Abstract
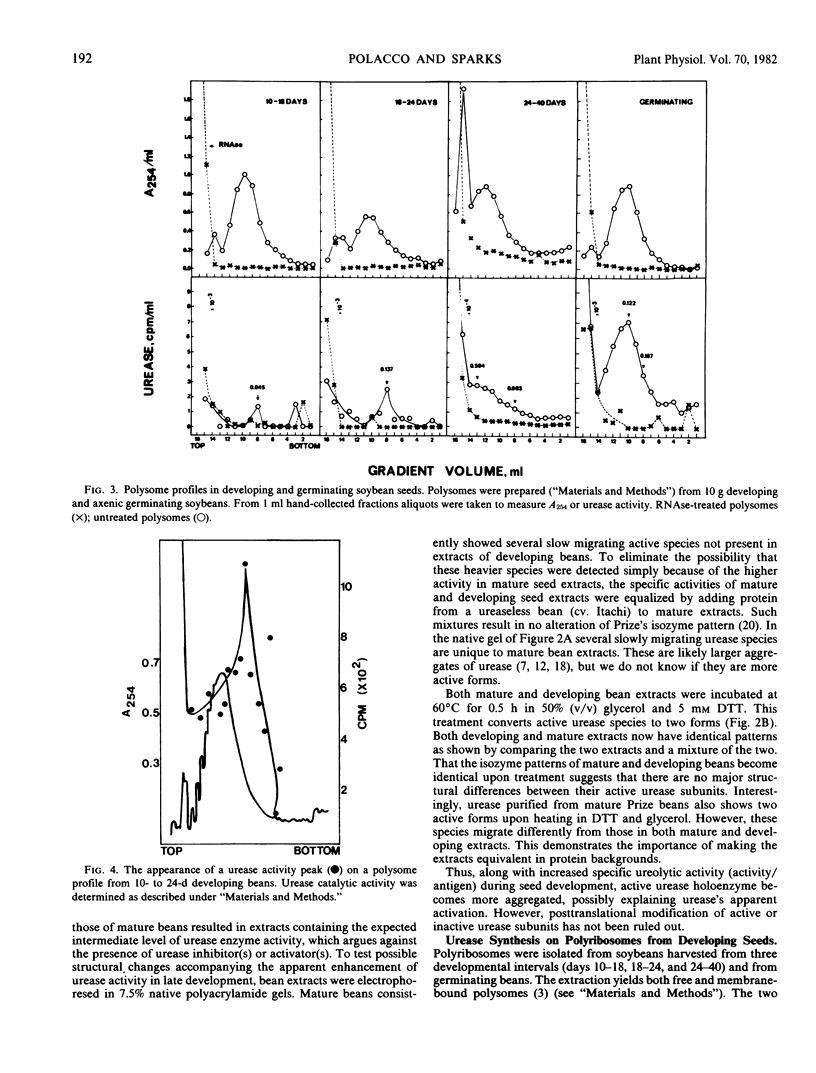
An examination of in vivo polysome-bound activity indicates that soybean (Glycine max, cv. Prize) seed urease is synthesized on large polysomes (n ≥ 15). In vitro urease synthesis is directed by a large RNA (3,000-3,300 nucleotides). Urease synthesis occurs throughout the normal protein biosynthetic phase of the developing seed. Surprisingly, the activity/antigen ratios of urease increase throughout development. Urease appears to be in a more highly polymerized state in mature beans versus beans in early development.
During the 55 days from pollination to maturity, urease specific antigen (antigen versus total seed protein) is greatest on the 20th day, representing 0.6% of total extractable protein. Its synthesis proceeds until the end of the protein biosynthetic phase, approximately day 40. In contrast, the appearance of urease enzyme activity lags that of antigen during early development (11-20 days) and plateaus in late development. Mixing experiments suggest no role for putative urease inhibitors or activators during development. However, several electrophoretically slow migrating forms are unique to the urease of mature beans. It is not known if these are more active species.
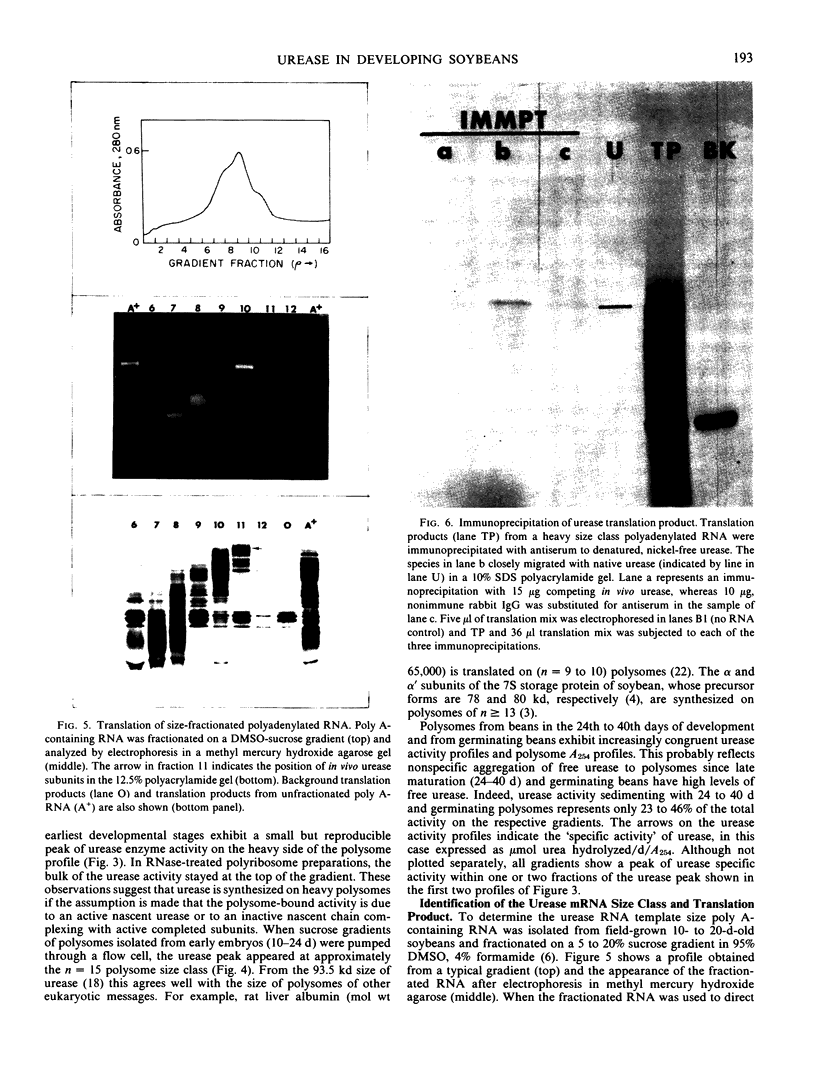
An active urease species exhibits an RNAse-sensitive cosedimentation with a heavy polyribosome class (n ≥ 15). Polyadenylated RNA, size-fractionated to 3,000 to 3,300 bases, directed the synthesis in vitro of a major translational product electrophoretically and immunologically similar to the in vivo-synthesized urease subunit.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy R. N., Jarvis N. P., Barton K. A. Biosynthesis of subunits of the soybean 7S storage protein. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachy R. N., Thompson J. F., Madison J. T. Isolation of polyribosomes and messenger RNA active in in vitro synthesis of soybean seed proteins. Plant Physiol. 1978 Feb;61(2):139–144. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A., Rubenstein I., Simon M. N. Purification and translation of zein messenger RNA from maize endosperm protein bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):696–700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Cline L. J. An improved stain for immunodiffusion tests. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):379–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon N. E., Gazzola C., Asher C. J., Lee D. S., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Jack been urease (EC 3.5.1.5). II. The relationship between nickel, enzymatic activity, and the "abnormal" ultraviolet spectrum. The nickel content of jack beans. Can J Biochem. 1980 Jun;58(6):474–480. doi: 10.1139/o80-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon N. E., Gazzola T. C., blakeley R. L., Zermer B. Letter: Jack bean urease (EC 3.5.1.5). A metalloenzyme. A simple biological role for nickel? J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jul 9;97(14):4131–4133. doi: 10.1021/ja00847a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein W. N., Nagarajan K., Scurzi W. Urease catalysis and structure. X. Alternate bonding-site isozymes of jackbean urease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):726–733. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Lingappa J. R., Prasad R., Ebner K. E., Blobel G. Coupled cell-free synthesis, segregation, and core glycosylation of a secretory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2338–2342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGILVERY R. W., MOKRASCH L. C. Purification and properties of fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):909–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacco J. C., Havir E. A. Comparisons of soybean urease isolated from seed and tissue culture. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1707–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacco J. C., Thomas A. L., Bledsoe P. J. A soybean seed urease-null produces urease in cell culture. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1233–1240. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Reithel F. J. Evidence for an active-inactive subunit complex in jack bean urease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jun;174(2):651–657. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Schimke R. T. Specific binding of albumin antibody to rat liver polysomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3597–3601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]