Abstract
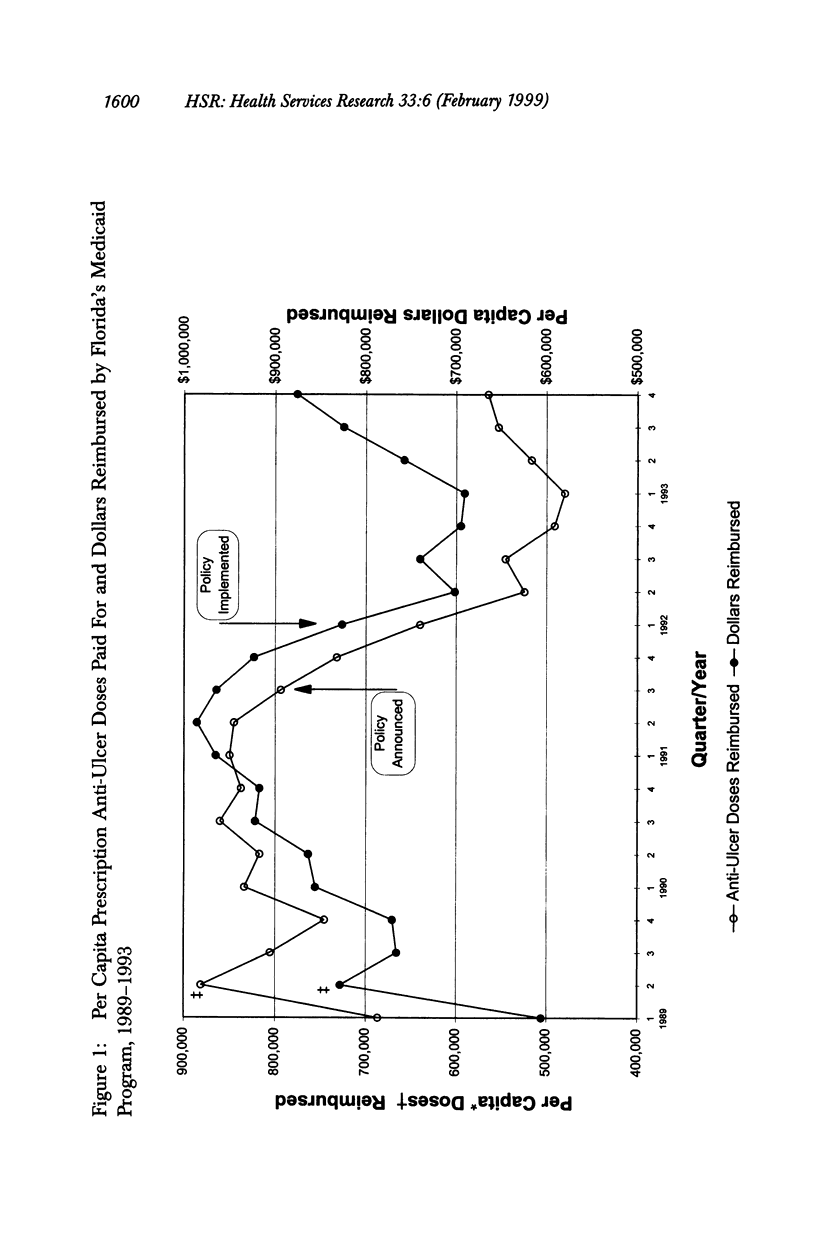
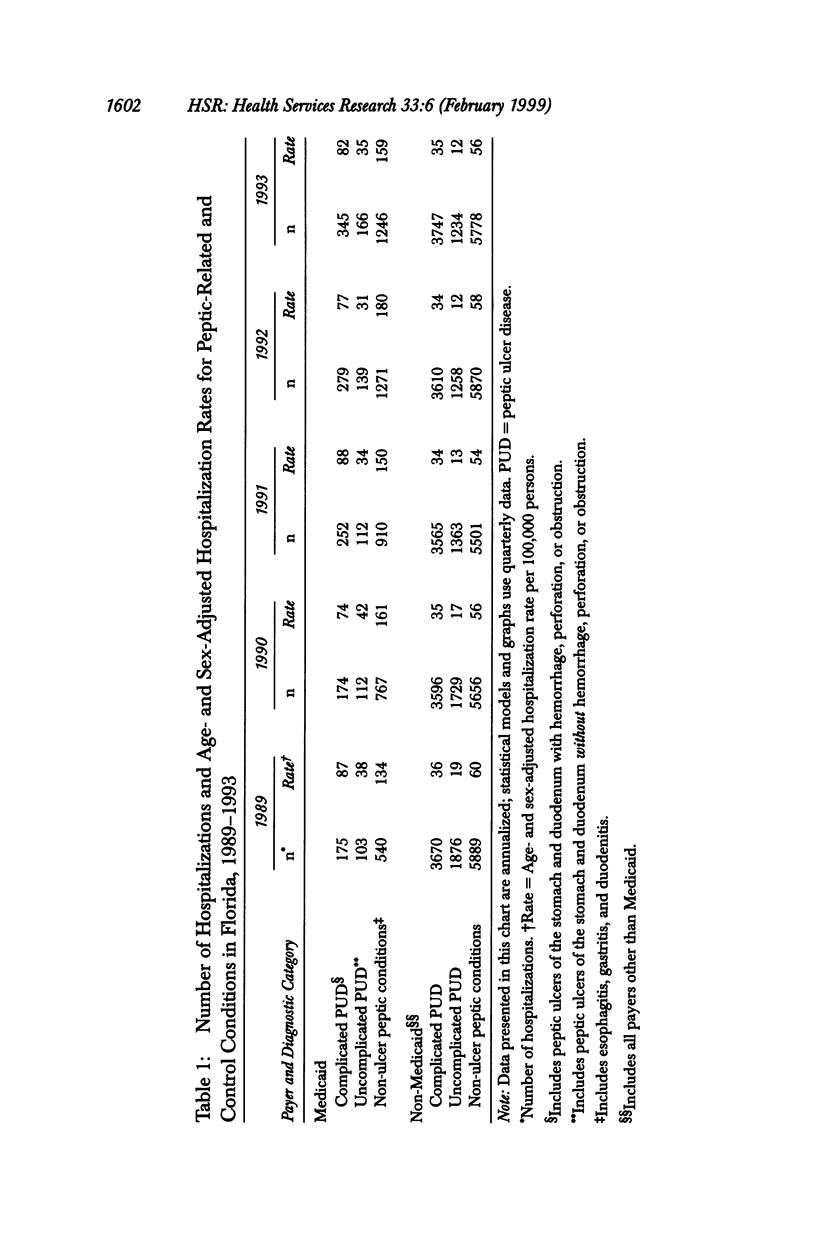
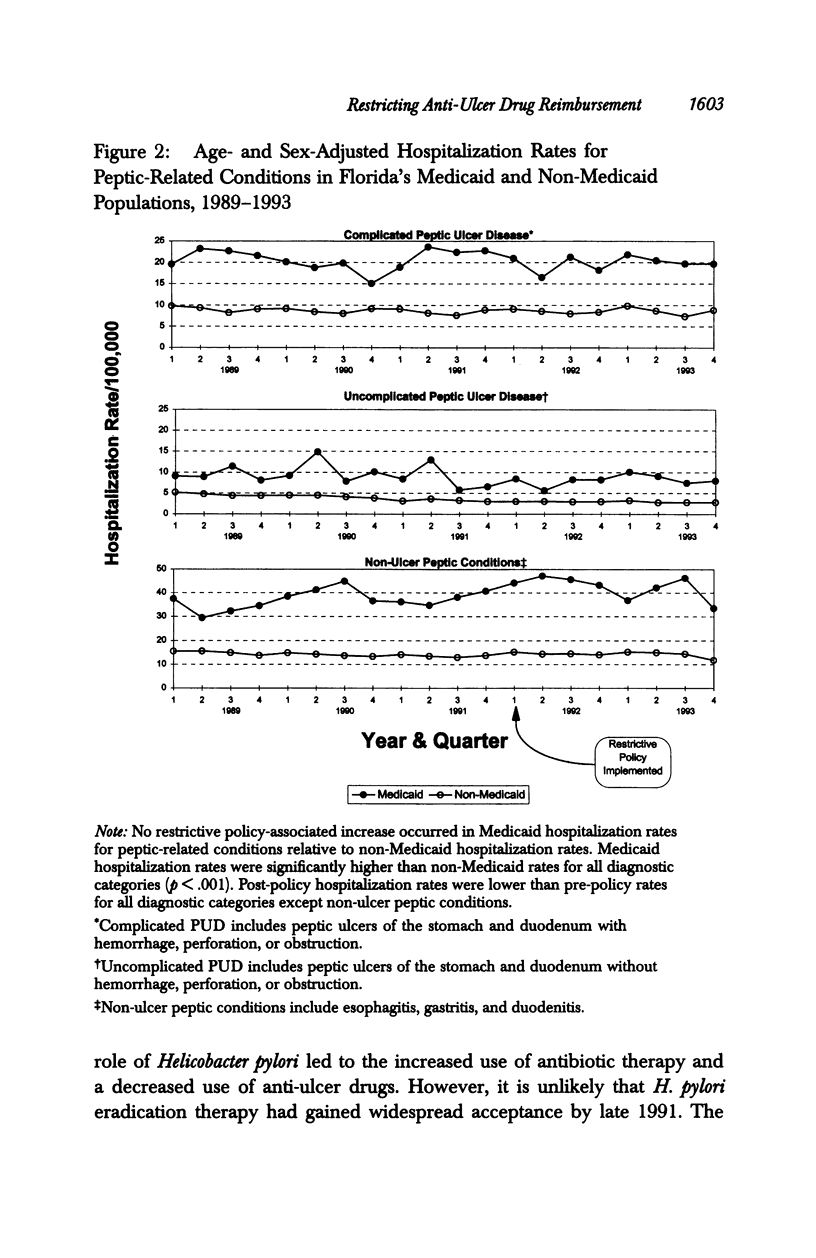
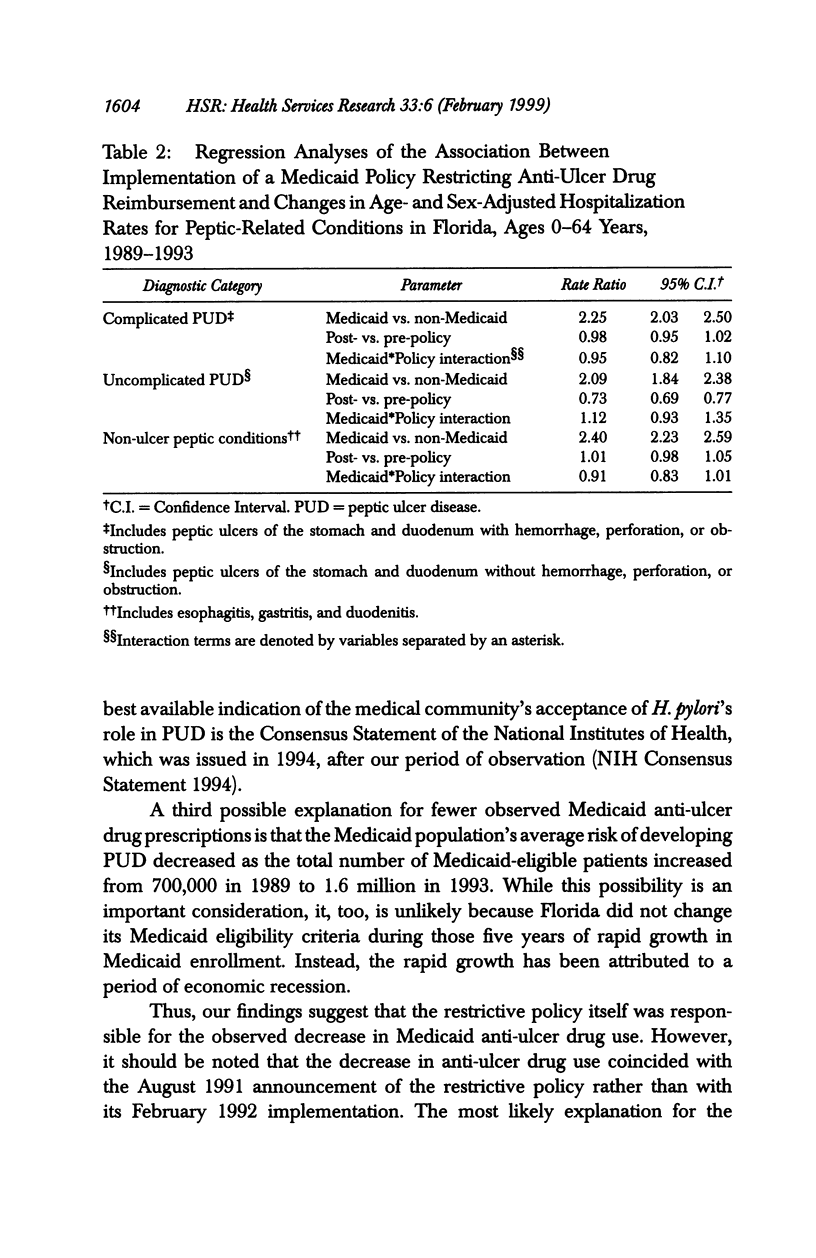
OBJECTIVE: To examine the impact of a policy restricting reimbursement for Medicaid anti-ulcer drugs on anti-ulcer drug use and peptic-related hospitalizations. DATA SOURCES/STUDY SETTING: In addition to U.S. Census Bureau data, all of the following from Florida: Medicaid anti-ulcer drug claims data, 1989-1993; Medicaid eligibility data, 1989-1993; and acute care nonfederal hospital discharge abstract data (Medicaid and non-Medicaid), 1989-1993. STUDY DESIGN: In this observational study, a Poisson multiple regression model was used to compare changes, after policy implementation, in Medicaid reimbursement for prescription anti-ulcer drugs as well as hospitalization rates between pre- and post-implementation periods in Medicaid versus non-Medicaid patients hospitalized with peptic ulcer disease. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: Following policy implementation, the rate of Medicaid reimbursement for anti-ulcer drugs decreased 33 percent (p < .001). No associated increase occurred in the rate of Medicaid peptic-related hospitalizations. CONCLUSIONS: Florida's policy restricting Medicaid reimbursement for anti-ulcer drugs was associated with a substantial reduction in outpatient anti-ulcer drug utilization without any significant increase in the rate of hospitalization for peptic-related conditions.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berstad A., Weberg R. Antacids for peptic ulcer: do we have anything better? Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;125:32–41. doi: 10.3109/00365528609093815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Lipowski E. E. Pharmacists' reactions to the Wisconsin Medicaid drug-use review program. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1993 Sep;50(9):1898–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A., Bousfield R., Christiansen J. Incidence of perforated and bleeding peptic ulcers before and after the introduction of H2-receptor antagonists. Ann Surg. 1988 Jan;207(1):4–6. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198801000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmand-Høyer E., Jensen K. B., Krag E., Rask-Madsen J., Rahbek I., Rune S. J., Wulff H. R. Prophylactic effect of cimetidine in duodenal ulcer disease. Br Med J. 1978 Apr 29;1(6120):1095–1097. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6120.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. O., Walker R. J., Crowe J., Gillies R. R., Gillies K. R., Gough K. R., Lorber S. Double-blind randomized multicenter study comparing Maalox TC tablets and ranitidine in healing of duodenal ulcers. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Jul;36(7):911–916. doi: 10.1007/BF01297140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay A. J., McArdle C. S. Cimetidine and perforated peptic ulcer. Br J Surg. 1982 Jun;69(6):319–320. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paimela H., Tuompo P. K., Peräkyl T, Saario I., Höckerstedt K., Kivilaakso E. Peptic ulcer surgery during the H2-receptor antagonist era: a population-based epidemiological study of ulcer surgery in Helsinki from 1972 to 1987. Br J Surg. 1991 Jan;78(1):28–31. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soumerai S. B., Avorn J., Ross-Degnan D., Gortmaker S. Payment restrictions for prescription drugs under Medicaid. Effects on therapy, cost, and equity. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 27;317(9):550–556. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708273170906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soumerai S. B., McLaughlin T. J., Ross-Degnan D., Casteris C. S., Bollini P. Effects of a limit on Medicaid drug-reimbursement benefits on the use of psychotropic agents and acute mental health services by patients with schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Sep 8;331(10):650–655. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199409083311006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soumerai S. B., Ross-Degnan D., Avorn J., McLaughlin T. j., Choodnovskiy I. Effects of Medicaid drug-payment limits on admission to hospitals and nursing homes. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 10;325(15):1072–1077. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110103251505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soumerai S. B., Ross-Degnan D., Fortess E. E., Abelson J. A critical analysis of studies of state drug reimbursement policies: research in need of discipline. Milbank Q. 1993;71(2):217–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman D. R., Collins T. M., Lipowski E. E., Sainfort F. Evaluation of a DUR intervention: a case study of histamine antagonists. Inquiry. 1994 Spring;31(1):89–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


