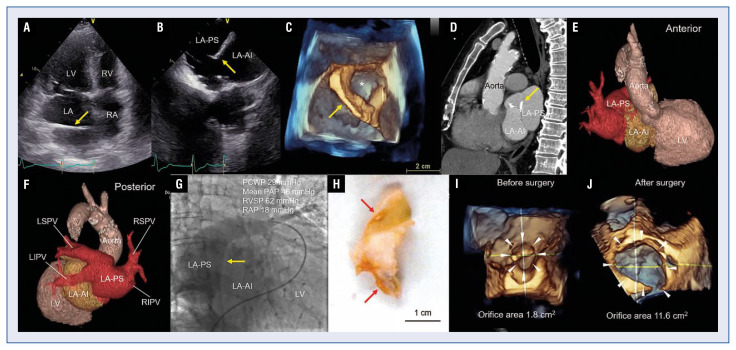
A 71-year-old man with a history of atrial fibrillation was hospitalized due to congestive heart failure. Two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) showed the membrane dividing the left atrium into the postero-superior chamber (LA-PS) and the antero-inferior chamber (LA-AI) (peak pressure gradient 15 mmHg and estimated right ventricular systolic pressure 61 mmHg) (Fig. 1A, B, yellow arrows). Three-dimensional (3D) TEE revealed the membrane (yellow arrow) with a single defect (Fig. 1C, asterisk). Cardiac computed tomography (CT) showed the membrane with a partial calcification in the left atrium (Fig. 1D, yellow arrow). Contrast-enhanced chest CT with 3D image reconstruction visualized the anatomical structure of cor triatriatum sinister (CTS), and showed that the right superior and inferior pulmonary veins (RSPV and RIPV), and the left superior and inferior pulmonary veins (LSPV and LIPV) were in communication with the LA-PS (Fig. 1E, F; Suppl. Video 1). Pulmonary artery angiogram showed that the contrast filling in the LA-AI was delayed compared to that in the LA-PS (Fig. 1G). Surgical resection of the membrane in the left atrium was performed. The membrane in the left atrium resected by surgery showed hyaline degeneration and calcification (Fig. 1H, red arrows). 3D TEE showed that the calculated orifice area of the membrane in the left atrium was increased from 1.8 cm2 to 11.6 cm2 after the surgery (Fig. 1I, J, white arrowheads). Multimodality assessment of CTS is important for preoperative and postoperative evaluation as well as the search for other cardiac abnormalities.
Figure 1.
A. Two-dimensional (2D) transthoracic echocardiogram (apical 4-chamber view) showing the membrane in the left atrium; LV — left ventricle; LA — left atrium; RV — right ventricle; RA — right atrium; B. 2D transesophageal echocardiography (TEE); LA-PS — left atrium into the postero-superior chamber; LA-AI — left atrium into the antero-inferior chamber; C. 3D TEE; D. Cardiac computed tomography (CT) (sagittal view); E, F. Contrast-enhanced 3D CT; RSPV — right superior pulmonary vein; RIPV — right inferior pulmonary vein; LSPV — left superior pulmonary vein; LIPV — left inferior pulmonary veins; G. Pulmonary artery angiogram; PCWP — pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; PAP — pulmonary artery pressure; RVSP — right ventricular systolic pressure; RAP — right atrial pressure; H. The membrane in the left atrium resected by surgery; I, J. 3D TEE showing the calculated orifice area of the membrane before (I) and after (J) the surgery.
Supplementary Information
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: None declared
Funding
This work was supported in part by the research grant from The Ito Foundation (The 27th Ito Foundation Grant, TK).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.