Abstract
El Ghawabi, S. H., Mansour, M. B., Youssef, F. L., El Ghawabi, M. H., and Abd El Latif, M. M. (1971).Brit. J. industr. Med.,28, 323-329. Decompression sickness in caisson workers. An investigation of 55 bridge construction workers is reported. The overall bends rate was 0·97%. (The term `bends' as used in this study is defined in the paper.) Chokes were encountered in 67·27% of workers. A clinical, haematological, and radiological study was performed.
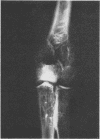
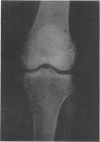
Definite bony changes were found in 43·6% of all workers; 91·6% of these had lesions around the elbow. The presence of dense areas in the neck of the scapula is reported in two cases for the first time. The relatively high haematocrit value is thought to play a part in the pathogenesis of bone infarction through its relation with blood viscosity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEHNKE A. R. Decompression sickness. Mil Med. 1955 Sep;117(3):257–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEVIC M., GENEVOIS M., MARIN A., ROCHE L. La tomographie osseuse dans l'ostéoarthropathie des caissons. Arch Mal Prof. 1956 Nov-Dec;17(6):597–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRIS G., SICCA U. Manifestazioni cutanee nei lavoratori dei cassoni pneumatici. Rass Med Ind Ig Lav. 1952 Sep-Oct;21(5):350–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDING F. C., GRIFFITHS P., HEMPLEMAN H. V., PATON W. D., WALDER D. N. Decompression sickness during construction of the Dartford Tunnel. Br J Ind Med. 1960 Jul;17:167–180. doi: 10.1136/oem.17.3.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuntini C. N. Considerazioni sulle osteoartropatie da aeroembolismo disbarico. Med Lav. 1967 Mar;58(3):161–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JULLIEN G. Etude des réactions pathologiques consécutives à la plongée sousmarine et au travail dans l'air comprimé. Arch Mal Prof. 1956 May-Jun;17(3):228–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINFELD M., WILSON J. T. Decompression sickness (compressed-air illness) in a tunneling operation. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1956 Dec;14(6):539–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS H. E., PATON W. D. Decompression sickness during the sinking of a caisson; a study of some factors in the pathogenesis of caisson disease. Br J Ind Med. 1957 Jan;14(1):5–12. doi: 10.1136/oem.14.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCALLUM R. I., WALDER D. N. Compressed-air illness on tyneside. Lancet. 1953 Mar 7;1(6758):464–467. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)91641-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. I. Decompression sickness: a review. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Jan;25(1):4–21. doi: 10.1136/oem.25.1.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONALD J. Aseptic necrosis of bone in caisson disease. Lancet. 1953 Oct 24;265(6791):855–856. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90521-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]