Abstract
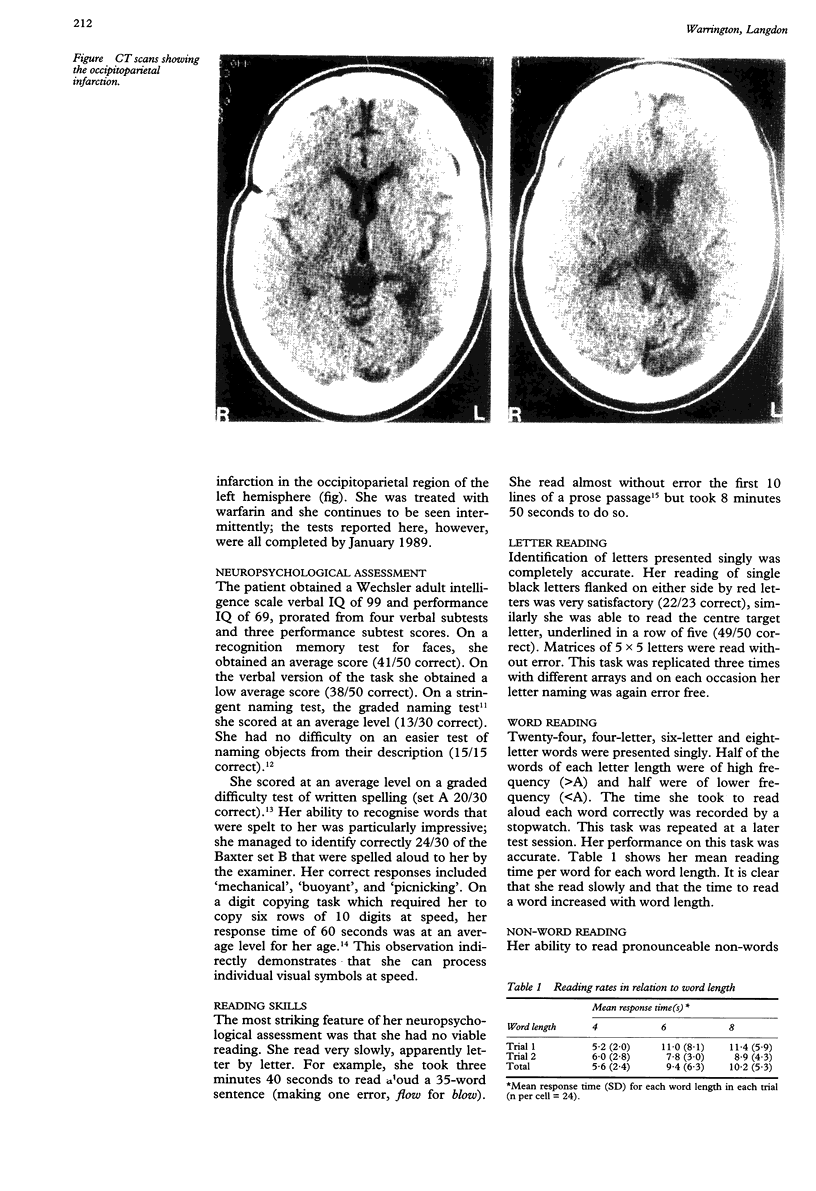
A patient with spelling dyslexia read both words and text accurately but slowly and laboriously letter by letter. Her performance on a test of lexical decision was slow. She had great difficulty in detecting a 'rogue' letter attached to the beginning or end of a word--for example, ksong--or in parsing two unspaced words, such as applepeach. By contrast she was immune to the effects of interpolating extraneous coloured letters in a word, a manipulation that affects normal readers. Therefore it is argued that this patient had damage to an early stage in the reading process, to the visual word form itself.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coslett H. B., Saffran E. M. Evidence for preserved reading in 'pure alexia'. Brain. 1989 Apr;112(Pt 2):327–359. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlan A. K., Warrington E. K. Word-comprehension and word-retrieval in patients with localized cerebral lesions. Brain. 1978 Mar;101(1):163–185. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSBOURNE M., WARRINGTON E. K. A disorder of simultaneous form perception. Brain. 1962 Sep;85:461–486. doi: 10.1093/brain/85.3.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSBOURNE M., WARRINGTON E. K. THE LOCALIZING SIGNIFICANCE OF LIMITED SIMULTANEOUS VISUAL FORM PERCEPTION. Brain. 1963 Dec;86:697–702. doi: 10.1093/brain/86.4.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy R., Warrington E. K. Phonological reading: phenomena and paradoxes. Cortex. 1986 Sep;22(3):359–380. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(86)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson K., Kay J. Letter-by-letter reading: psychological descriptions of a neurological syndrome. Q J Exp Psychol A. 1982 Aug;34(Pt 3):411–441. doi: 10.1080/14640748208400852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacter D. L., Rapscak S. Z., Rubens A. B., Tharan M., Laguna J. Priming effects in a letter-by-letter reader depend upon access to the word form system. Neuropsychologia. 1990;28(10):1079–1094. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(90)90142-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., Shallice T. Semantic access dyslexia. Brain. 1979 Mar;102(1):43–63. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., Shallice T. Word-form dyslexia. Brain. 1980 Mar;103(1):99–112. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]