Abstract
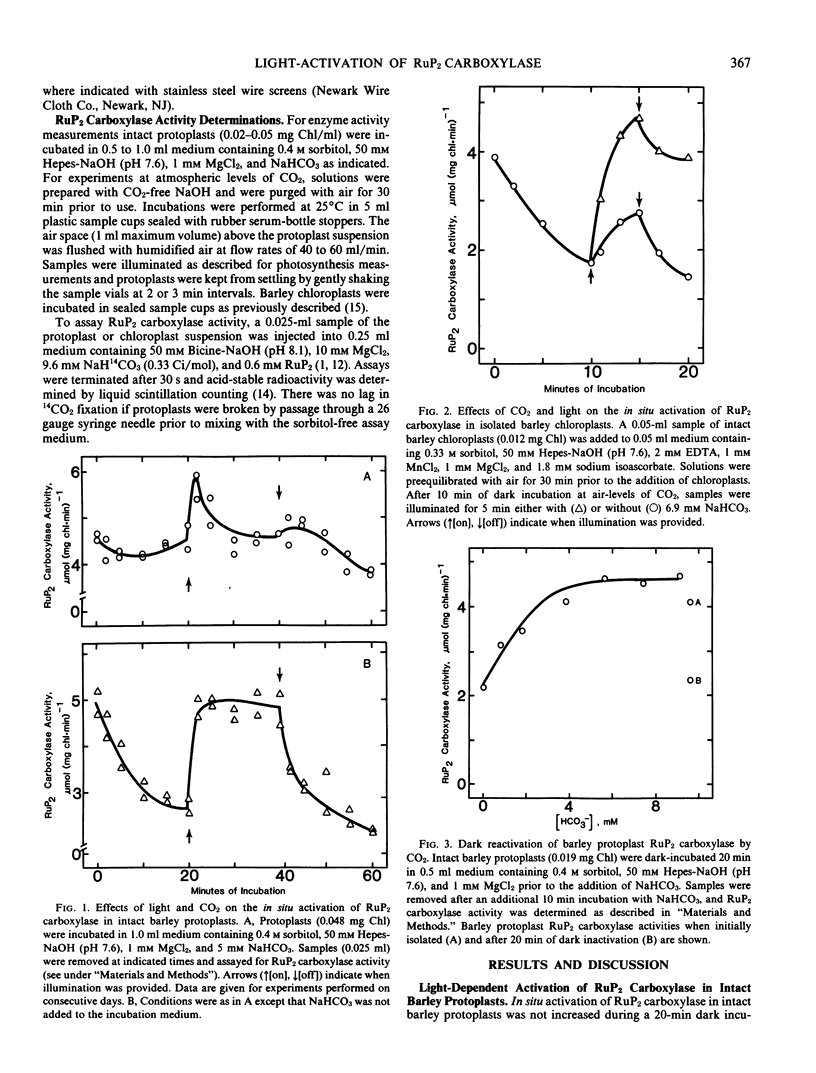
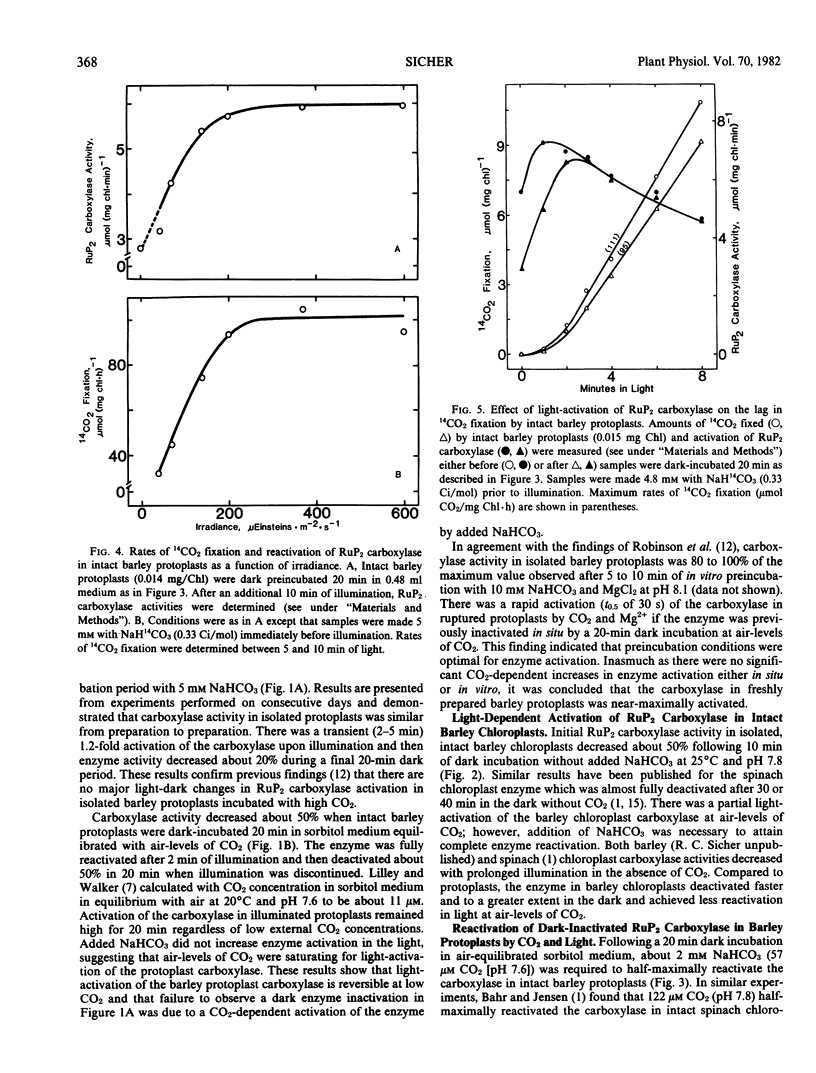
The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase displayed near-maximal activity in isolated, intact barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv. Pennrad) mesophyll protoplasts. The carboxylase deactivated 40 to 50% in situ when protoplasts were dark-incubated 20 minutes in air-equilibrated solutions. Enzyme activity was fully restored after 1 to 2 minutes of light. Addition of 5 millimolar NaHCO3 to the incubation medium prevented dark-inactivation of the carboxylase. There was no permanent CO2-dependent activation of the protoplast carboxylase either in light or dark. Activation of the carboxylase from ruptured protoplasts was not increased significantly by in vitro preincubation with CO2 and Mg2+. In contrast to the enzyme in protoplasts, the carboxylase in intact barley chloroplasts was not fully reactivated by light at atmospheric CO2 levels. The lag phase in carbon assimilation was not lengthened by dark-adapting protoplasts to low CO2 demonstrating that light-activation of the carboxylase was not involved in photosynthetic induction. Irradiance response curves for reactivation of the the carboxylase and for CO2 fixation by isolated barley protoplasts were similar. The above results show that there was a fully reversible light-activation of the carboxylase in isolated barley protoplasts at physiologically significant CO2 levels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in intact chloroplasts by CO2 and light. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G. E., Robinson S. P., Tyler N. J., Walker D. A. Photosynthesis by isolated protoplasts, protoplast extracts, and chloroplasts of wheat: influence of orthophosphate, pyrophosphate, and adenylates. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):313–319. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. C. Effect of photosynthetic intermediates on the magnesium inhibition of oxygen evolution by barley chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Apr;63(4):754–757. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.4.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M., Walker D. A. Carbon dioxide assimilation by leaves, isolated chloroplasts, and ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from spinach. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jun;55(6):1087–1092. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H. Evidence for the existence of discrete activator and substrate sites for CO2 on ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5599–5601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., McNeil P. H., Walker D. A. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase--lack of dark inactivation of the enzyme in experiments with protoplasts. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. P., Walker D. A. The significance of light activation of enzymes during the induction phase of photosynthesis in isolated chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):617–623. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90469-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Bahr J. T., Jensen R. G. Measurement of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate from spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):876–879. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicher R. C., Hatch A. L., Stumpf D. K., Jensen R. G. Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate and activation of the carboxylase in the chloroplast. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):252–255. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. E., Kremer D. F., Lee D. R. Carbon assimilation and translocation in soybean leaves at different stages of development. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):54–58. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


