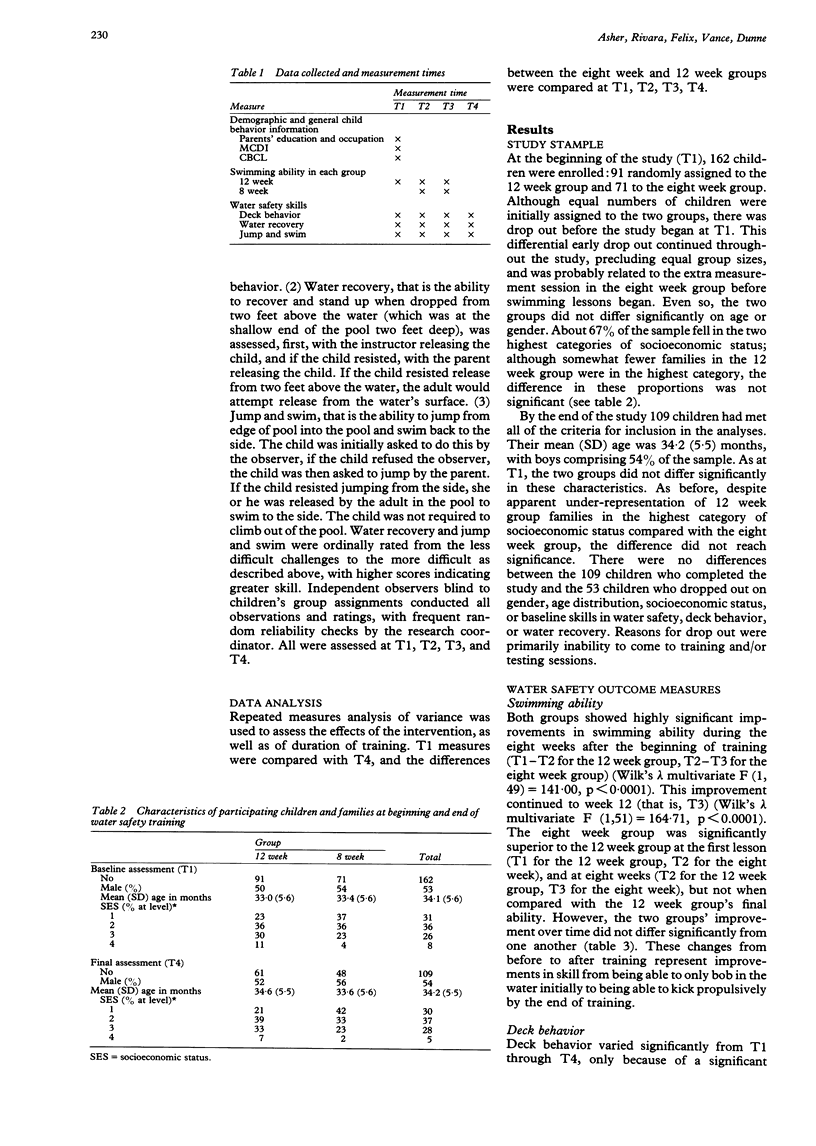
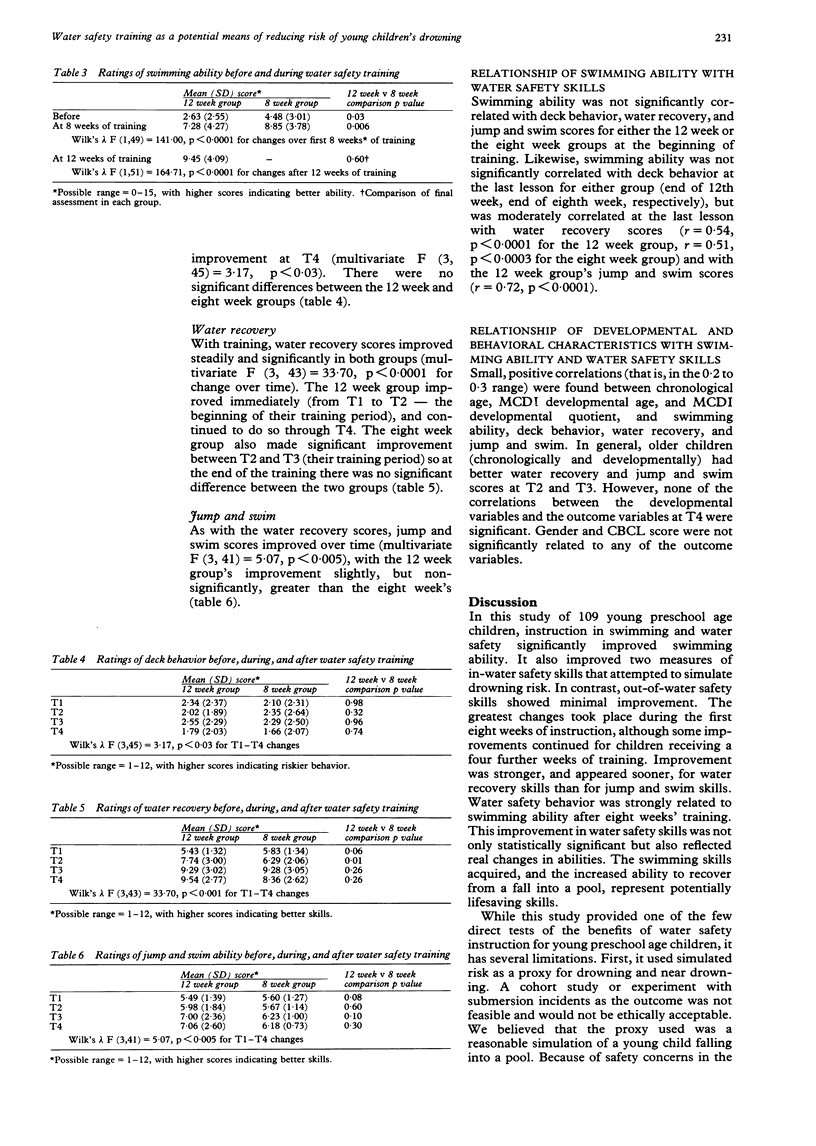
Abstract
OBJECTIVES: To determine the effects of training in swimming and water safety on young preschool-children's ability to recover safely from a simulated episode of falling into a swimming pool. DESIGN: Randomized trial of 12 or eight weeks' duration water safety and swimming lessons for children 24 to 42 months old. OUTCOME MEASURES: Swimming ability, deck behavior, water recovery, and swimming to side after jumping into pool were measured before, during, and after the training program. RESULTS: 109 children completed the study (61 in the 12 week group, 48 in the eight week group). The average age was 34.2 months, 54% were male. Swimming ability, deck behavior, water recovery, and jump and swim skills improved over baseline levels in both groups. By the end of training, the 12 week group improved more than the eight week group only in swimming ability. Improvements in water recovery and jump and swim skills were associated positively with changes in swimming ability. CONCLUSIONS: Swimming ability and safety skills of young preschool children can be improved through training. Such programs may offer some protection for children at risk of drowning and there was no indication that this program increased the risk of drowning. However, pool fencing, other barriers around water, and parental supervision still remain the most important prevention strategies to reduce drowning in young children.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achenbach T. M., Edelbrock C., Howell C. T. Empirically based assessment of the behavioral/emotional problems of 2- and 3- year-old children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1987 Dec;15(4):629–650. doi: 10.1007/BF00917246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond E. F. Swimming instruction for pre-school children. J Sports Med. 1975 Mar-Apr;3(2):58–60. doi: 10.1177/036354657500300202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbaugh S. J. Assessment of swimming performance of preschool children. Percept Mot Skills. 1978 Dec;47(3 Pt 2):1179–1182. doi: 10.2466/pms.1978.46.3f.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbaugh S. J. Effects of aquatic training on swimming skill development of preschool children. Percept Mot Skills. 1986 Apr;62(2):439–446. doi: 10.2466/pms.1986.62.2.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg W. K., Fandal A. W., Thornton S. M. Revision of Denver Prescreening Developmental Questionnaire. J Pediatr. 1987 Apr;110(4):653–657. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80573-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney F. J., Farley T. A., Kelso K. Y., Wilson S. A., Horan J. M., McFarland L. M. An outbreak of hepatitis A associated with swimming in a public pool. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):613–618. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carroll P. W., Alkon E., Weiss B. Drowning mortality in Los Angeles County, 1976 to 1984. JAMA. 1988 Jul 15;260(3):380–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan L., Gore E. J., Wentz K., Allen J., Novack A. H. Ten-year study of pediatric drownings and near-drownings in King County, Washington: lessons in injury prevention. Pediatrics. 1989 Jun;83(6):1035–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivara F. P. Traumatic deaths of children in the United States: currently available prevention strategies. Pediatrics. 1985 Mar;75(3):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson L. S. Crash involvement of teenaged drivers when driver education is eliminated from high school. Am J Public Health. 1980 Jun;70(6):599–603. doi: 10.2105/ajph.70.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintemute G. J. Childhood drowning and near-drowning in the United States. Am J Dis Child. 1990 Jun;144(6):663–669. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150300061018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintemute G. J., Kraus J. F., Teret S. P., Wright M. Drowning in childhood and adolescence: a population-based study. Am J Public Health. 1987 Jul;77(7):830–832. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.7.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright M., de Silva P., Sinha S. Hyponatraemia in children. BMJ. 1992 Jul 4;305(6844):51–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6844.51-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


