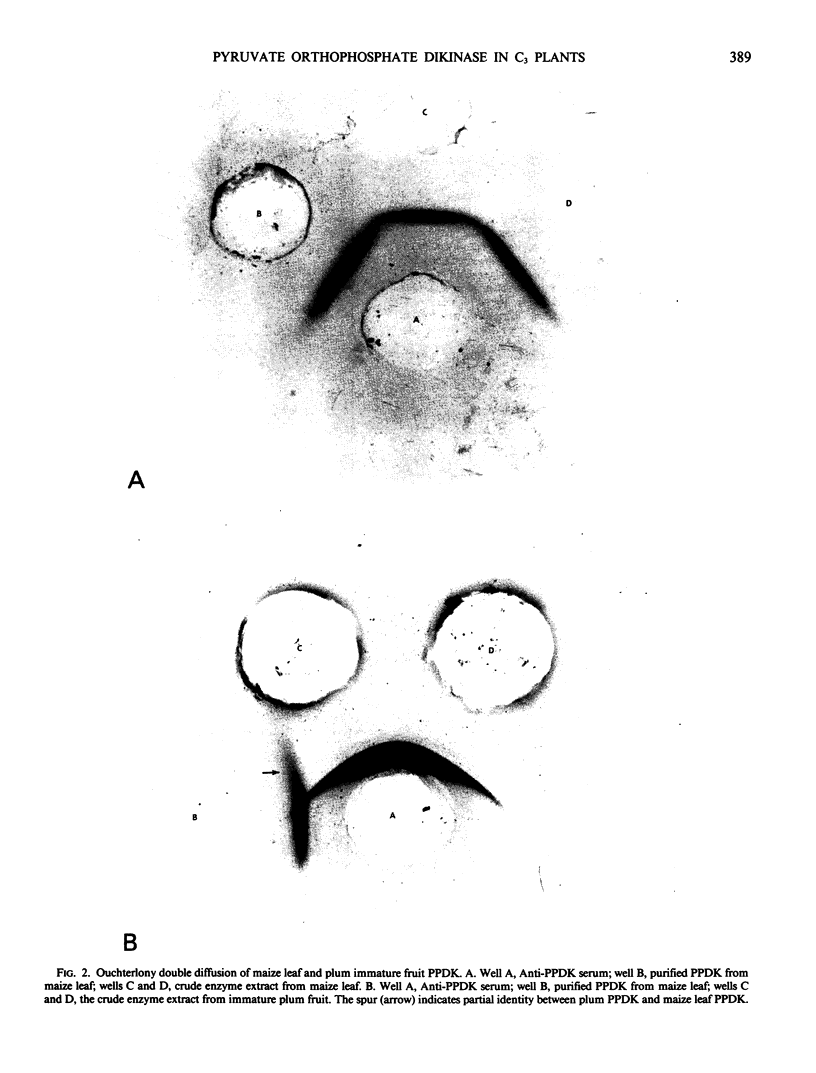
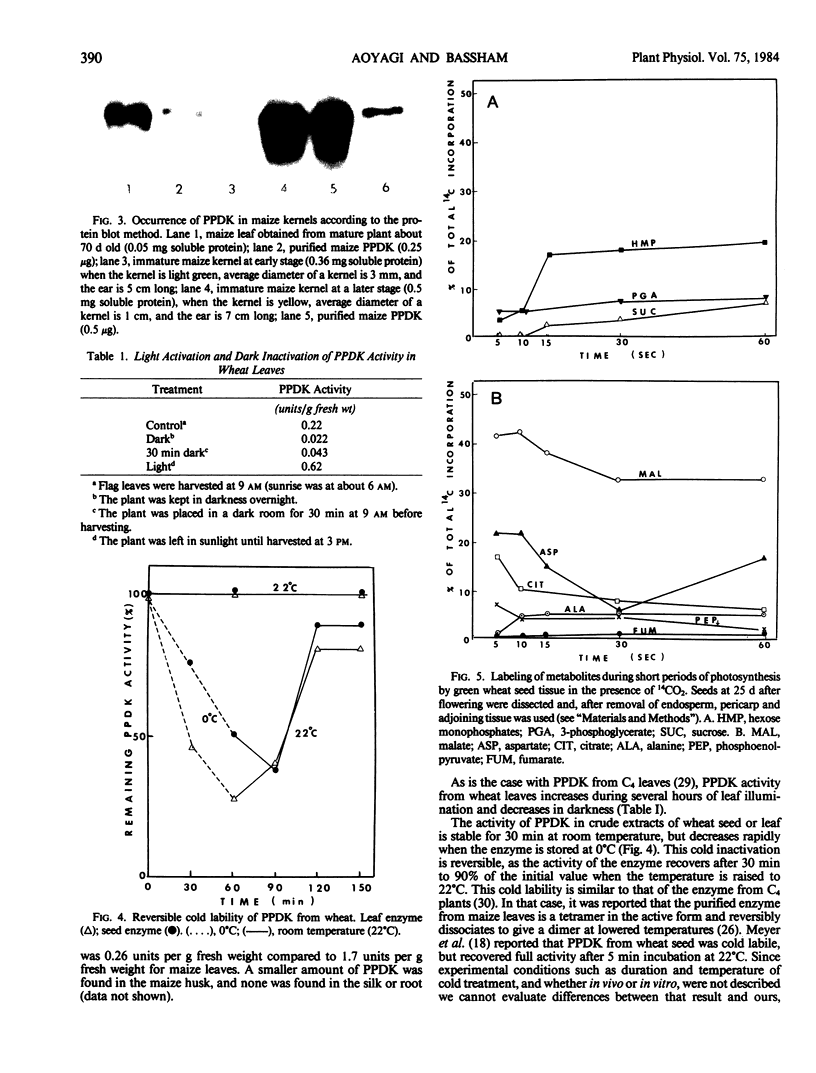
Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase (PPDK) was found in various immature seeds of C3 plants (wheat, pea, green bean, plum, and castor bean), in some C3 leaves (tobacco, spinach, sunflower, and wheat), and in C4 (maize) kernels. The enzyme in the C3 plants cross-reacts with rabbit antiserum against maize PPDK. Based on protein blot analysis, the apparent subunit size of PPDK from wheat seeds and leaves and from sunflower leaves is about 94 kdaltons, the same as that of the enzyme from maize, but is slightly less (about 90 kdaltons) for the enzyme from spinach and tobacco leaves. The amount of this enzyme per mg of soluble protein in C3 seeds and leaves is much less than in C4 leaves. PPDK is present in kernels of the C4 plant, Zea mays in amounts comparable to those in C4 leaves.
Regulatory properties of the enzyme from C3 tissues (wheat) are similar to those of the enzyme from C4 leaves with respect to in vivo light activation and dark inactivation (in leaves) and in vivo cold lability (seeds and leaves).
Following incorporation of 14CO2 by illuminated wheat pericarp and adjoining tissue for a few seconds, the labeled metabolites were predominantly products resulting from carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate, with lesser labeling of compounds formed by carboxylation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate and operation of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle of photosynthesis. PPDK may be involved in mechanisms of amino acid interconversions during seed development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A., Greene F. C. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene expression in developing wheat seeds. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):393–396. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi K., Bassham J. A. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):853–854. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Hitzeman R., Carbon J. Selection of specific clones from colony banks by screening with radioactive antibody. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:436–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Slack C. R. A new enzyme for the interconversion of pyruvate and phosphopyruvate and its role in the C4 dicarboxylic acid pathway of photosynthesis. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1060141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer A. O., Kelly G. J., Latzko E. Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase from the immature grains of cereal grasses. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):7–10. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutbeam A. R., Duffus C. M. Evidence for C4 photosynthesis in barley pericarp tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 21;70(4):1198–1203. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt S., Reich R., Witt H. T. Electrochromism of chlorophylls and carotenoids in multilayers and in chloroplasts. Naturwissenschaften. 1971 Aug;58(8):414–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00591523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahashi K., Hayakawa S., Sugiyama T. Cold lability of pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase in the maize leaf. Plant Physiol. 1978 Nov;62(5):826–830. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.5.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T. Purification, molecular, and catalytic properties of pyruvate phosphate dikinase from the maize leaf. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 17;12(15):2862–2868. doi: 10.1021/bi00739a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]