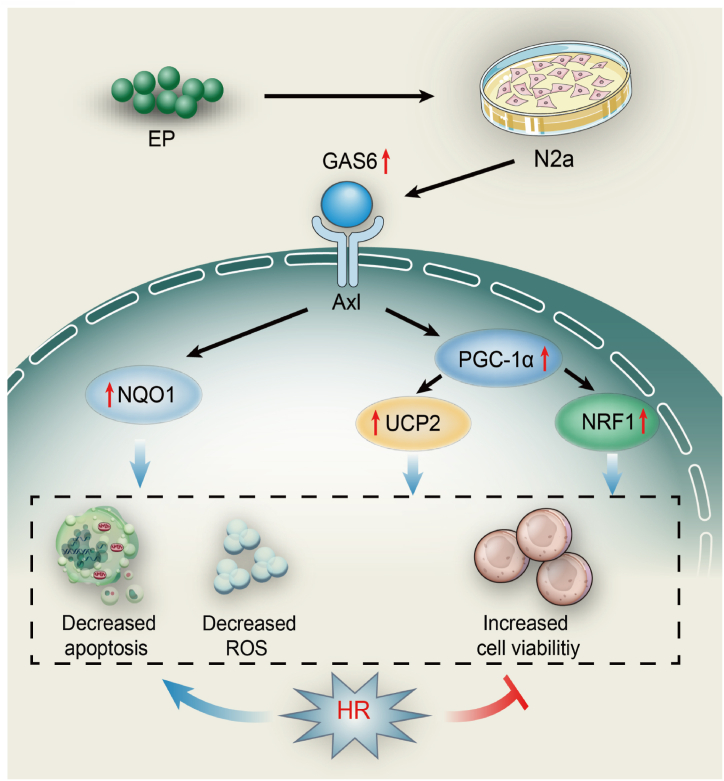
Fig. 7.
GAS6/Axl signaling-dependent mechanism of EP-induced neuroprotective effects against HR injury. EP treatment promotes GAS6/Axl axis activation, which further upregulates PGC-1α and UCP2 expression, thus elevating their downstream targets, such as NQO1 and NRF1, which further inhibit HR-induced oxidative stress and the subsequent apoptosis of neurons. These results suggest that EP treatment may be a valuable therapeutic strategy against cerebral IRI.