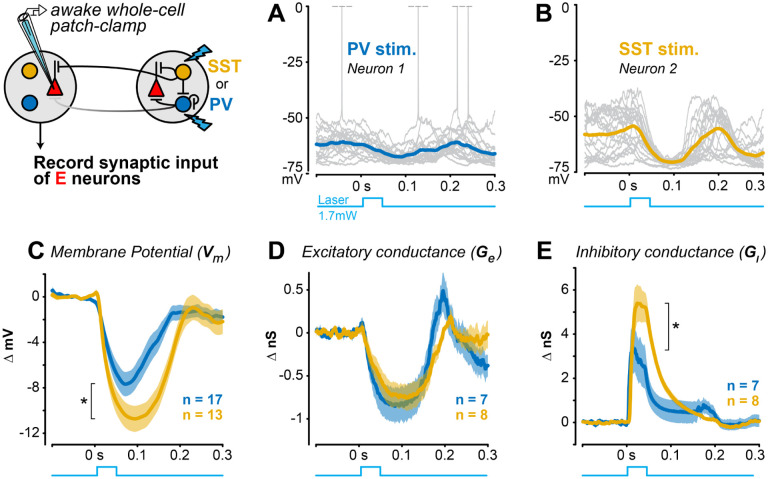
Figure 6. Stronger lateral inhibition from distal SST versus PV neurons A.
Example current clamp recording of membrane potential from an RS neuron during distal PV stimulation in awake V1 (20 trials). Spikes truncated at 0 mV.
B. Same as A for an example RS neuron during distal SST stimulation.
C. Distal SST stimulation causes greater hyperpolarization of excitatory neurons , mean ± SEM, 13 RS neurons; mean ΔVm from 0–0.2s) than distal PV stimulation excitatory neurons; , 1-tail Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
D. Distal PV or SST stimulation decreased excitatory conductance to a similar degree (PV stim: neurons; SST stim: RS neurons; ; mean from ).
E. Inhibitory conductance significantly larger with distal SST versus PV stimulation (SST stim: neurons; stim: neurons; ; mean from ).