Abstract
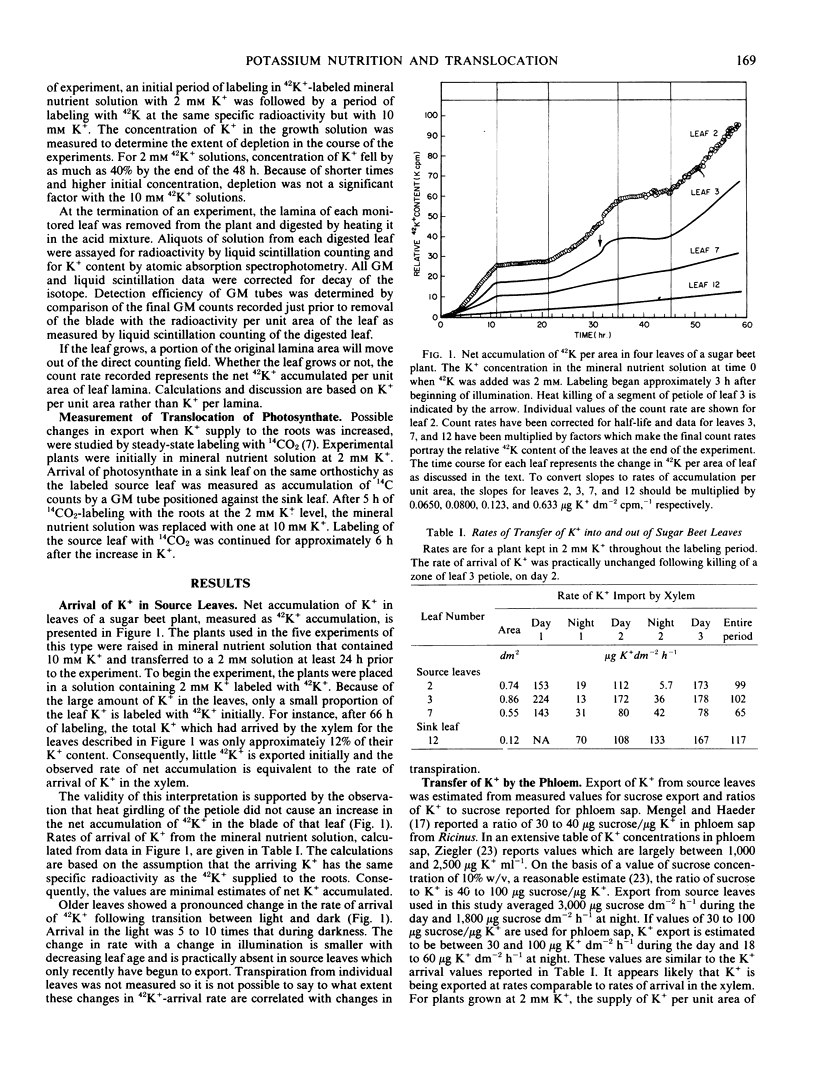
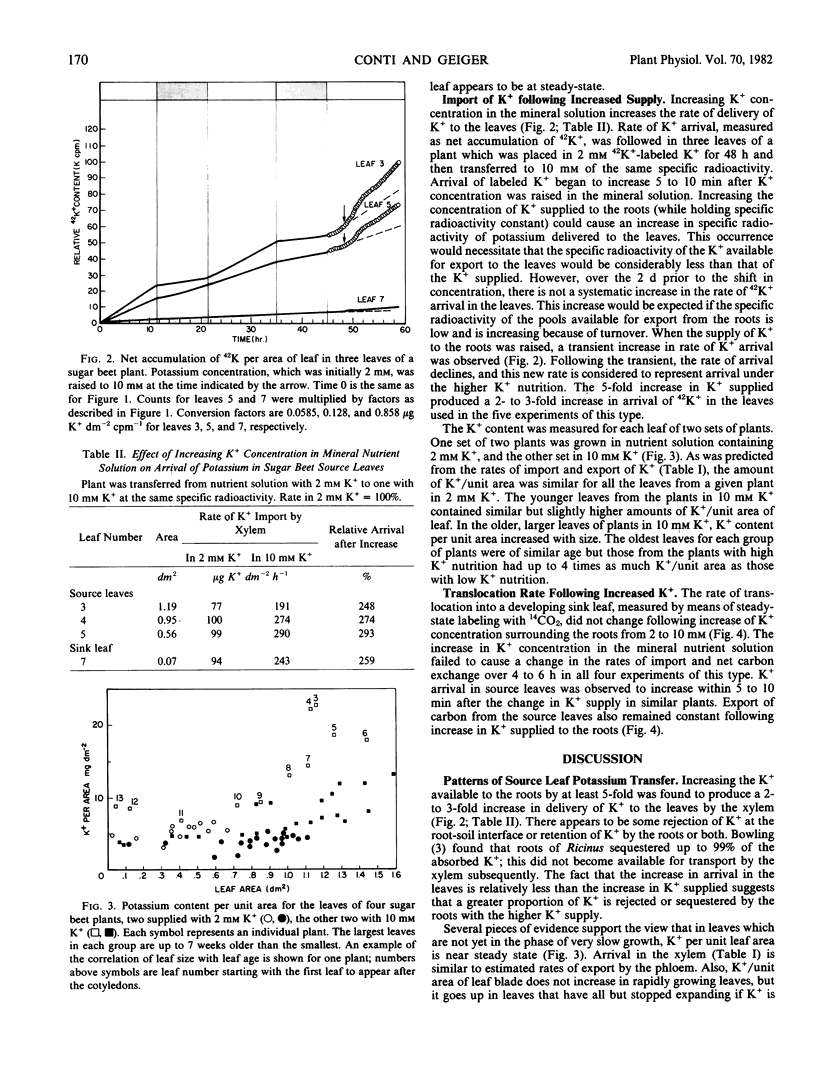
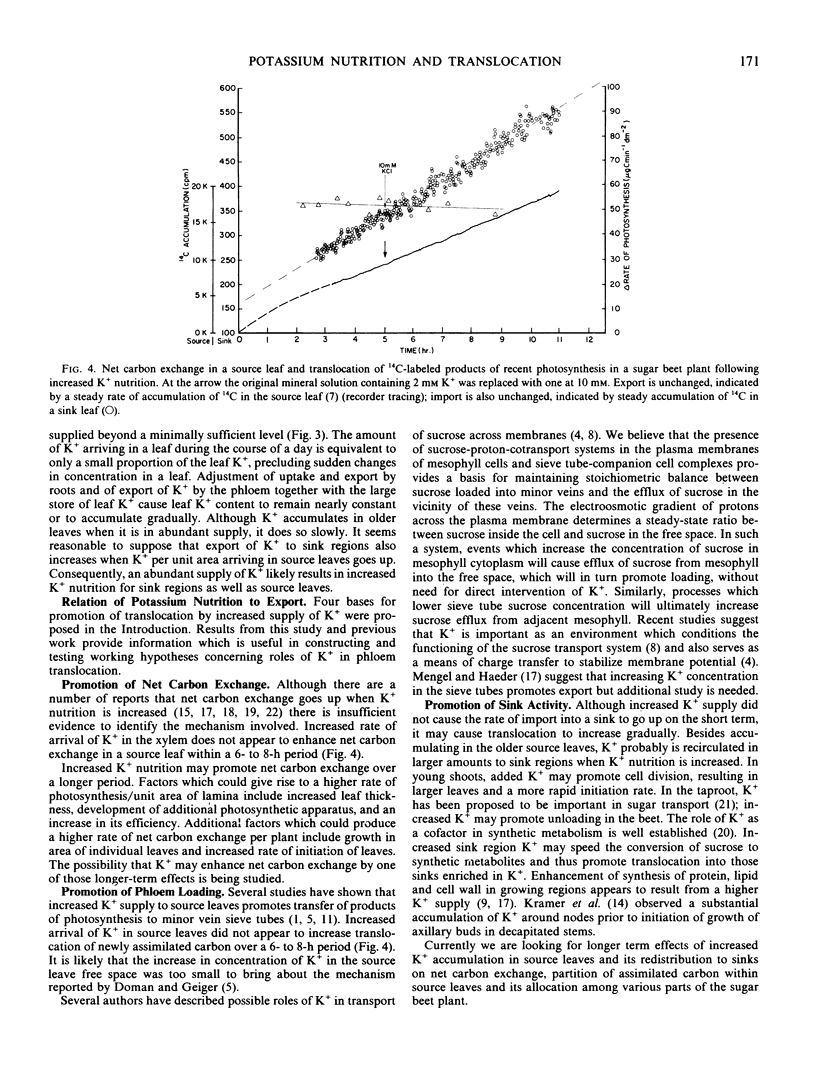
The effect of increased net foliar K+ accumulation on translocation of carbon was studied in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris, L. var. Klein E and US H20) plants. Net accumulation of recently absorbed K+ was studied by observing arrival of 42K+ per unit area of leaf. Labeled K+ was added to give an initial concentration at 2 or 10 millimolar K+ in mineral nutrient solution. Because the newly arrived K+ constitutes a small part of the total leaf K+ in plants raised in 10 millimolar K+, export of 42K+ by phloem was negligible over the 2- to 3-day period; consequently, accumulation is a measure of arrival in the xylem. In leaves from plants in 2 millimolar K+, export by the phloem was estimated to be of the same order as import by the xylem; K+ per area was observed to remain at a steady-state level. Increasing the supply of K+ to 10 millimolar caused arrival in the xylem to increase 2- to 3-fold; K+ per area increased gradually in the mature leaves. Neither net carbon exchange nor translocation of sugar increased in response to a faster rate of arrival of K+ over a 6- to 8-hour period. In the absence of short-term effects, it is suggested that K+-promoted increase in synthetic metabolism may be the basis of the increased carbon assimilation and translocation in plants supplied with an above-minimal level of K+.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doman D. C., Geiger D. R. Effect of Exogenously Supplied Foliar Potassium on Phloem Loading in Beta vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1979 Oct;64(4):528–533. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.4.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger D. R., Fondy B. R. A method for continuous measurement of export from a leaf. Plant Physiol. 1979 Sep;64(3):361–365. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartt C. E. Effect of potassium deficiency upon translocation of C in attached blades and entire plants of sugarcane. Plant Physiol. 1969 Oct;44(10):1461–1469. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.10.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longstreth D. J., Nobel P. S. Nutrient Influences on Leaf Photosynthesis: EFFECTS OF NITROGEN, PHOSPHORUS, AND POTASSIUM FOR GOSSYPIUM HIRSUTUM L. Plant Physiol. 1980 Mar;65(3):541–543. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengel K., Haeder H. E. Effect of Potassium Supply on the Rate of Phloem Sap Exudation and the Composition of Phloem Sap of Ricinus communis. Plant Physiol. 1977 Feb;59(2):282–284. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peoples T. R., Koch D. W. Role of Potassium in Carbon Dioxide Assimilation in Medicago sativa L. Plant Physiol. 1979 May;63(5):878–881. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.5.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saftner R. A., Wyse R. E. Alkali Cation/Sucrose Co-transport in the Root Sink of Sugar Beet. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):884–889. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry N., Ulrich A. Effects of potassium deficiency on the photosynthesis and respiration of leaves of sugar beet. Plant Physiol. 1973 Apr;51(4):783–786. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.4.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


