Abstract
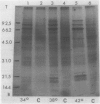
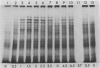
Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L. cv Wisconsin 38) cells grown in suspension culture at 26°C produce heat shock proteins (HSPs) when exposed to elevated temperature of 34 to 42°C. At 34 and 38°C, synthesis of normal proteins is maintained while HSPs are expressed within 30 minutes after initiation of the shock. At 42°C, HSPs are still expressed but normal proteins are made at a reduced rate or not at all. Exposure of cells to 38°C allows for a full expression of HSPs without inhibition of the synthesis of normal proteins. Induced synthesis of HSPs at 38°C is maximal 1 to 2 hours after elevation of temperature and diminishes thereafter through at least 6 hours. Cells growing asynchronously in the logarithmic phase of growth produce HSPs at a much higher rate than those in the stationary phase. The ability to synthesize HSPs disappears about one generation time before the cells reach a growth plateau.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):215–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Zeuthen E. Heat shock proteins in Tetrahymena studied under growth conditions. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jul;128(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn G. M., Li G. C. Thermotolerance and heat shock proteins in mammalian cells. Radiat Res. 1982 Dec;92(3):452–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. Temperature-resistant variants in clonal populations of pig kidney cells. Exp Cell Res. 1967 May;46(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle K. J., Dethlefsen L. A. Heat fractionation and thermotolerance: a review. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):1843–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Lin C. Y., Chen Y. M. Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Bernier D., Chrétien P., Nicole L. M., Tanguay R. M., Marceau N. Synthesis and degradation of heat shock proteins during development and decay of thermotolerance. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2457–2461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C. Induction of thermotolerance and enhanced heat shock protein synthesis in Chinese hamster fibroblasts by sodium arsenite and by ethanol. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):116–122. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Shrieve D. C. Thermal tolerance and specific protein synthesis in Chinese hamster fibroblasts exposed to prolonged hypoxia. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Dec;142(2):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister L., Finkelstein D. B. Heat shock proteins and thermal resistance in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):819–824. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read R. A., Fox M. H., Bedford J. S. The cell cycle dependence of thermotolerance. I. CHO cells heated at 42 degrees C. Radiat Res. 1983 Jan;93(1):93–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves O. R. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to acute heat shock in cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Apr;79(2):157–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040790202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenberg-Frascino A., Moustacchi E. Lethal and mutagenic effects of elevated temperature on haploid yeast. I. Variations in sensitivity during the cell cycle. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(3):243–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00268888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westra A., Dewey W. C. Variation in sensitivity to heat shock during the cell-cycle of Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(5):467–477. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]