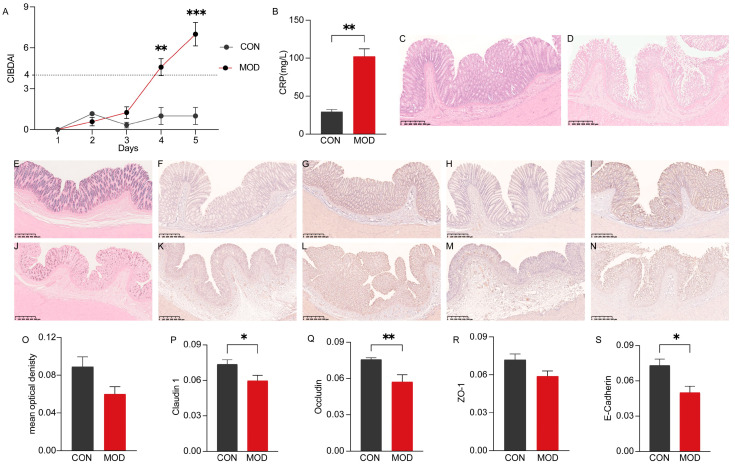
Figure 1.
Effect of DSS-induced IBD in dogs. (A) Canine inflammatory bowel disease activity indices (CIBDAIs). (B) Comparison of C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in serum between the CON and MOD groups. (C) Representative hematoxylin–eosin (H.E) histological sections of the CON group. (D) Representative H.E histological sections of the MOD group. (E) Representative AB staining sections of the CON group. (F–I) Immunohistochemical staining of Claudin 1, Occludin, ZO-1, E-Cadherin in the CON group. (J) Representative AB staining sections of the MOD group. (K–N) Immunohistochemical staining of Claudin 1, Occludin, ZO-1, E-Cadherin in the MOD group. (O) Comparison of mucus expression in the colon between the CON and MOD groups. (P) Comparison of Claudin 1 expression in the colon between the CON and MOD groups. (Q) Comparison of Occludin expression in the colon between the CON and MOD groups. (R) Comparison of ZO-1 expression in the colon between the CON and MOD groups. (S) Comparison of E-Cadherin expression in the colon between the CON and MOD groups. *, ** and *** indicate p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively. CIBDAI: Canine inflammatory bowel disease activity index. CRP: C-reactive protein. H.E: Hematoxylin–eosin staining. AB: Alcian Blue staining.