Abstract
Transfer of the nitrogen and carbon of allantoin to amino acids and protein of leaflets, stems and petioles, apices, peduncles, pods, and seeds of detached shoots of nodulated cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp. cv. Caloona) plants was demonstrated following supply of [2-14C], [1,3-15N]allantoin in the transpiration stream. Throughout vegetative and reproductive growth all plant organs showed significant ureolytic activity and readily metabolized [2-14C]allantoin to 14CO2. A metabolic pathway for ureide nitrogen utilization via allantoic acid, urea, and ammonia was indicated. Levels of ureolytic activity in extracts from leaves and roots of nodulated cowpea were consistently maintained at higher levels than in non-nodulated, NO3− grown plants.
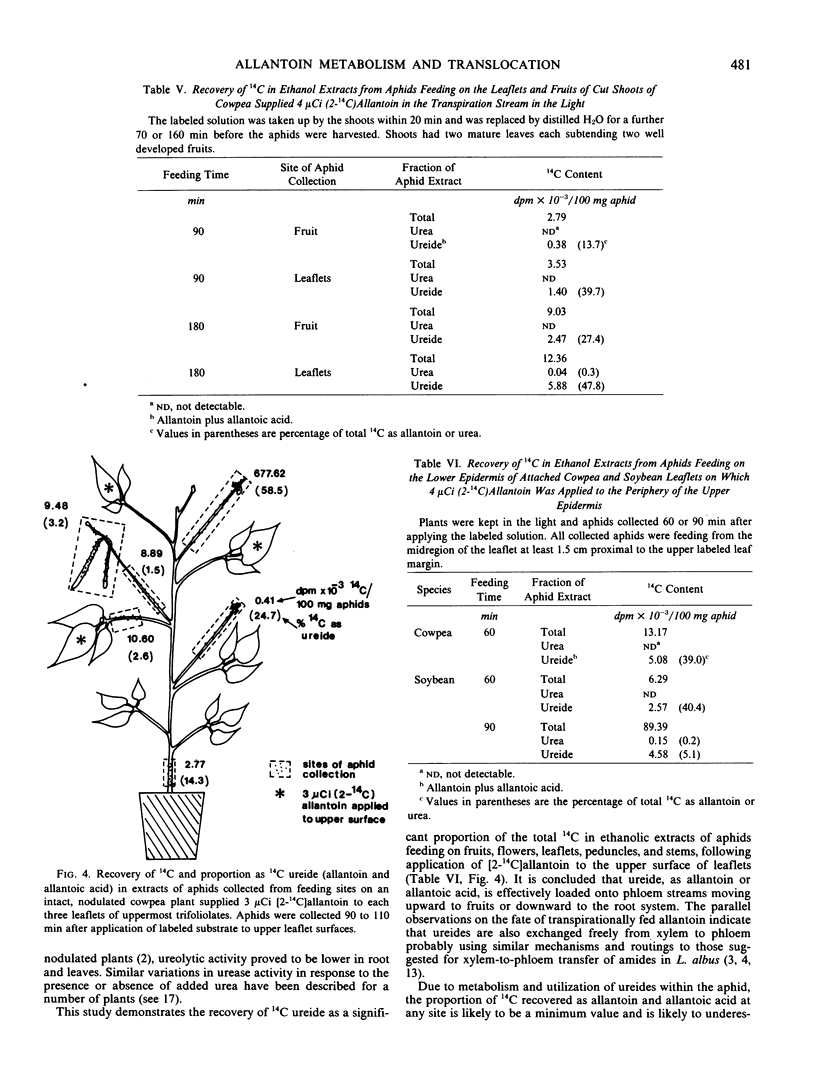
[14C]Ureides were recovered in extracts of aphids (Aphis craccivora and Macrosiphum euphorbieae) feeding at different sites on cowpea plants supplied with [2-14C]allantoin through the transpiration stream or to the upper surface of single leaflets. The data indicated that the ureides were effectively transferred from xylem or leaf mesophyll to phloem, and then translocated in phloem to fruits, apices, and roots.
Full text
PDF
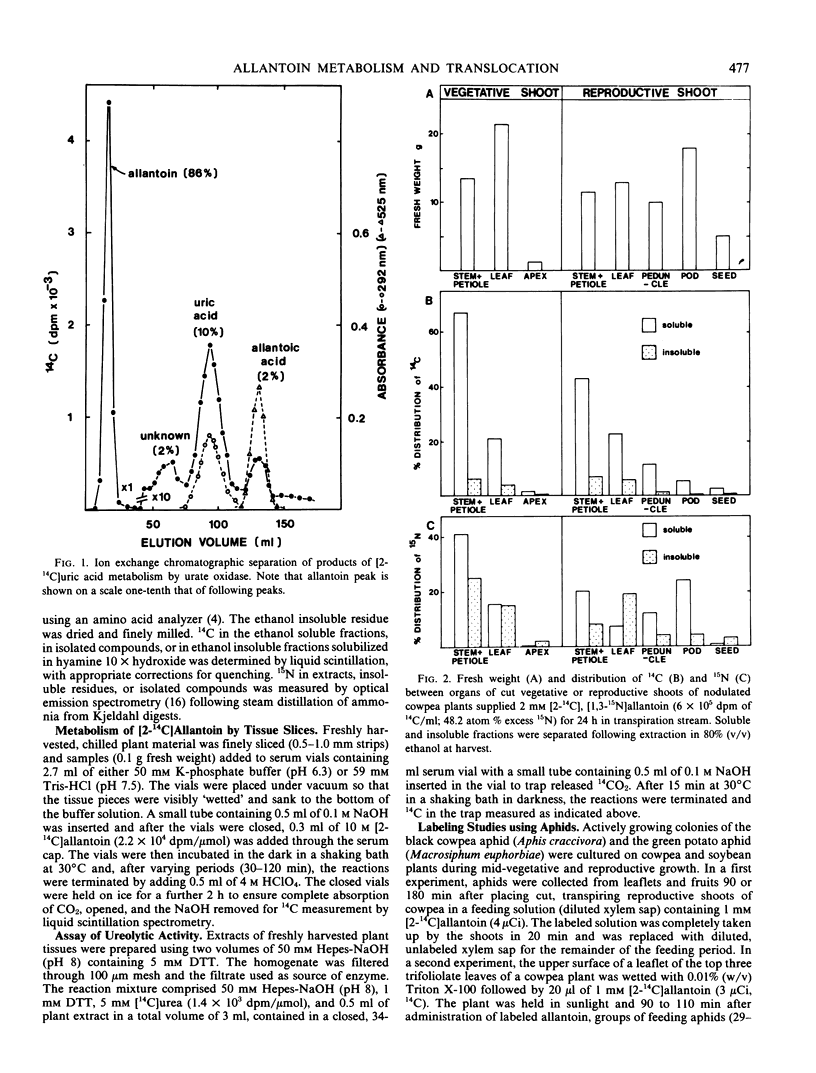
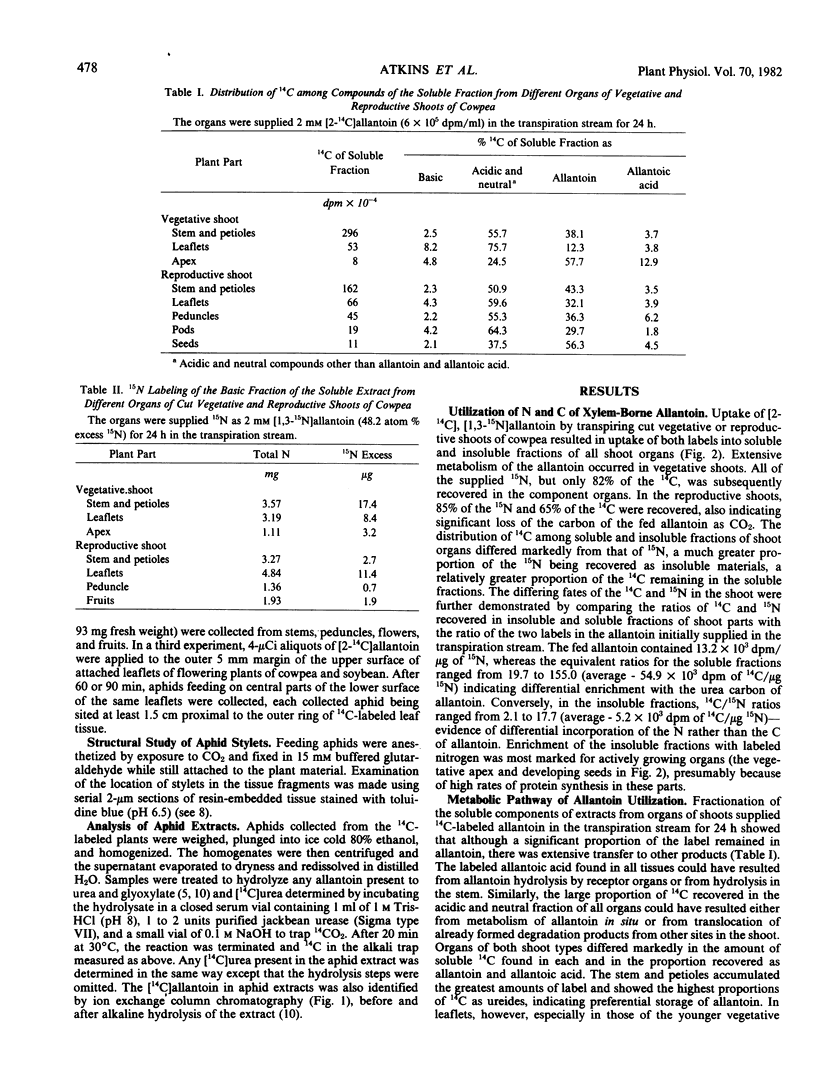
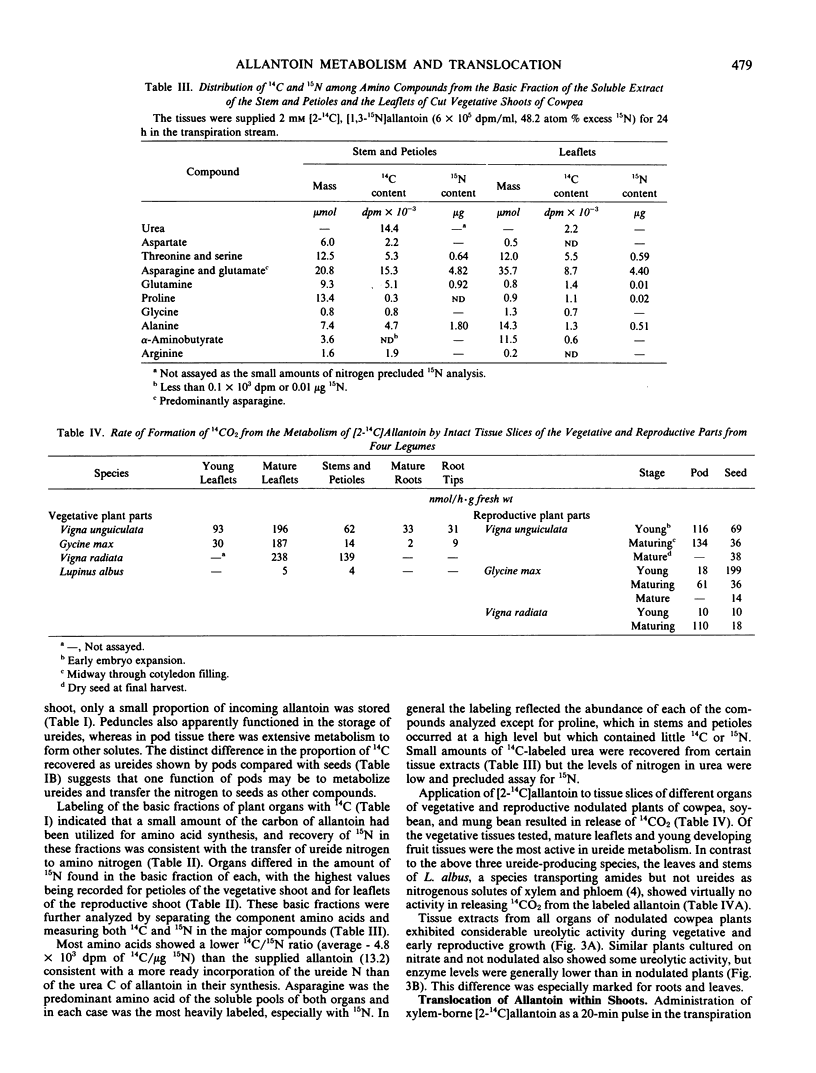
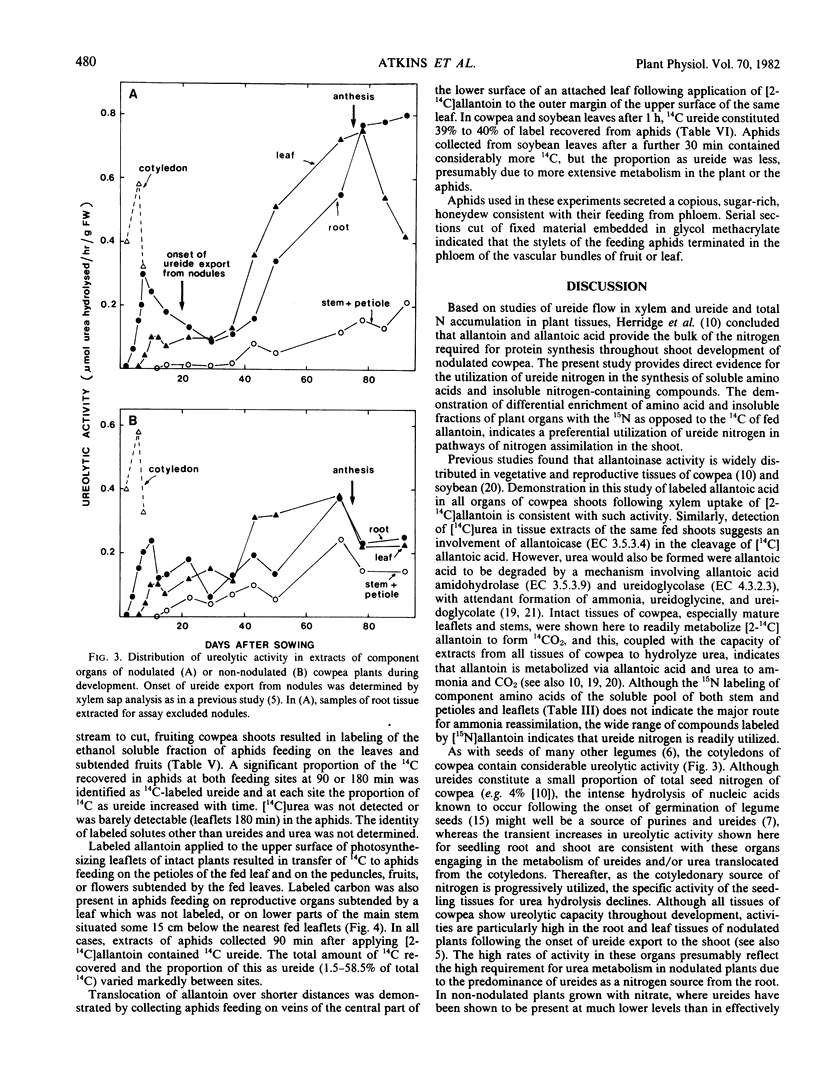

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Griffiths G. J., White S. T. Economy of Carbon and Nitrogen in Nodulated and Nonnodulated (NO(3)-grown) Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):978–983. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Sharkey P. J. Asparagine metabolism-key to the nitrogen nutrition of developing legume seeds. Plant Physiol. 1975 Dec;56(6):807–812. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihara S., Yamaguchi M. Effects of Allopurinol [4-Hydroxypyrazolo(3,4-d)Pyrimidine] on the Metabolism of Allantoin in Soybean Plants. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):134–138. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herridge D. F., Atkins C. A., Pate J. S., Rainbird R. M. Allantoin and Allantoic Acid in the Nitrogen Economy of the Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.). Plant Physiol. 1978 Oct;62(4):495–498. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzell D. B., Pate J. S., Atkins C. A., Canvin D. T. Partitioning of carbon and nitrogen and the nutrition of root and shoot apex in a nodulated legume. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):30–36. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley R. M. Isolation of Functionally Intact Rhodoplasts from Griffithsia monilis (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):5–8. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure P. R., Israel D. W. Transport of nitrogen in the xylem of soybean plants. Plant Physiol. 1979 Sep;64(3):411–416. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skokut T. A., Filner P. Slow adaptive changes in urease levels of tobacco cells cultured on urea and other nitrogen sources. Plant Physiol. 1980 May;65(5):995–1003. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.5.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter J. G. Allantoin and Allantoic Acid in Tissues and Stem Exudate from Field-grown Soybean Plants. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):478–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. J., Schrader L. E. The Assimilation of Ureides in Shoot Tissues of Soybeans : 1. CHANGES IN ALLANTOINASE ACTIVITY AND UREIDE CONTENTS OF LEAVES AND FRUITS. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):973–976. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):403–468. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.403-468.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


