Abstract
Fifteen patients who experienced epileptic seizures while playing video games are described together with a review of 20 cases in the English literature. Nine of the 15 cases and all but two of the reported cases experienced their first seizure while playing video games. Two thirds of patients had idiopathic generalised epilepsy and mainly reported generalised tonic clonic seizures, but some had typical absence seizures and myoclonic jerks while playing video games. In this series, 30% with idiopathic generalised epilepsy had juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Overall, 70% of patients with idiopathic generalised epilepsy were photosensitive to intermittent photic stimulation and the mechanism of seizure provocation was probably similar to that of television induced seizures, although sensitivity to specific patterns was sometimes important. Two children had self induced video game seizures. Non-photic factors such as excitement, fatigue, sleep deprivation, cognitive processing, and diurnal variation in susceptibility seemed to be important seizure precipitants, particularly in non-photo-sensitive patients. Twenty nine per cent of patients had partial (mainly occipital) video game associated seizures. Occipital spikes were common in the EEG of these patients. Photosensitivity to intermittent photic stimulation may have been important in two patients but in the others, who all played arcade video games, other mechanisms need to be considered. Video game associated seizures are a feature of several epileptic syndromes and differ in precipitants and appropriate management.
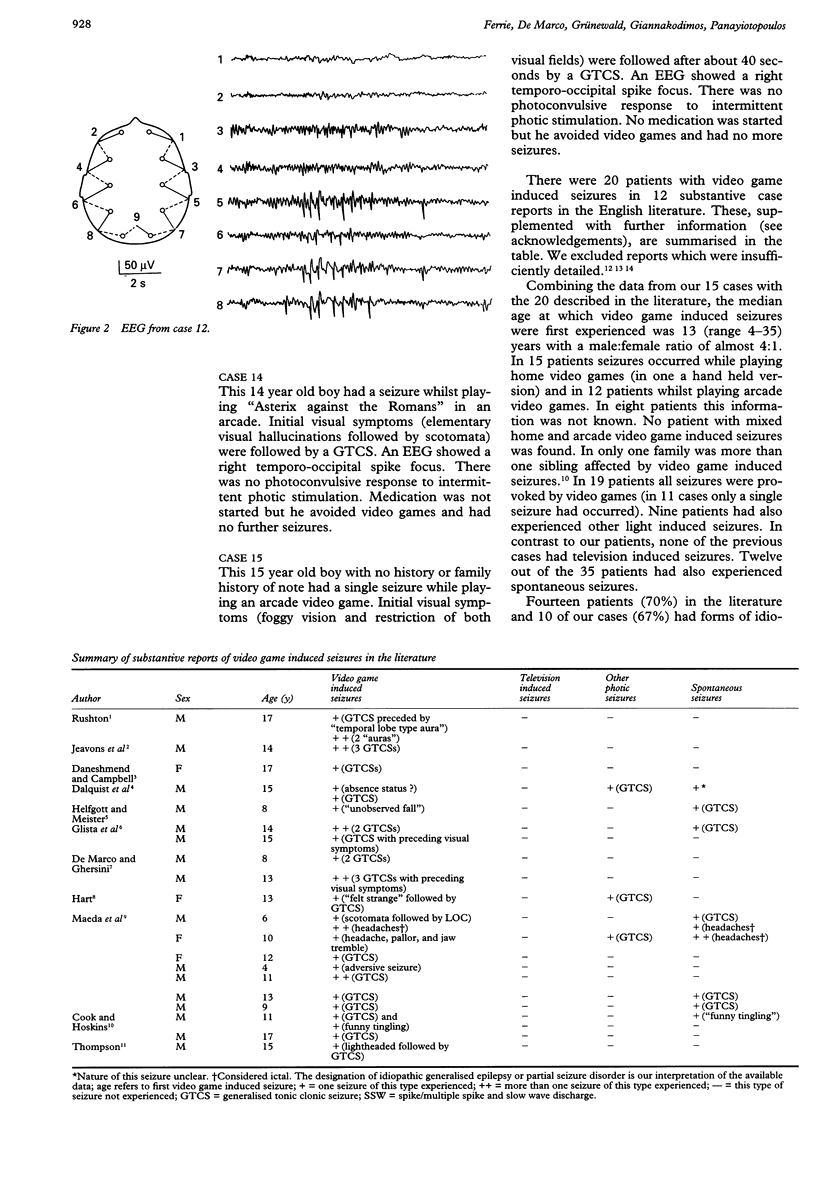
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahlquist N. R., Mellinger J. F., Klass D. W. Hazard of video games in patients with light-sensitive epilepsy. JAMA. 1983 Feb 11;249(6):776–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneshmend T. K., Campbell M. J. Dark Warrior epilepsy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jun 12;284(6331):1751–1752. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6331.1751-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco P., Ghersini L. Videogames and epilepsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1985 Aug;27(4):519–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1985.tb04577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk J. B. Reevaluating the impact of video games. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1993 Feb;32(2):86–90. doi: 10.1177/000992289303200205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens L. A., Andermann F., Andermann E., Remillard G. M. Reflex seizures induced by calculation, card or board games, and spatial tasks: a review of 25 patients and delineation of the epileptic syndrome. Neurology. 1990 Aug;40(8):1171–1176. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.8.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünewald R. A., Panayiotopoulos C. P. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. A review. Arch Neurol. 1993 Jun;50(6):594–598. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540060034013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart E. J. Nintendo epilepsy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 17;322(20):1473–1473. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005173222020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfgott P. C., Meister J. Seizures apparently triggered by video games. JAMA. 1983 Sep 9;250(10):1273–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeavons P. M., Barton M. E., Bishop A. Seizures and hand-held space invaders. Lancet. 1981 Oct 3;2(8249):758–758. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeavons P. M., Harding G. F., Panayiotopoulos C. P., Drasdo N. The effect of geometric patterns combined with intermittent photic stimulation in photosensitive epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Aug;33(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenité D. G., Binnie C. D., Meinardi H. Photosensitive patients: symptoms and signs during intermittent photic stimulation and their relation to seizures in daily life. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Nov;50(11):1546–1549. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.11.1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Kurokawa T., Sakamoto K., Kitamoto I., Ueda K., Tashima S. Electroclinical study of video-game epilepsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1990 Jun;32(6):493–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1990.tb16974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayiotopoulos C. P., Obeid T., Tahan A. R. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: a 5-year prospective study. Epilepsia. 1994 Mar-Apr;35(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1994.tb02432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayiotopoulos C. P. Self-induced pattern-sensitive epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1979 Jan;36(1):48–50. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500370078021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton D. N. "Space invader" epilepsy. Lancet. 1981 Feb 28;1(8218):501–501. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal K. R., Dietz W. H. Physiologic responses to playing a video game. Am J Dis Child. 1991 Sep;145(9):1034–1036. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1991.02160090086030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefánsson S. B., Darby C. E., Wilkins A. J., Binnie C. D., Marlton A. P., Smith A. T., Stockley A. V. Television epilepsy and pattern sensitivity. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 9;2(6079):88–90. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6079.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. J. Video game induced generalised epileptic convulsion. N Z Med J. 1993 Mar 10;106(951):88–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins A. J., Andermann F., Ives J. Stripes, complex cells and seizures. An attempt to determine the locus and nature of the trigger mechanism in pattern-sensitive epilepsy. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):365–380. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins A. J., Darby C. E., Binnie C. D. Neurophysiological aspects of pattern-sensitive epilepsy. Brain. 1979 Mar;102(1):1–25. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


