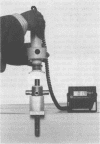
Abstract
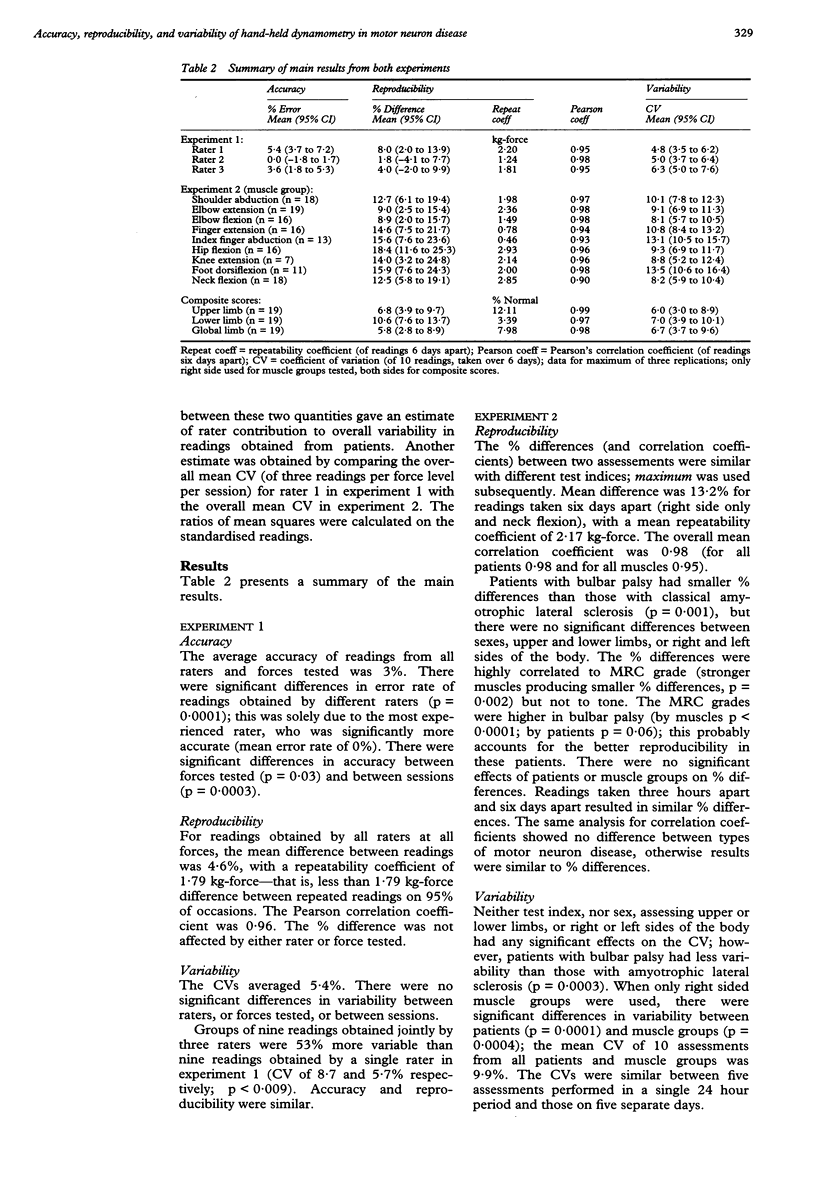
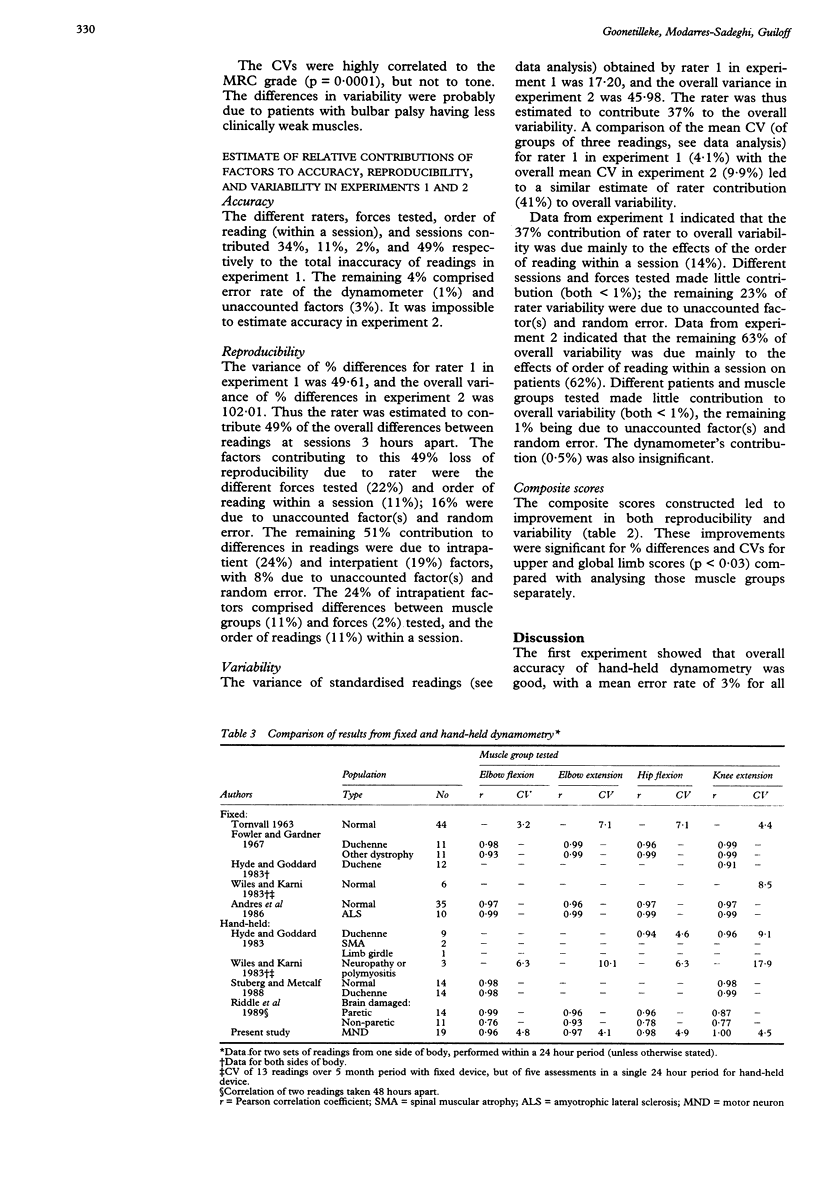
A spring-loaded device that "breaks" at preset forces was used to assess readings obtained by hand-held dynamometry by three raters with varying experience in the method. Overall accuracy (3%), but not reproducibility or variability, was improved by greater experience. Readings obtained jointly by three raters had 53% greater variability than those obtained by a single rater. Nine muscle groups in 19 patients with motor neuron disease were assessed at 10 sessions (three replications per session) over six days by the experienced rater. Muscle force was expressed relative to that of 22 matched normal controls. The reproducibility was good with a mean % difference of 13.2 and repeatability coefficient of 2.17 kg-force for readings six days apart; the overall correlation coefficient was 0.98. The mean coefficient of variation (CV) of 10 readings was 9.9%. The poorer reproducibility and greater variability seen in clinically weaker muscles may account for differences in patients with bulbar palsy and classical amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; the degree of spasticity had no effect. The rater was estimated to contribute 37% of the total variability when testing patients. The use of a composite score by combining normalised dynamometry readings of eight limb muscles improved mean % difference to 6.7 and mean CV to 5.8%. The reproducibility and variability of hand-held dynamometry readings obtained by a single rater compare well with those of fixed devices. Readings from single raters, irrespective of experience, have similar reproducibility and variability. If, however, multiple raters are used in longitudinal assessments of individual patients, as occurs in clinical trials, the variability of their combined readings should be estimated when calculating the same size required.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre J. C., Magness J. L., Hull S. Z., Wright K. C., Baxter T. L., Patterson R., Stradel L. Strength testing with a portable dynamometer: reliability for upper and lower extremities. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1987 Jul;68(7):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres P. L., Hedlund W., Finison L., Conlon T., Felmus M., Munsat T. L. Quantitative motor assessment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology. 1986 Jul;36(7):937–941. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.7.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEASLEY W. C. Influence of method on estimates of normal knee extensor force among normal and postpolio children. Phys Ther Rev. 1956 Jan;36(1):21–41. doi: 10.1093/ptj/36.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon R. W., Andrews A. W. Interrater reliability of hand-held dynamometry. Phys Ther. 1987 Jun;67(6):931–933. doi: 10.1093/ptj/67.6.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohannon R. W. Test-retest reliability of hand-held dynamometry during a single session of strength assessment. Phys Ther. 1986 Feb;66(2):206–209. doi: 10.1093/ptj/66.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denys E. H., Norris F. H., Jr Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Impairment of neuromuscular transmission. Arch Neurol. 1979 Apr;36(4):202–205. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500400056008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., McDonnell M. Hand-held dynamometer for evaluating voluntary-muscle function. Lancet. 1974 Sep 28;2(7883):757–758. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90947-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. M., Jr, Gardner G. W. Quantitative strength measurements in muscular dystrophy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1967 Dec;48(12):629–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiloff R. J., Eckland D. J., Demaine C., Hoare R. C., MacRae K. D., Lightman S. L. Controlled acute trial of a thyrotrophin releasing hormone analogue (RX77368) in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Oct;50(10):1359–1370. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.10.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiloff R. J., Eckland D. J. Observations on the clinical assessment of patients with motor neuron disease. Experience with a TRH analogue. Neurol Clin. 1987 Feb;5(1):171–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosking J. P., Bhat U. S., Dubowitz V., Edwards R. H. Measurements of muscle strength and performance in children with normal and diseased muscle. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Dec;51(12):957–963. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.12.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde S. A., Goddard C. M., Scott O. M. The myometer: the development of a clinical tool. Physiotherapy. 1983 Dec;69(12):424–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheault W., Beal J. L., Kubik K. R., Nowak T. A., Shepley J. A. Intertester reliability of the hand-held dynamometer for wrist flexion and extension. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989 Dec;70(13):907–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle D. L., Finucane S. D., Rothstein J. M., Walker M. L. Intrasession and intersession reliability of hand-held dynamometer measurements taken on brain-damaged patients. Phys Ther. 1989 Mar;69(3):182–194. doi: 10.1093/ptj/69.3.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuberg W. A., Metcalf W. K. Reliability of quantitative muscle testing in healthy children and in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy using a hand-held dynamometer. Phys Ther. 1988 Jun;68(6):977–982. doi: 10.1093/ptj/68.6.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles C. M., Karni Y. The measurement of muscle strength in patients with peripheral neuromuscular disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Nov;46(11):1006–1013. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.11.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg R. J., Fidler V., Oosterhuis H. J. Hand-held myometry: reference values. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Mar;54(3):244–247. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.3.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg R. J., Oosterhuis H. J., Reuvekamp J. Measuring muscle strength. J Neurol. 1984;231(4):200–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00313939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]