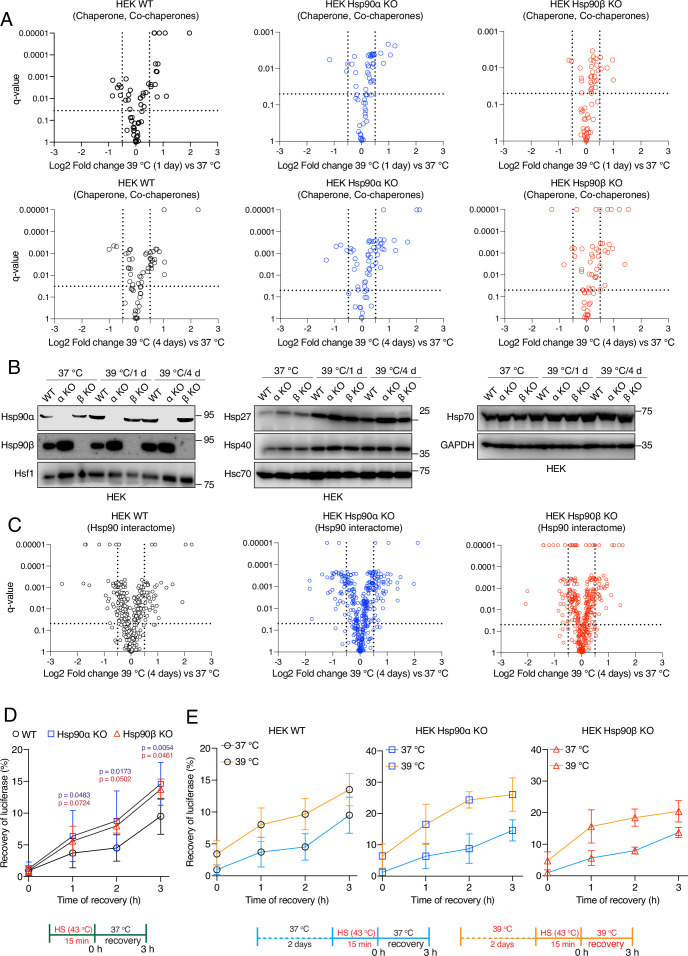
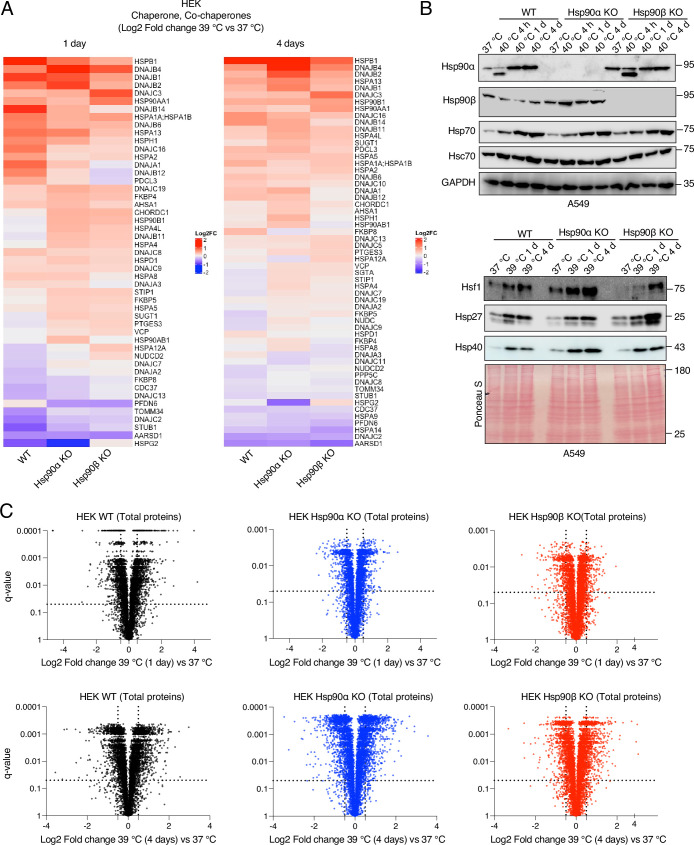
Figure 4. Hsp90α/β KO cells maintain chaperones, co-chaperones, and Hsp90 interactors during chronic stress adaptation.
(A) Volcano plots of the normalized fold changes of molecular chaperones and co-chaperones after 1 and 4 days (first and second rows, respectively) of chronic HS determined by quantitative label-free proteomic analyses of Hsp90α/β KO and WT HEK cells. Each genotype was compared with its respective 37 °C control (n=3 biologically independent samples). Log2 fold changes of >0.5 or <–0.5 with q-values (adjusted p-values) of <0.05 (indicated as stippled lines) were considered significant differences for a particular protein. (B) Immunoblots of different molecular chaperones in HEK WT and Hsp90α/β KO cells (α KO, Hsp90αKO; β KO, Hsp90βKO). GAPDH serves as the loading control for all three panels (representative of n=2 independent experiments). (C) Volcano plots of the normalized fold changes of the Hsp90 interactors (list obtained from https://www.picard.ch/Hsp90Int) after 4 days of chronic HS determined by quantitative label-free proteomic analyses of Hsp90α/β KO and WT HEK cells. Each genotype was compared with its respective 37 °C control (n=3 biologically independent samples). (D and E) In vivo refolding of heat-denatured luciferase of control cells (blue line) and cells heat-adapted to 39 °C (orange line). Luciferase activity before the acute HS (at 43 °C) is set to 100% (n=3 biologically independent samples). See scheme of the experiment below. Note the different scales of the Y axes of the bar graphs in panel E. The data are represented as mean values ± SEM for all bar graphs. The statistical significance between the groups was analyzed by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-tests. The p-values for Hsp90α and Hsp90β KO cells are in blue and red, respectively. All p-values are for comparisons to the respective WT.