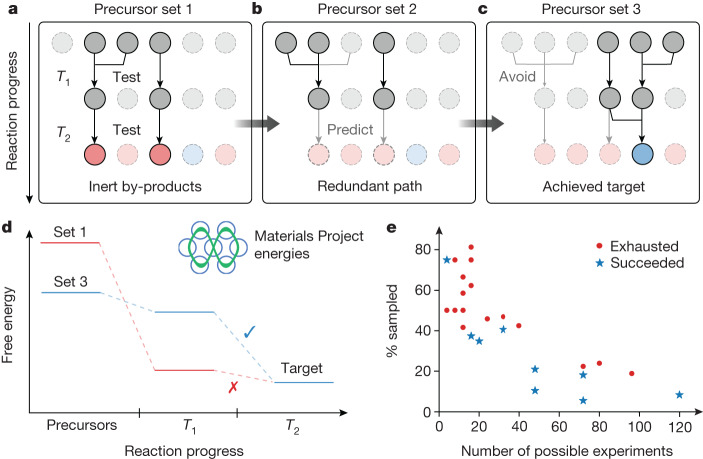
Fig. 3. Active learning with pairwise reaction analysis.
a, From a failed synthesis attempt, the A-Lab determines which pairwise reactions occurred. b, New precursors are recommended by substituting at least one precursor involved in the unfavourable pairwise reaction. In cases in which the new precursor set leads to identical intermediates as a previously tested set, it is not explored at any higher temperatures. c, The successful precursor set avoids all the unfavourable pairwise reactions. d, The free energy at each step in the reaction pathway, calculated using data from the Materials Project, which shows that the successful pathway maintains a large driving force at the target-forming step. e, Following this approach, the scatter plot shows the number of experiments required to exhaust all unique reaction paths for each target (red) or to identify an optimal path with high yield (blue), plotted with respect to the total size of each experimental search space.