Abstract
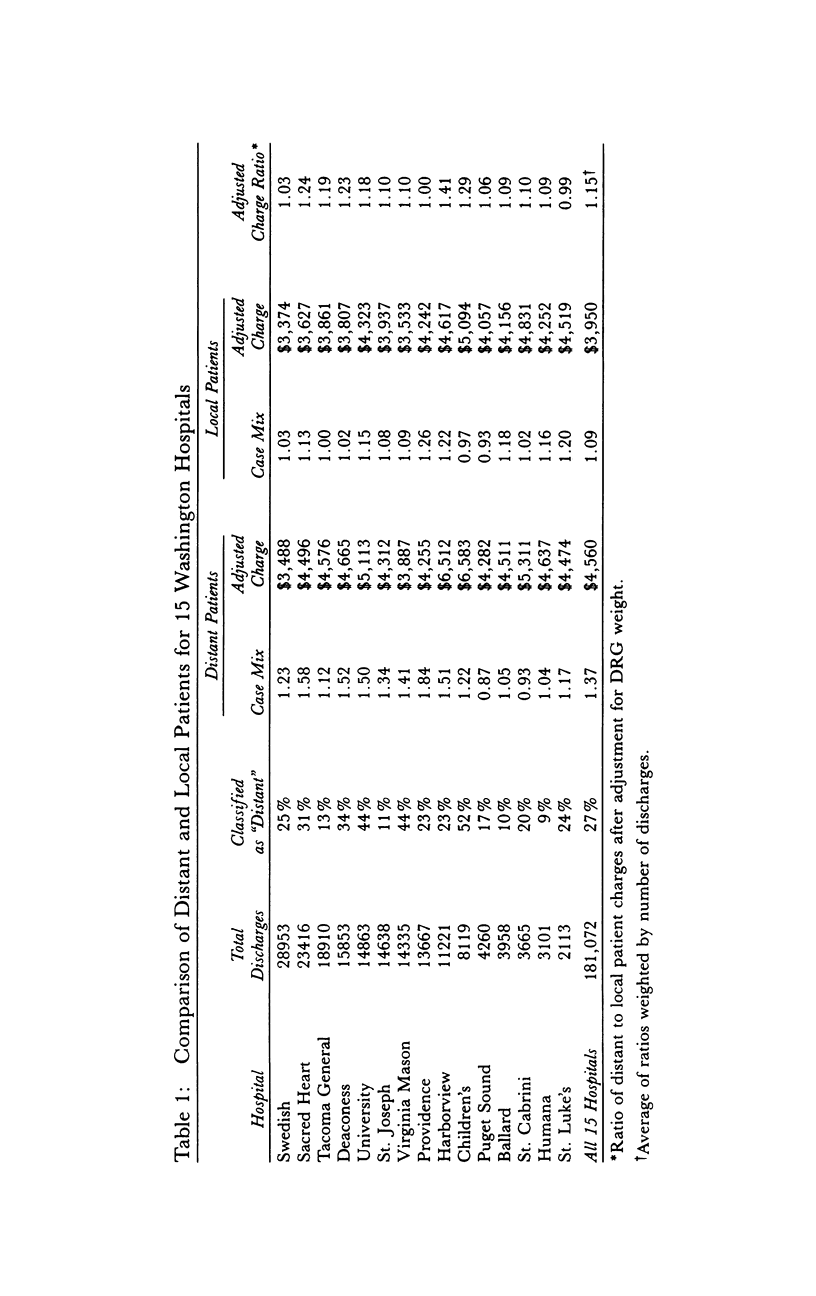
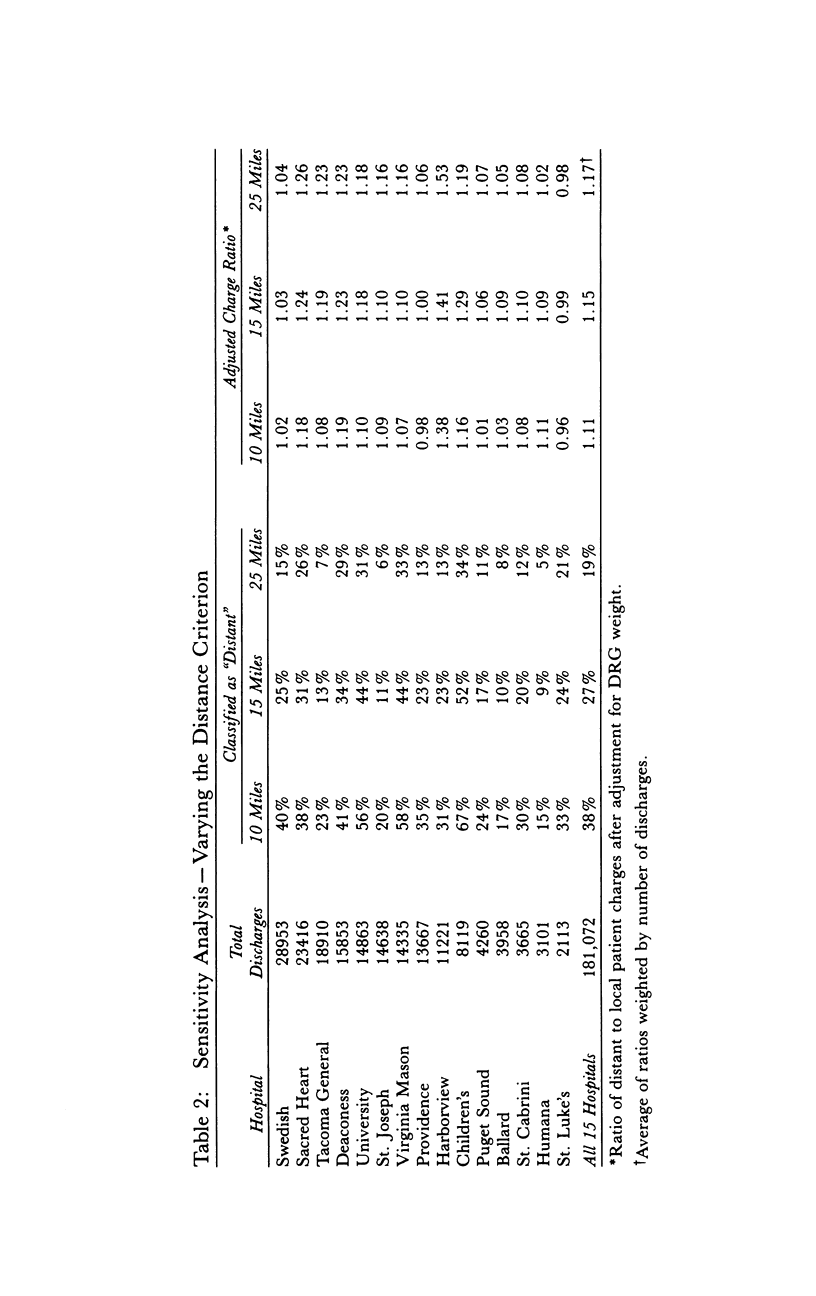
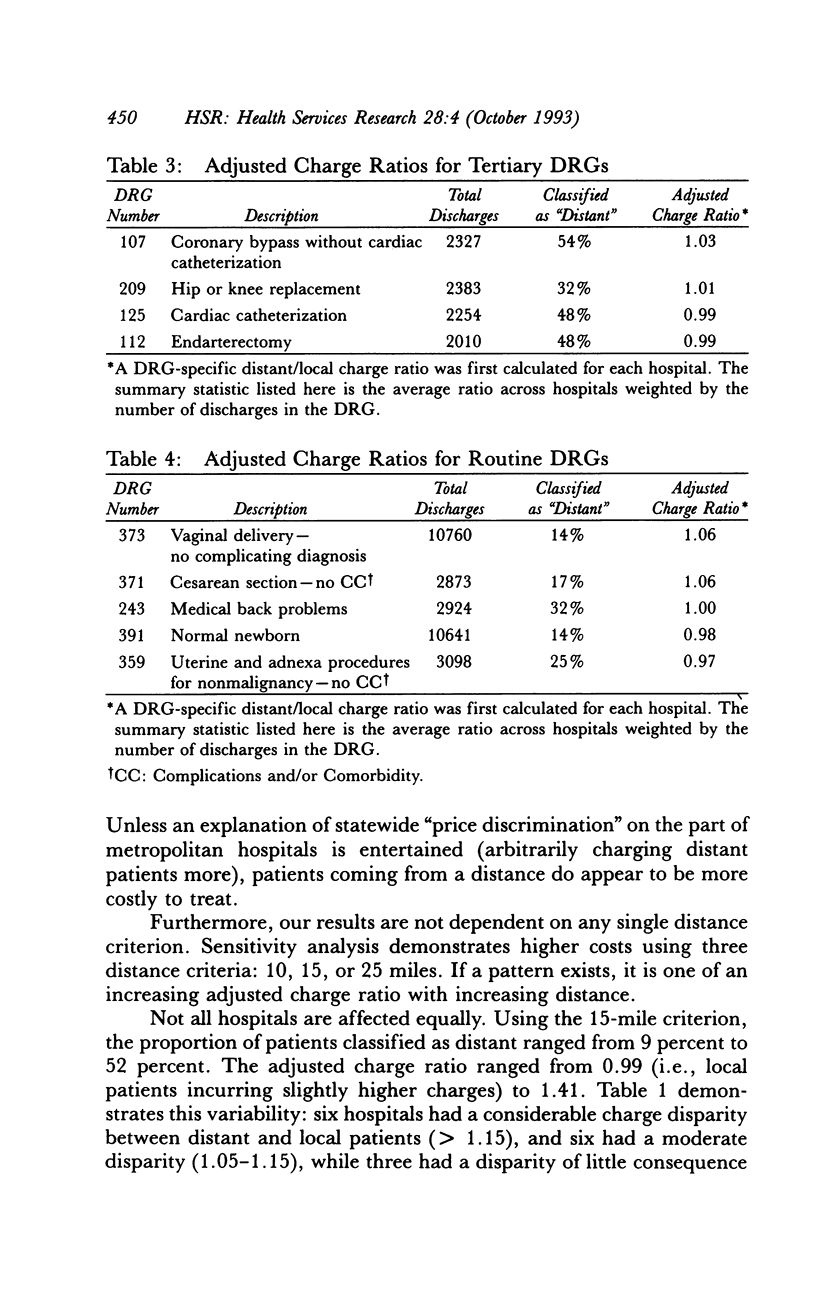
OBJECTIVE. We test the hypothesis that hospital costs, after adjusting for DRG mix, are higher in distant patients than in local patients. DATA SOURCES AND STUDY SETTING. Data were obtained from the Washington State Commission Hospital Abstract Reporting System (CHARS) and included all patients discharged from 15 metropolitan hospitals in the state of Washington during fiscal year 1987 (N = 181,072). STUDY DESIGN. Distant patients were initially defined as those patients residing outside a 15-mile radius of the hospital from which they were discharged; all other patients were considered local. Distance was determined using the patient's residence zip code. Hospital charge, calculated for all patients regardless of payer, served as a proxy for cost and was adjusted using the DRG weight. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS. Average charge (adjusted for DRG weight) was higher for distant patients in all but two hospitals. Overall adjusted charge for distant patients was 15 percent higher (p < .001). This finding persisted when different distances were used to dichotomize distant and local patients. When the 20 most common DRGs were examined individually, little charge difference was found in surgical DRGs that require tertiary center services (tertiary DRGs) and in those DRGs with both moderate and predictable resource use (routine DRGs); the charge difference seemed most prominent in those DRGs with a wide array of possible resource use (heterogeneous DRGs). CONCLUSIONS. Results suggest that patients traveling long distances use more resources and incur higher hospital charges than local patients. This is not accounted for in prospective payment. We postulate that distance might serve in part as a proxy for severity-of-illness.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman R. A., Green J., Kwo D., Safian K. F., Botnick L. Severity of illness and the teaching hospital. J Med Educ. 1986 Jan;61(1):1–9. doi: 10.1097/00001888-198601000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster A. C., Karlin B. G., Hyde L. A., Jacobs C. M., Bradbury R. C., Chae Y. M. MEDISGRPS: a clinically based approach to classifying hospital patients at admission. Inquiry. 1985 Winter;22(4):377–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkler S. A. The distinction between cost and charges. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):102–109. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella J. S., Hornbrook M. C., Louis D. Z. Staging of disease. A case-mix measurement. JAMA. 1984 Feb 3;251(5):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S. D., Bulkley G., Sharkey P. D., Chambers A. F., Horn R. A., Schramm C. J. Interhospital differences in severity of illness. Problems for prospective payment based on diagnosis-related groups (DRGs). N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 4;313(1):20–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507043130105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S. D., Horn R. A. Reliability and validity of the Severity of Illness Index. Med Care. 1986 Feb;24(2):159–178. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198602000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S. D., Horn R. A., Sharkey P. D., Chambers A. F. Severity of illness within DRGs. Homogeneity study. Med Care. 1986 Mar;24(3):225–235. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198603000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn S. D., Horn R. A., Sharkey P. D. The Severity of Illness Index as a severity adjustment to diagnosis-related groups. Health Care Financ Rev. 1984;Suppl:33–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jencks S. F., Bobula J. D. Does receiving referral and transfer patients make hospitals expensive? Med Care. 1988 Oct;26(10):948–958. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198810000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jencks S. F., Dobson A. Refining case-mix adjustment. The research evidence. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 10;317(11):679–686. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709103171106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer J. D. The distance behavior of hospital patients: a disaggregated analysis. Soc Sci Med. 1983;17(12):819–827. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(83)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuirk M. A., Porell F. W. Spatial patterns of hospital utilization: the impact of distance and time. Inquiry. 1984 Spring;21(1):84–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. C., Luft H. S., McPhee S. J., Hunt S. S. Hospital competition and surgical length of stay. JAMA. 1988 Feb 5;259(5):696–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simborg D. W. DRG creep: a new hospital-acquired disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 25;304(26):1602–1604. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106253042611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits H. L., Fetter R. B., McMahon L. F., Jr Variation in resource use within diagnosis-related groups: the severity issue. Health Care Financ Rev. 1984;Suppl:71–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock R. Distance and the utilization of health facilities in rural Nigeria. Soc Sci Med. 1983;17(9):563–570. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(83)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F., Fox J., Clemmer T. P., Orme J. F., Jr, Vincent G. M., Menlove R. L. The financial impact of Medicare diagnosis-related groups. Effect upon hospitals receiving cardiac patients referred for tertiary care. Chest. 1987 Mar;91(3):418–423. doi: 10.1378/chest.91.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F., Larsen K., Clemmer T. P., Burke J. P., Orme J. F., Jr, Napoli M., Christison E. Impact of prospective payments on a tertiary care center receiving large numbers of critically ill patients by aeromedical transport. Crit Care Med. 1986 Mar;14(3):227–230. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198603000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe K. E., Brecher C. Improved access to care for the uninsured poor in large cities: do public hospitals make a difference? J Health Polit Policy Law. 1987 Summer;12(2):313–324. doi: 10.1215/03616878-12-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. P., Draper E. A. Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE II) and Medicare reimbursement. Health Care Financ Rev. 1984;Suppl:91–105. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden G. D., Saffle J. R., Kravitz M. Potential DRG reimbursement vs actual cost for burn care. II. Referral distance. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1986 Jan-Feb;7(1):48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. W. Incorporating severity of illness and comorbidity in case-mix measurement. Health Care Financ Rev. 1984;Suppl:23–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


