Abstract
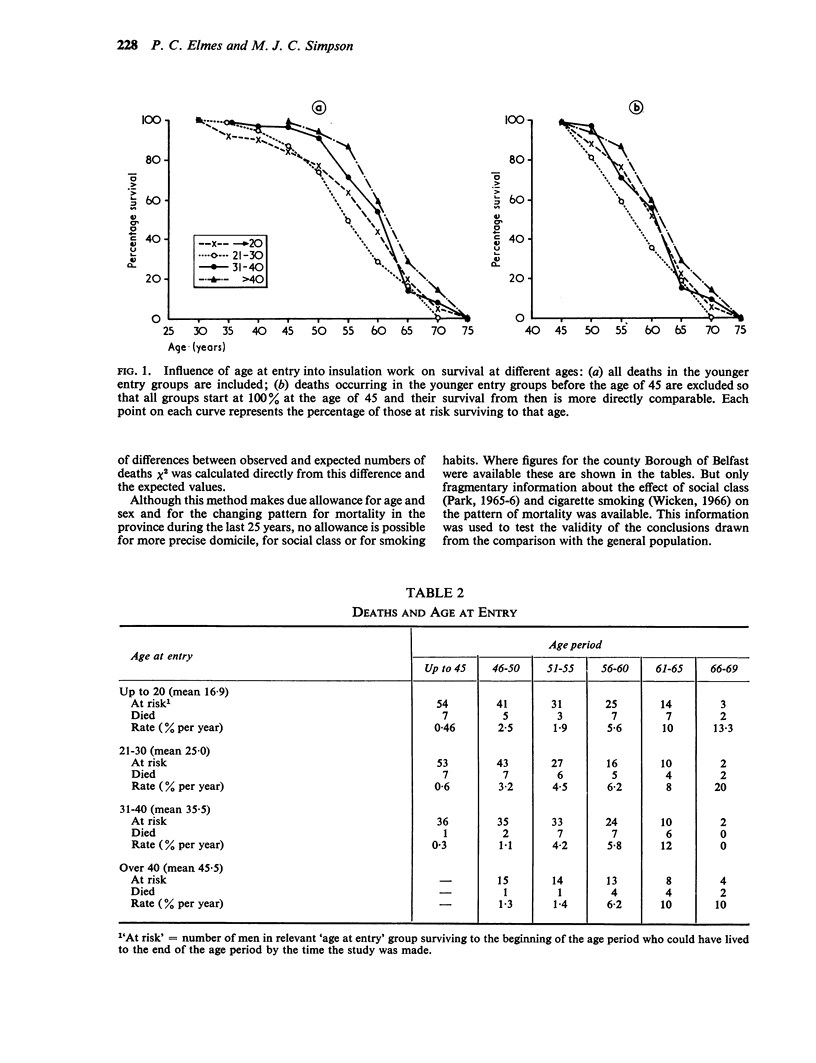
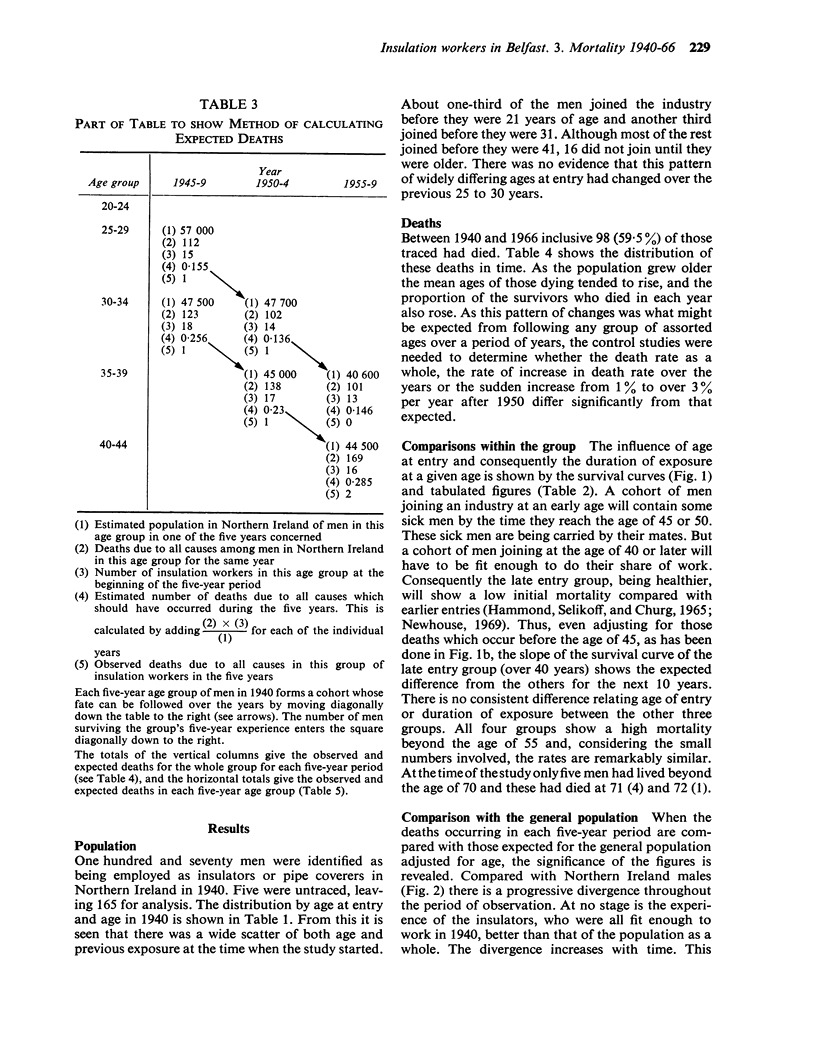
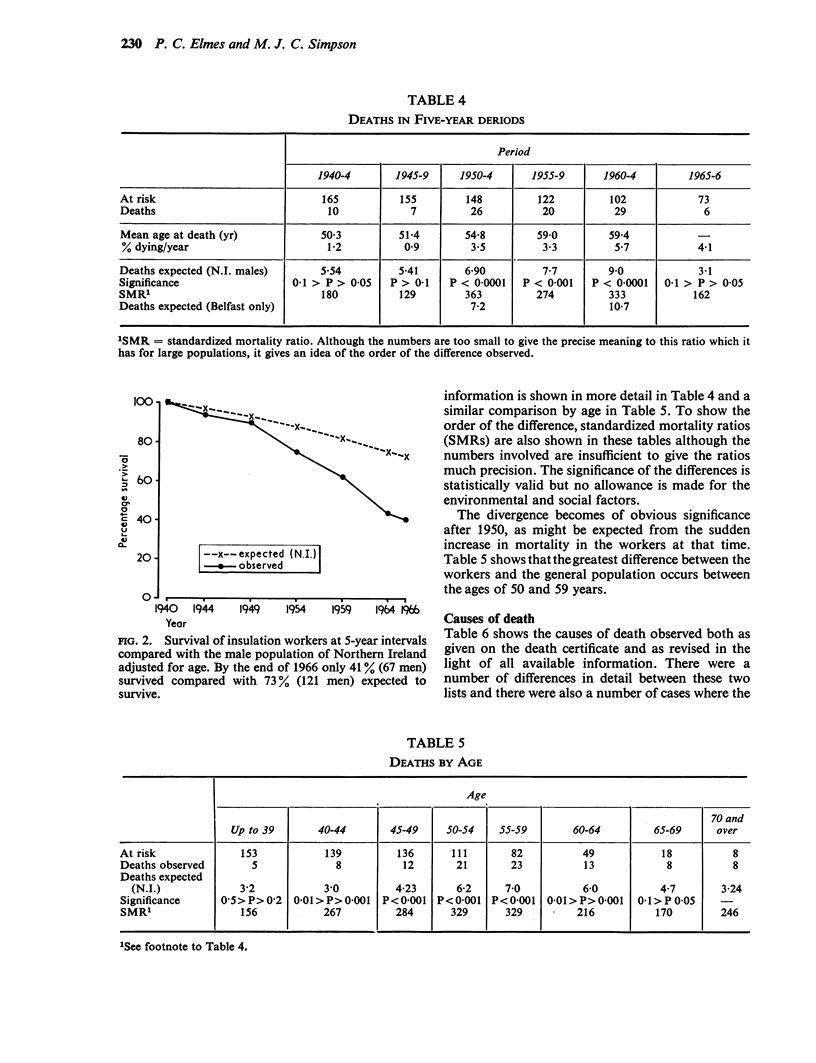
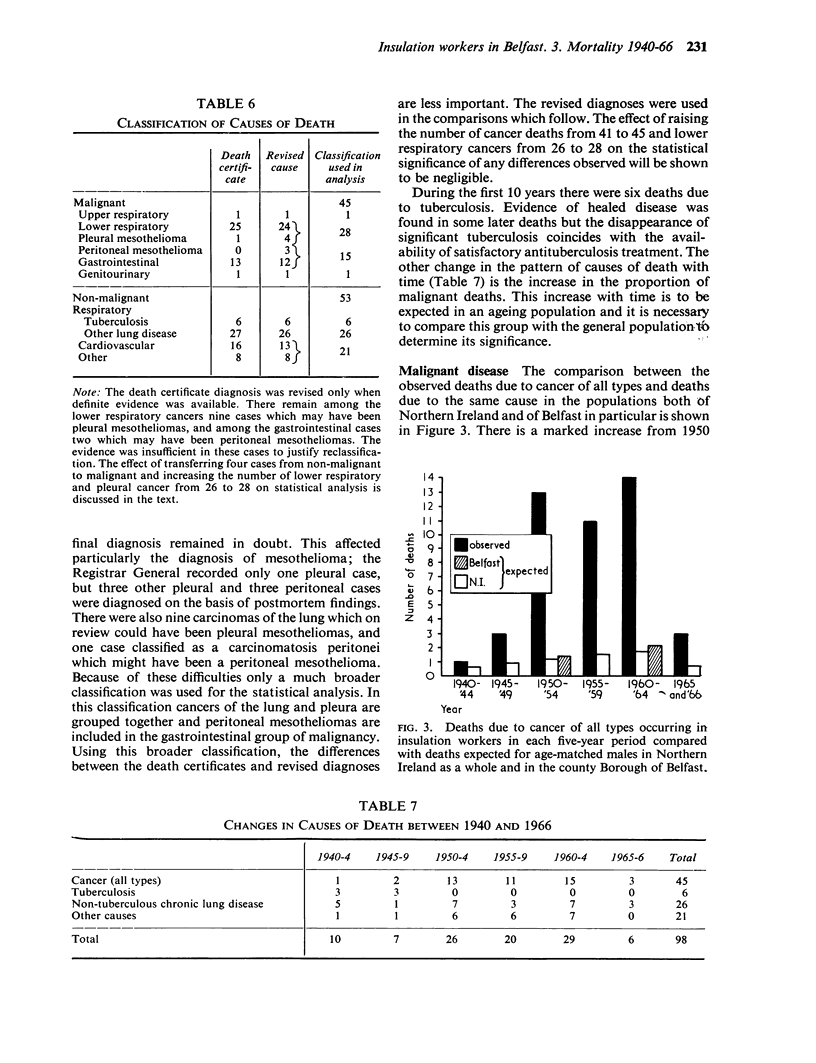
Elmes, P. C., and Simpson, Marion J. C. (1971).Brit. J. industr. Med.,28, 226-236. Insulation workers in Belfast. 3. Mortality 1940-66. One hundred and seventy men were identified as making up the total population of insulation workers in Belfast in 1940. This is an analysis of all the information about deaths that has emerged from tracing these men up to the end of 1966. Five remain untraced, and the mortality experience of the remainder is compared with that of other men in Northern Ireland over the period. There were 98 deaths when only 37 were expected. The number of deaths occurring exceeded those expected throughout the period 1940-66 and the increase was statistically significant during the period 1950-55 and onwards. There was an especially high mortality (compared with other Northern Ireland males) due to cancer of the lung, mesothelioma of the pleura and peritoneum, cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, and fibrotic lesions of the lungs. The ratio of observed over expected deaths was 2·6 for all causes, 3·9 for all cancers, and 17·6 for cancers of the lower respiratory tract and pleura. Those men finally classified as dying from lung cancer showed evidence of lung fibrosis whereas those classified as dying from mesothelioma did not. Comparisons within the group failed to show any relationship between age at first exposure or duration of exposure and the excessive mortality. There were too few non-smokers to show the significance of smoking.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchanan W. D. Asbestosis and primary intrathoracic neoplasms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):507–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmes P. C. The epidemiology and clinical features of asbestosis and related diseases. Postgrad Med J. 1966 Oct;42(492):623–635. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.42.492.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmes P. C., Wade O. L. Relationship between exposure to asbestos and pleural malignancy in Belfast. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):549–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond E. C., Selikoff I. J., Churg J. Neoplasia among insulation workers in the United States with special reference to intra-abdominal neoplasia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox J. F., Doll R. S., Hill I. D. Cohort analysis of changes in incidence of bronchial carcinoma in a textile asbestos factory. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):526–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlands J. H., Wallace W. F., Simpson M. J. Insulation workers in Belfast. 2. Morbidity in men still at work. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jul;28(3):217–225. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhouse M. L. A study of the mortality of workers in an asbestos factory. Br J Ind Med. 1969 Oct;26(4):294–301. doi: 10.1136/oem.26.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhouse M. L., Wagner J. C. Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers. Br J Ind Med. 1969 Oct;26(4):302–307. doi: 10.1136/oem.26.4.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smither W. J. Secular changes in asbestosis in an asbestos factory. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Dec 31;132(1):166–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb41099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace W. F., Langlands J. H. Insulation workers in Belfast. 1. Comparison of a random sample with a control population. Br J Ind Med. 1971 Jul;28(3):211–216. doi: 10.1136/oem.28.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



