Figure 1. Targeted nanoscale photobiotinylation using Femto-seq.
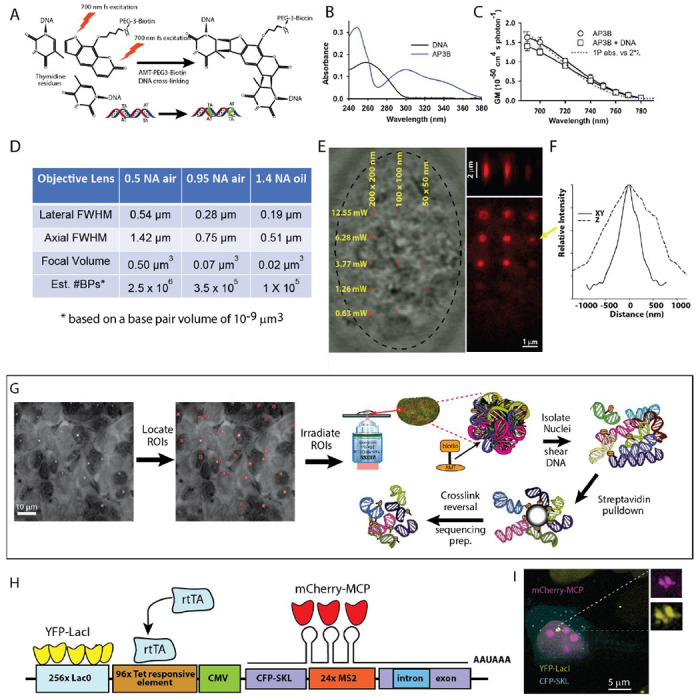
A. 4’-aminomethyltrioxsalen (4’-AMT) is a psoralen family DNA cross-linker, which forms covalent bonds primarily with thymidine residues when excited by UV or UV-like two-photon (2P) irradiation. The photoactivatable reagent used is 4′-Aminomethyltrioxsalen-PEG3-Biotin (AP3B), which enables covalent attachment of biotin to DNA. B. Absorbance spectra of AP3B. Use of 700 nm 2P excitation or longer UV (~360 nm) avoids shorter wavelength DNA absorptions. C. Two-photon absorption cross-sections of the AP3B photobiotinylation probe. D. The minimal volume (assuming a single XYZ spot) calculated for three different numerical aperture (NA) objectives. Using high NA, it is possible to biotinylate extremely small volumes within the nucleus. E. Streptavidin-Alexa 647 labeling of different sized photo-biotinylated regions (1x1, 2x2 and 4x4 pixel ROI box sizes) in a FISH-fixed U2OS nucleus after photo-biotinylation taken at 5 different cross-linking intensities. The 700 nm femtosecond pulses were delivered through 63x/1.4 Zeiss objective lens. Pixel size was 50 nm (5.3x zoom) and the pixel dwell time as 4.1μs and 30 passes over the ROI was used (123 μs per 0.0025 μm3) for all crosslinking powers shown. F. Lateral and axial dimensions a one-pixel region cross-linked using 6.28 mW at the above scanning parameters. G. Overview of the Femto-seq method (see text). H. U2OS transgene structure (adapted from ref. 3) used for Femto-seq validation experiments. I. U2OS cell after gene activation (+DOX) and IPTG removal to allow YFP-LacI binding for visualization of transgene site showing colocalization of the YFP-LacI and MCP-mCherry.
