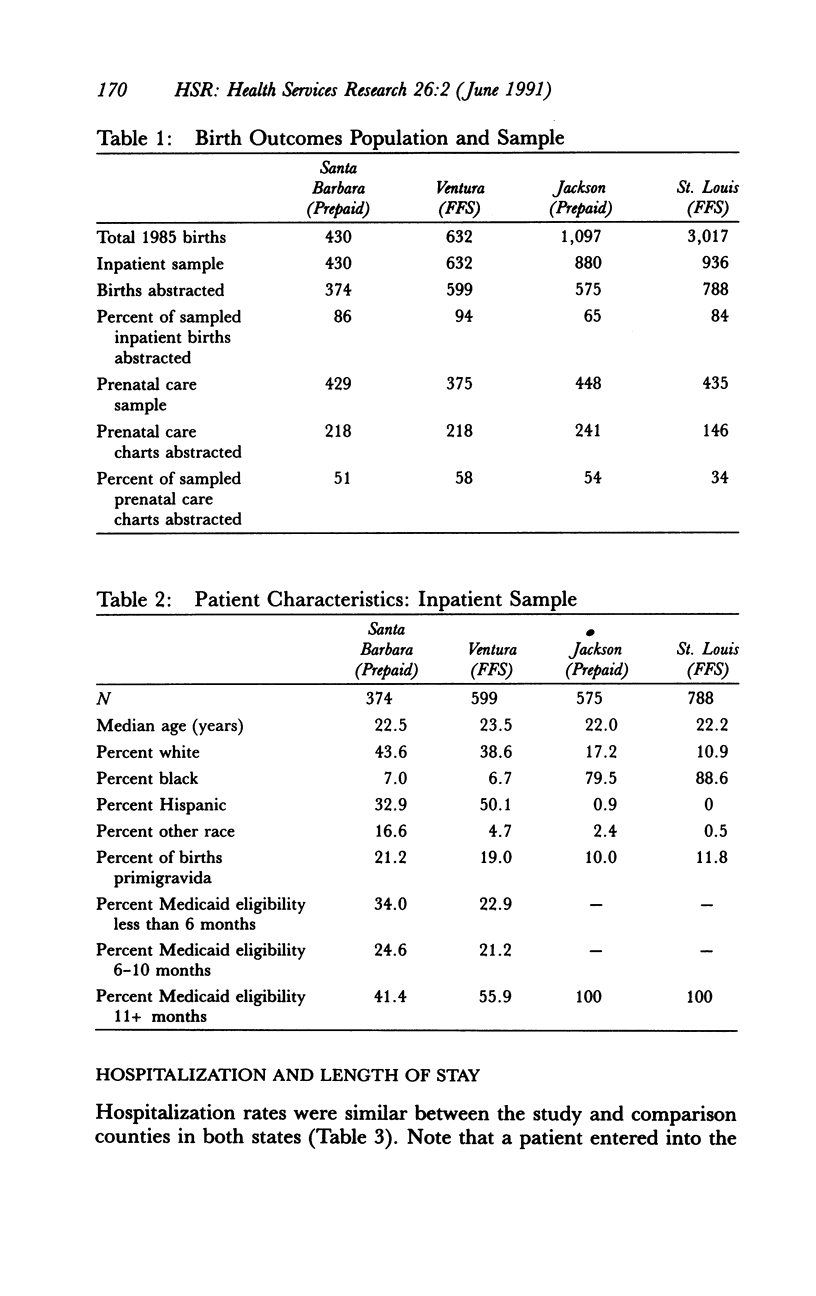
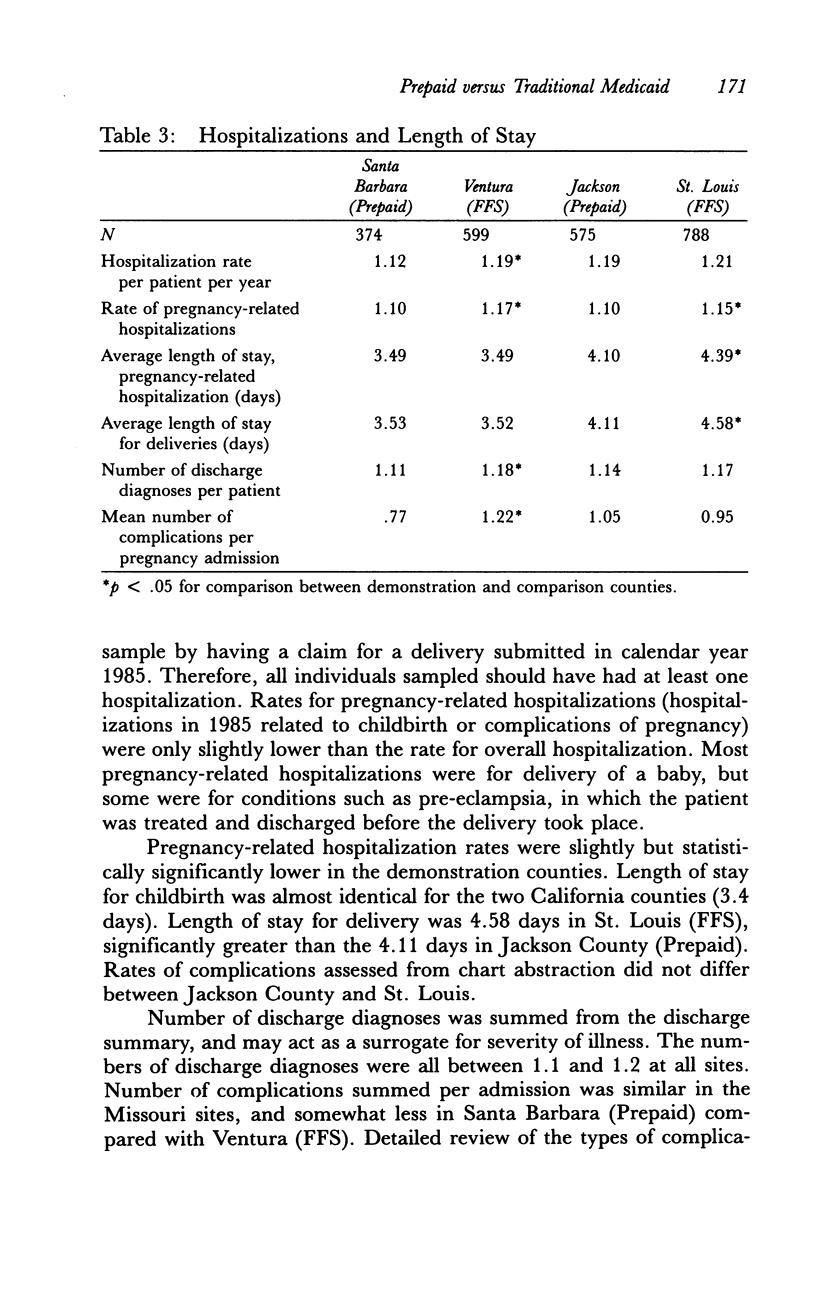
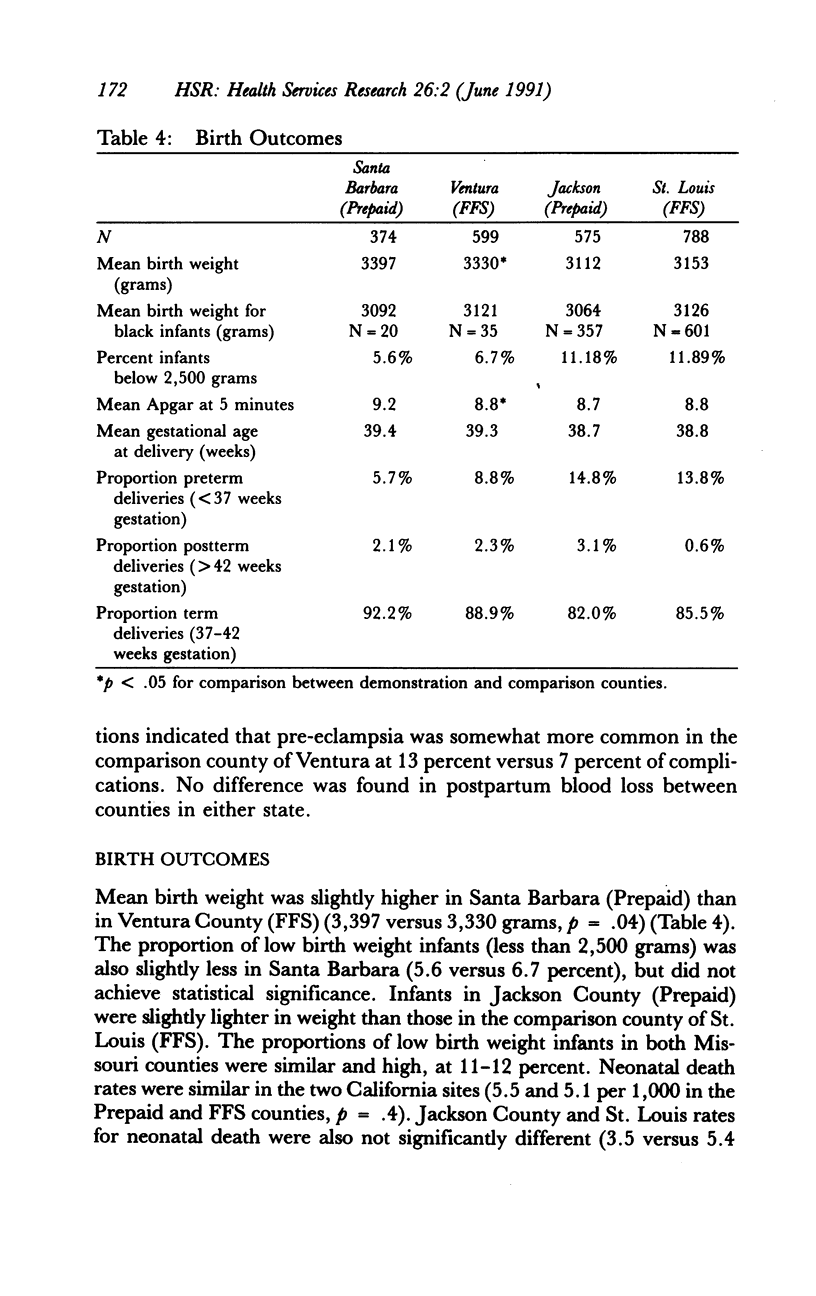
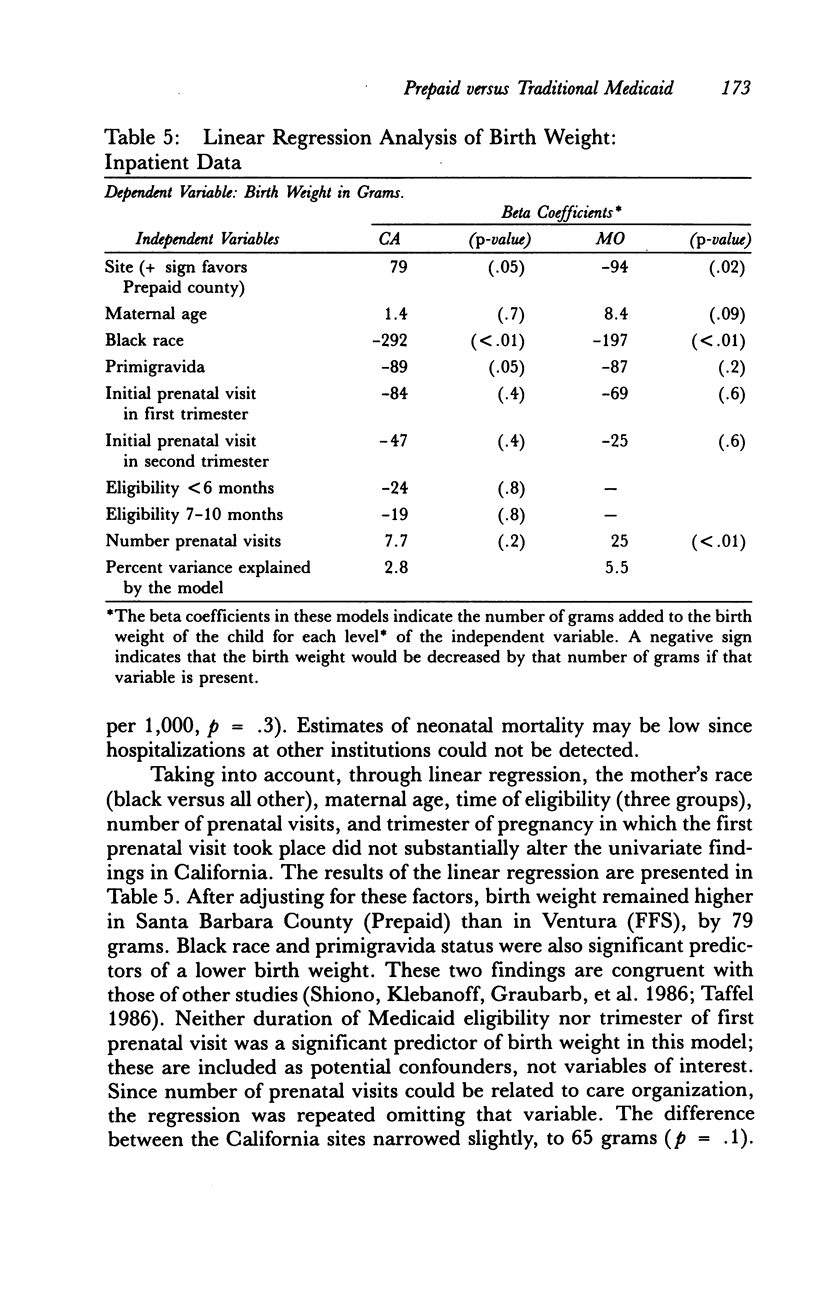
Abstract
Enrollment of Medicaid recipients into capitated, case-managed systems has been advocated as a method of controlling cost. We studied prenatal care and birth outcomes for women and children enrolled in Aid to Families with Dependent Children (AFDC) in two capitated programs in Santa Barbara, California and Jackson County, Missouri (Prepaid), compared with similar but fee-for-service comparison medical communities in Ventura County, California and St. Louis, Missouri (FFS). At the sites of care, 2,336 inpatient and 823 prenatal care records were abstracted. Women at all sites received fewer than the recommended number of prenatal visits. At no site did more than 40 percent of women receive prenatal care in the first trimester of pregnancy. Mean birth weight and proportion of children of low birth weight (less than 2,500 grams) were similar between the demonstration and comparison counties. Complications of pregnancy and cesarean section rates were also similar between demonstration and comparison counties. This study did not demonstrate a decreased quality of care provided to enrollees in capitated, case-managed Medicaid programs compared with fee-for-service. Basic prenatal care was provided only to some members of this population, regardless of the type of physician payment.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooney J. P. What determines the start of prenatal care? Prenatal care, insurance, and education. Med Care. 1985 Aug;23(8):986–997. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198508000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund D. A. Competitive health plans and alternative payment arrangements for physicians in the United States: public sector examples. Health Policy. 1987 Apr;7(2):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0168-8510(87)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund D. A., Rossiter L. F., Fox P. D., Meyer J. A., Hurley R. E., Carey T. S., Paul J. E. Evaluation of the Medicaid competition demonstrations. Health Care Financ Rev. 1989 Winter;11(2):81–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley R. E., Freund D. A. A typology of Medicaid managed care. Med Care. 1988 Aug;26(8):764–774. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198808000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. D., Makuc D., Kleinman J. C. National and state trends in use of prenatal care, 1970-83. Am J Public Health. 1986 Apr;76(4):415–423. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman E., Ryan K. J., Monson R. R., Schoenbaum S. C. Risk factors accounting for racial differences in the rate of premature birth. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 17;317(12):743–748. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709173171206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft H. S. Assessing the evidence on HMO performance. Milbank Mem Fund Q Health Soc. 1980 Fall;58(4):501–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning W. G., Leibowitz A., Goldberg G. A., Rogers W. H., Newhouse J. P. A controlled trial of the effect of a prepaid group practice on use of services. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 7;310(23):1505–1510. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406073102305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quick J. D., Greenlick M. R., Roghmann K. J. Prenatal care and pregnancy outcome in an HMO and general population: a multivariate cohort analysis. Am J Public Health. 1981 Apr;71(4):381–390. doi: 10.2105/ajph.71.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiono P. H., Klebanoff M. A., Graubard B. I., Berendes H. W., Rhoads G. G. Birth weight among women of different ethnic groups. JAMA. 1986 Jan 3;255(1):48–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloss E. M., Keeler E. B., Brook R. H., Operskalski B. H., Goldberg G. A., Newhouse J. P. Effect of a health maintenance organization on physiologic health. Results from a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Jan;106(1):130–138. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-1-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobino D. M., Chase G. A., Kim Y. J., Crawley B. E., Salim J. H., Baruffi G. The impact of the Mississippi Improved Child Health Project on prenatal care and low birthweight. Am J Public Health. 1986 Mar;76(3):274–278. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.3.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. E., Jr, Brook R. H., Rogers W. H., Keeler E. B., Davies A. R., Sherbourne C. D., Goldberg G. A., Camp P., Newhouse J. P. Comparison of health outcomes at a health maintenance organisation with those of fee-for-service care. Lancet. 1986 May 3;1(8488):1017–1022. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91282-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


