Abstract
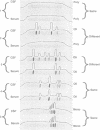
The Committee of the European Concerted Action for Multiple Sclerosis (Charcot Foundation) organised five workshops to discuss CSF analytical standards in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. This consensus report from 12 European countries summarises the results of those workshops. It is hoped that neurologists will confer with their colleagues in clinical chemistry to arrange the best possible local practice. The most sensitive method for the detection of oligoclonal immunoglobulin bands is isoelectric focusing. The same amounts of IgG in parallel CSF and serum samples are used and oligoclonal bands are revealed with IgG specific antibody staining. All laboratories performing isoelectric focusing should check their technique at least annually using "blind" standards for the five different CSF and serum patterns. Quantitative measurements of IgG production in the CNS are less sensitive than isoelectric focusing. The preferred method for detection of blood-CSF barrier dysfunction is the albumin quotient. The CSF albumin or total protein concentrations are less satisfactory. These results must be interpreted with reference to the age of the patient and the local method of determination. Cells should be counted. The normal value is no more than 4 cells/microliters. Among evolving optional tests, measurement of the combined local synthesis of antibodies against measles, rubella, and/or varicella zoster could represent a significant advance if it offers higher specificity (not sensitivity) for identifying chronic rather than acute inflammation. Other tests that may have useful correlations with clinical indices include those for oligoclonal free light chains, IgM, IgA, or myelin basic protein concentrations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blennow K., Fredman P., Wallin A., Gottfries C. G., Karlsson I., Långström G., Skoog I., Svennerholm L., Wikkelsö C. Protein analysis in cerebrospinal fluid. II. Reference values derived from healthy individuals 18-88 years of age. Eur Neurol. 1993;33(2):129–133. doi: 10.1159/000116919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagnart O. C., Sindic C. J., Laterre C. Free kappa and lambda light chain levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Aug;19(1-2):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K. Protein size and cerebrospinal fluid composition. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Dec 15;52(24):1158–1164. doi: 10.1007/BF01466734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K., Reiber H. The diagnostic significance of antibody specificity indices in multiple sclerosis and herpes virus induced diseases of the nervous system. Clin Investig. 1992 Jan;70(1):28–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00422934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K., Schädlich H. J., Nekic M., Ackermann R. Cerebrospinal fluid virus antibodies. A diagnostic indicator for multiple sclerosis? J Neurol Sci. 1985 Dec;71(2-3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgenhauer K., Schädlich H. J. The compartmental IgM and IgA response within the central nervous system. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Feb;77(2-3):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frequin S. T., Barkhof F., Lamers K. J., Hommes O. R., Borm G. F. CSF myelin basic protein, IgG and IgM levels in 101 MS patients before and after treatment with high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone. Acta Neurol Scand. 1992 Sep;86(3):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo P., Tavolato B., Bergenbrant S., Sidén A. Immunoglobulin light chain patterns in the cerebrospinal fluid. A study with special reference to the occurrence of free light chains in cerebrospinal fluid with and without oligoclonal immunoglobulin G. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Dec;94(1-3):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keir G., Luxton R. W., Thompson E. J. Isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin G: an annotated update. Ann Clin Biochem. 1990 Sep;27(Pt 5):436–443. doi: 10.1177/000456329002700504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostulas V. K. Oligoclonal IgG bands in cerebrospinal fluid. Methodological and clinical aspects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1985;103:1–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. III. Evaluation of IgG synthesis within the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):397–401. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livrea P., Trojano M., Simone I. L., Zimatore G. B., Lamontanara G., Leante R. Intrathecal IgG synthesis in multiple sclerosis: comparison between isoelectric focusing and quantitative estimation of cerebrospinal fluid IgG. J Neurol. 1981;224(3):159–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00313278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolli F., Halawa I., Link H. Intrathecal synthesis of IgG, IgA, IgM and IgD in untreated multiple sclerosis and controls. Acta Neurol Scand. 1989 Sep;80(3):238–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1989.tb03869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolli F., Siracusa G., Amato M. P., Fratiglioni L., Dal Pozzo G., Galli E., Amaducci L. Intrathecal synthesis of free immunoglobulin light chains and IgM in initial multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991 Apr;83(4):239–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1991.tb04689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luxton R. W., McLean B. N., Thompson E. J. Isoelectric focusing versus quantitative measurements in the detection of intrathecal local synthesis of IgG. Clin Chim Acta. 1990 Mar 15;187(3):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(90)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luxton R. W., Thompson E. J. Affinity distributions of antigen-specific IgG in patients with multiple sclerosis and in patients with viral encephalitis. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 7;131(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino G., Servalli C., Filippi M., Buscemi M., Martinelli V., Furlan R., Comi G., Grimaldi L. M. Absence of oligoclonally restricted immunoglobulins in tears from multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 May;44(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massaro A. R., Scivoletto G., Tonali P. Cerebrospinal fluid markers in neurological disorders. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(6):537–547. doi: 10.1007/BF02337436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P. D., Patrick B. A., Miller J. A. Absence of oligoclonal IgA in CSF and serum of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1984 Feb;6(1):67–69. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(84)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nespolo A., Bianchi G., Salmaggi A., Lazzaroni M., Cerrato D., Malesani Tajoli L. Immunoblotting techniques with picogram sensitivity in cerebrospinal fluid protein detection. Electrophoresis. 1989 Jan;10(1):34–40. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman S., Ernerudh J., Forsberg P., Henriksson A., von Schenck H., Vrethem M. Comparison of seven formulae and isoelectrofocusing for determination of intrathecally produced IgG in neurological diseases. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992 Jul;29(Pt 4):405–410. doi: 10.1177/000456329202900406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser C. M., Paty D. W., Scheinberg L., McDonald W. I., Davis F. A., Ebers G. C., Johnson K. P., Sibley W. A., Silberberg D. H., Tourtellotte W. W. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiber H., Felgenhauer K. Protein transfer at the blood cerebrospinal fluid barrier and the quantitation of the humoral immune response within the central nervous system. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Mar 30;163(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiber H., Lange P. Quantification of virus-specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: sensitive and specific detection of antibody synthesis in brain. Clin Chem. 1991 Jul;37(7):1153–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller E. A., Benabdallah S., Sagar H. J., Reboul J. A., Tömpe L. C. IgG synthesis within the central nervous system. Comparison of three formulas. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jun;44(6):600–604. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520180024010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller E., Sagar H. J. Local synthesis of CSF immunoglobulins. A neuroimmunological classification. J Neurol Sci. 1981 Sep;51(3):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(81)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Thompson E. J. Distribution of cerebrospinal fluid oligoclonal IgM bands in neurological diseases: a comparison between agarose electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing. J Neurol Sci. 1992 May;109(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Thompson E. J. Intrathecal immunoglobulin M synthesis in multiple sclerosis. Relationship with clinical and cerebrospinal fluid parameters. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1A):181–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Thompson E. J. The predictive value of intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis and magnetic resonance imaging in acute isolated syndromes for subsequent development of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):147–151. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindic C. J., Delacroix D. L., Vaerman J. P., Laterre E. C., Masson P. L. Study of IgA in the cerebrospinal fluid of neurological patients with special reference to size, subclass and local production. J Neuroimmunol. 1984 Dec;7(2-3):65–75. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(84)80007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindic C. J., Laterre E. C. Oligoclonal free kappa and lambda bands in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. An immunoaffinity-mediated capillary blot study. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jul;33(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souverijn J. H., Serrée H. M., Peet R., Grenzebach Smit W., Bruyn G. W. Intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis. Comparison of various formulae with the 'gold standard' of isoelectric focusing. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Mar;102(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90087-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbling G., Link H., Ohman S. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):385–390. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. W., Potvin A. R., Fleming J. O., Murthy K. N., Levy J., Syndulko K., Potvin J. H. Multiple sclerosis: measurement and validation of central nervous system IgG synthesis rate. Neurology. 1980 Mar;30(3):240–244. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakaet A., Thompson E. J. Free light chains in the cerebrospinal fluid: an indicator of recent immunological stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Oct;48(10):995–998. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.10.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandvik B. Oligoclonal IgG and free light chains in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis and infectious diseases of the central nervous system. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(9):913–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. W., Keir G., Johnson M. H., Thompson E. J. A rapid method for detecting oligoclonal IgG in unconcentrated CSF, by agarose isoelectric focusing, transfer to cellulose nitrate and immunoperoxidase staining. J Neuroimmunol. 1983 Apr;4(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(83)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikkelsö C., Andersson M., Andersson R., Blomstrand C. Isoelectric focusing followed by silver staining. A suitable method for routine investigation of cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Eur Neurol. 1984;23(4):306–312. doi: 10.1159/000115747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]