Abstract
In this research, the amoxicillin (AMX) removal was studied on a prepared nanosorbent from MOFs. The aim of this research work is to prepare nanohybrids based on metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) as an efficient nanosorbent for the absorption of amoxicillin drug. In this study, UIO-66 nanoparticles (UIO-66 NPs) were prepared from Zirconium (Zr) metal and 1,4-benzene dicarboxylic acid (BDC). Then UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid was synthesized by hydrothermal method. Structural and physicochemical properties of nanohybrid UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 were characterized by different analyses such as X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), therapeutic goods administration (TGA), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). The effect of four fundamental variables effective on adsorption was optimized by the central composite response surface methodology (CCRSM). This parameters including loading percentage of Cr-MIL-101 NPs (10–30%), initial concentration of AMX (20–140 mg L−1), contact time (20–60 min), and pH (20–10). The removal percentage (Re%) of AMX equal to 99.50% was obtained under the following conditions: The loading value of 20% Wt%, the initial concentration of AMX 80 mg L−1, contact time 20 min, and pH = 6. Also, the experimental data were investigated with famous kinetic models and isotherms, and it was observed that AMX removal by nanohybrid is correlated with the PSO kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm.
Subject terms: Environmental sciences, Environmental social sciences, Chemistry, Materials science, Nanoscience and technology
Introduction
In recent years, due to the growth of population and various industries, environmental pollution has increased due to drugs and antibiotics, becoming one of the serious and leading problems in the field of environment. Since they are used as a solution for treating diseases and improving health in human societies, the consumption of antibiotics directly or indirectly leads to their entry into the environment. As a result, these chemical substances can remain in the environment for a long time and act as environmental pollutants. In addition, excessive use of drugs and antibiotics can create resistance in bacteria and microorganisms, which can lead to problems such as the emergence of drug-resistant diseases1. Removing drugs and antibiotics from the environment and water is a complex challenge that requires scientific and practical solutions. These solutions include: using advanced wastewater treatment systems2, using nanotechnology and active NPs, nanofiltration, and nanoabsorbents3, using biological activities of bacteria and fungi to decompose drugs4, using physical activities and filtration methods, adsorption5–10, oxidation and ultrasonic methods11–15, providing necessary training to patients and physicians to reduce drug consumption16, recycling drugs17, removing expired drugs and preventing their entry into the environment18, and using ultraviolet radiation and hydrogen peroxide oxidation to reduce and disinfect antibiotic residues19. Among these methods, the use of nanoadsorbents for the removal of antibiotics from water has emerged as a new and efficient method for combating water pollution due to the presence of drugs and antibiotics due to their selectivity and high efficiency. Nanoadsorbents are considered smart and highly sensitive absorbents to environmental components. As shown in a report20, these absorbents selectively absorb antibiotics from water using their nanoscale properties, instead of using chemical and physical processes for antibiotic removal. Nanoadsorbents, due to their larger surface area compared to larger adsorbents such as activated carbon21, for example, can improve the efficiency of antibiotic removal from water adsorption methods. Additionally, due to their limited movement in the environment, nanoadsorbents can selectively absorb antibiotics from water and remove them faster and with higher efficiency22.
Currently, many nanoadsorbents have been studied and researched for the removal of antibiotics from water, including metal NPs (silver, iron, and gold NPs)23, carbon24, silica NPs25, and zinc oxide NPs26. The use of MOFs as nanoadsorbents for adsorption process has recently gained attention27–31. These types of nanoadsorbents are very powerful and, with their structural complexity, can selectively absorb various drugs from water. One of the advantages of using MOFs compared to the aforementioned nanoadsorbents is their ability to regulate their chemical nature. By changing the type of metal used in the construction of MOFs, their adsorption properties can be altered and used for the adsorption of various drugs. Additionally, by changing the type of organic compounds used in the construction of MOFs, their adsorption properties can also be altered32,33. So far, different MOFs have been identified and studied as strong adsorbents for various antibiotics34,35. The results of Methotrexate adsorption by Cr-MIL-101 NPs from water showed that this nanoadsorbent selectively absorbed Methotrexate from water with the highest efficiency. Additionally, this nanoadsorbent can be reused due to its easy recovery36,37. Paracetamol is a type of analgesic used in the treatment of pain and fever and is commonly found in municipal water and wastewater. In a study, UIO-66 NPs were used as a nanoadsorbent for the adsorption of Paracetamol from water, which was effective in selectively adsorbing Paracetamol with high efficiency38. Overall, UIO-66 NPs have been identified as a powerful nanoadsorbent for drug adsorption from water and are used for various applications such as drinking water and wastewater. Additionally, combining two MOFs creates a more complex structure with increased internal surface area, allowing larger molecules, such as drugs, to be adsorbed39.
The aim of this study is to use the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid for the adsorption of the antibiotic AMX (see Table 1). The XRD results confirmed the crystallinity of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, and the particle size of this nanohybrid was between 8 and 110 nm (based on the SEM results). AMX, as a large molecule with high molecular weight, is adsorbed on the internal surface of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101. The attractive and repulsive forces between the adsorbent's internal surface and AMX cause AMX to be trapped in the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 structure. Design-Expert software was used to achieve maximum adsorption and optimize effective parameters for adsorption, and the optimal parameters and experimental results were analyzed for the study of reaction kinetics and thermodynamics. General, UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is a class of nanomaterials that have been shown to be effective adsorbents for a variety of pollutants, including amoxicillin. Amoxicillin is a widely used antibiotic, but it can also be a contaminant in wastewater and surface water. Adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid has several advantages over other methods of amoxicillin removal, including: (1) high adsorption capacity: UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid have a high surface area and porosity, which allows them to adsorb large amounts of amoxicillin. (2) selectivity: UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid can be functionalized to selectively adsorb amoxicillin from other pollutants in water. (3) regeneration: UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid can be regenerated and reused, making them a more sustainable option than other adsorbents. In addition to these advantages, UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid are also relatively inexpensive and easy to produce. This makes them a promising technology for the removal of amoxicillin from wastewater and surface water. Overall, UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid are a promising technology for the removal of amoxicillin from wastewater and surface water. They have a high adsorption capacity, selectivity, and can be regenerated and reused.
Table 1.
The physiochemical properties of the AMX.
| Molecular structure | 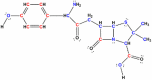 |
| Molecular formula | C16H19N3O5S |
| Molecular weight (g mol−1) | 365.4 |
| λmax (nm) | 270 |
Experimental section
Materials
The substances used in this study were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) as follows: Zirconium (IV) chloride (ZrCl4), BDC, Chromium nitrate nonahydrate (Cr (NO3)3⋅9H2O, ammonium fluoride (NH4F), absolute methanol (MeOH (99.0%)), absolute ethanol (EeOH (99.0%)), absolute N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF (97.0%)), absolute hydrofluoric acid (HF (40%)), and distilled water (DW).
Preparation of UIO-66 NPs
The UiO-66 NPs were prepared using the reported procedure by Michael et al.40.
Solution 1
ZrCl4 (0.125 g), DMF (5 ml), and concentrated HCl (1 ml) were added to a 10-dram glass vial, and the mixture solution was sonicated for 25 min.
Solution 2
BDC linker (0.123 g) and DMF (10 ml) were added into another vial, and then the mixture was stirred until to completely dissolving of the BDC linker.
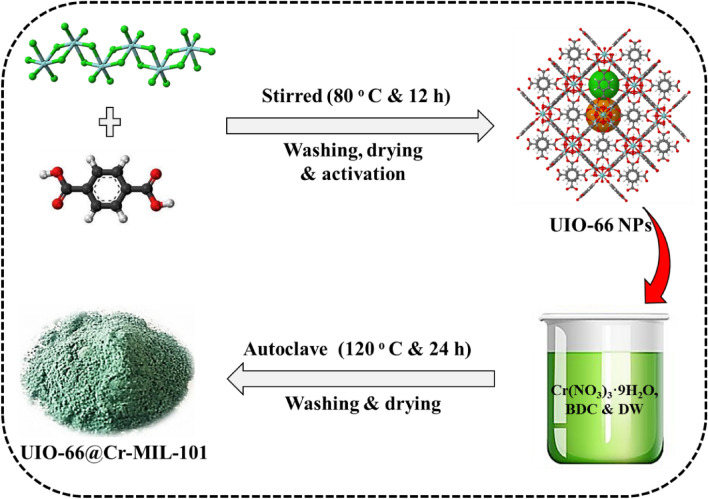
Then solution 2 was added to solution 1 and was sonicated for 20 min. The resulting mixture was stirred for 12 h at 80 °C. The obtained milky solution was cooled to room temperature, and its precipitate was separated by centrifugation. The precipitate was washed three times with DMF and two times with EtOH. The resulting white UIO-66 NPs are dried in an oven under 80 °C and then activated in a vacuum oven under a temperature of 150 °C for 24 h (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
Schem image of synthesis of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
Preparation of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid
UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid were synthesized by hydrothermal method, UIO-66 NPs (1 g), Cr (NO3)3⋅9H2O (8 g), and BDC (3.31 g) were added to 95 ml of DW and stirred for 25 min. Then, 20 mmol of HF was added to the mixture, and it was vigorously stirred for another 20 min. The resulting suspension was transferred to the autoclave and kept in the oven for 24 h at 220 °C. The obtained green product was cooled to room temperature and centrifuged for the washing process (Fig. 1).
Post-synthesis and purification
To purify the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid samples from unreacted BDC species, the sample was washed as follows: firstly, the samples were washed with DMF (three times, at 80 °C) and with DW (five times, at 100 °C) and centrifuged. Then the samples were refluxed for 8 h in DMF at 80 °C and separated by centrifuge after cooling. The resulting product was soaked in MeOH for four days at 25 °C (Note: MeOH was regularly changed every day). After that, the powders were activated in a vacuum oven at 140 °C for 12 h. Finally, to remove the residual BDC, the samples were stirred in NH4F aqueous solution at 65 °C for 5 h (NH4F amount: 100 cm3 of 30 mM solution per 1 g of dried powder in the previous step). To remove any remaining NH4F molecules inside the pores, UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrids were washed three times with DW (100 °C) and centrifuged. The obtained UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid was activated for 12 h in a vacuum oven at 140 °C. The prepared product is denoted as UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 10% nanohybrid. The preparation of other sorbents of A (15–30%) was carried out with this method but with different amounts of Zn and BDC.
Batch adsorption experiments
The batch adsorption method was used to investigate the removal of AMX by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, study the equilibrium isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. According to the conditions of 30 runs proposed by CCRSM, concentration of initial AMX, pH, contact time and temperature variables were examined. A shaker incubator was used to adsorption experiments at identified temperature and 175 rpm. The adsorption amount of the AMX was measurement by UV–Vis instrument at 270 nm.
AMX Re% and equilibrium adsorption capacity (qe (mg g−1)) were calculated under different experimental conditions including initial concentration of AMX, pH, contact time and temperature. The Re% and qe of AMX is calculated using Eqs. (1) and (2), respectively:
| 1 |
| 2 |
where C0 (mg g−1), Ce (mg g−1), V (l), and m (g) are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of AMX, volume of the solution, and the adsorbent, respectively.
Results and discussion
Figure 2A shows the FT-IR spectra of Cr-MIL-101 NPs, UIO-66 NPs, and UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. For the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, compared to the other two nanoadsorbents, the spectrum at around 486 cm−1 is related to the asymmetric stretching vibration of Zr–OC, the spectrum at around 590 cm−1 is related to the Cr–O stretching vibration, and the spectrum at around 700 cm−1 is indicative of the C–H stretching vibration of the BDC organic ligand41,42. Additionally, the spectrum in the range of 1200–1000 cm−1 is attributed to the nitrogen and carbonyl groups in the organic ligand41. The symmetric carboxyl group stretching of BDC ligand can be observed in the spectrum at around 1400 cm−1. The spectra at around 1600 and 1700 cm−1 are indicative of the asymmetric stretching vibration of O–C–O and the carboxyl group –COO– in the organic ligand, respectively21. The O–H stretching vibration band (at around 3421 cm−1) of the UIO-66 NPs in the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid confirms the loading of UIO-66 NPs in the Cr-MIL-101 NPs39,43. To verify adsorption mechanisms, the FT-IR spectra of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid were compared before and after adsorption. As shown in Fig. 2A-d, the band peak of hydroxyl shifted from 3421 to 3361.92 cm−1 after adsorption. The adsorption peak changing from 1569 to 1565 cm−1 was stretching vibration of C–O in the carboxyl group44, which indicated hydrogen bonding interaction between O in UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid and H in AMX.
Figure 2.
(A) FT-IR results of (a) UIO-66 NPs, (b) Cr-MIL-101 NPs, (c) UIO-66@ Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, (d) after AMX adsorption; (B) XRD pattern of (a) UIO-66 NPs, (b) Cr-MIL-101 NPs, (c) UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, (d) after AMX adsorption.
The XRD patterns in Fig. 2B show that the diffraction patterns of UiO-66 NPs, Cr-MIL-101 NPs, and UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrids are very similar and consistent with published data45,46. The maximum diffraction peak for the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid sample is at 2θ = 44° (see Fig. 2B), while for UiO-66 NPs and Cr-MIL-101 NPs, it is observed at 2θ = 43.5° and 2θ = 42.3°, respectively. The presence of this peak indicates the successful preparation of UiO-66 NPs and a successful combination with Cr-MIL-101 NPs, as shown in Fig. 2B-a,B-b. The XRD pattern of the sample shows typical peaks at 2θ = 9.9°, 18°, and 24.2°, which confirm the successful synthesis of UIO-66 NPs. These peaks were observed in the hybrid sample at θ = 10.9°, 2θ = 17.47°, and 2θ = 24.9°, respectively, indicating that the topology structure of UIO-66 NPs was not significantly affected and that UIO-66 NPs was well combined with Cr-MIL-101. In addition, the XRD pattern of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid shows that there is no change in the main peaks of the binary. However, the intensity of the peaks in the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is significantly reduced compared to UiO-66 NPs, which can be attributed to the good distribution of UIO-66 NPs in the Cr-MIL-101 NPs sample43.
Furthermore, according to the XRD of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid after the adsorption process, no specific changes were observed, that confirms the stability of the sample (Fig. 2B).
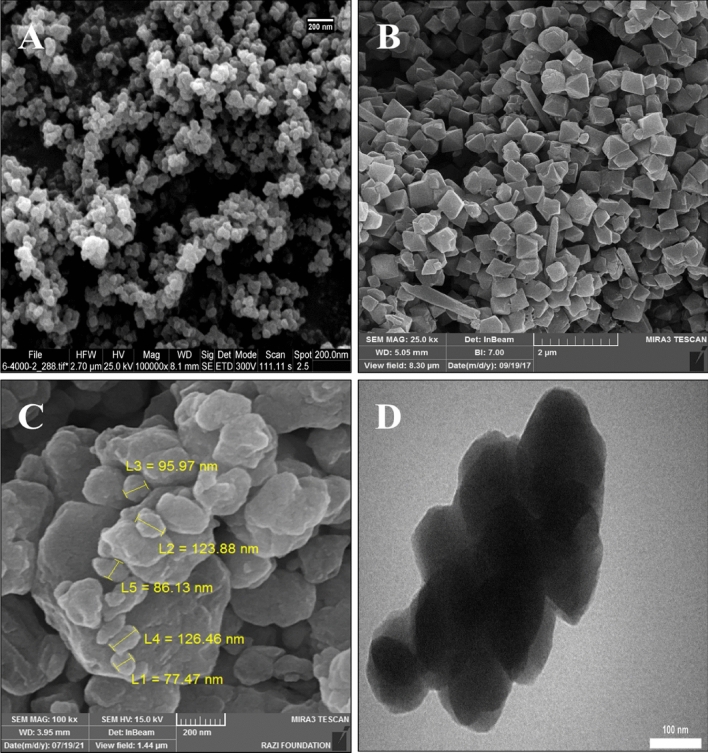
The morphology of the UIO-66 NPs, Cr-MIL-101, and UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid structures is shown in Fig. 3. As seen in Fig. 3A, UIO-66 NPs crystals have homogeneous and uniform cubic shapes with edges of about 50 nm. Figure 3B shows nanocrystals of Cr-MIL-101 with a regular geometrical shape of a polyhedron, approximately 400 nm in size, and with sharp and non-intersecting corners. In Fig. 3C, the Cr-MIL-101 NPs and UIO-66 NPs crystals are integrated, and the UIO-66 NPs include the regular crystals of Cr-MIL-101, changing their geometrical shape so that the regular geometrical shape is no longer visible. As evident from Fig. 3D, the TEM image shows the porous network of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 hybrid, which includes the hierarchical structure of the UIO-66 NPs crystals and the Cr-MIL-101 NPs crystals. At the same time, the elements C, O, Fe, Si, and Zr were directly observed from the EDX pattern of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid in Fig. 4. The presence of iron and silicon elements was helpful evidence that showed the successful preparation of the nanohybrid core–shell structure47.
Figure 3.
SEM images of (A) UIO-66 NPs, (B) Cr-MIL-101 NPs, (C) UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; (D) TEM image UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
Figure 4.
EDX analysis and elemental mapping images of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
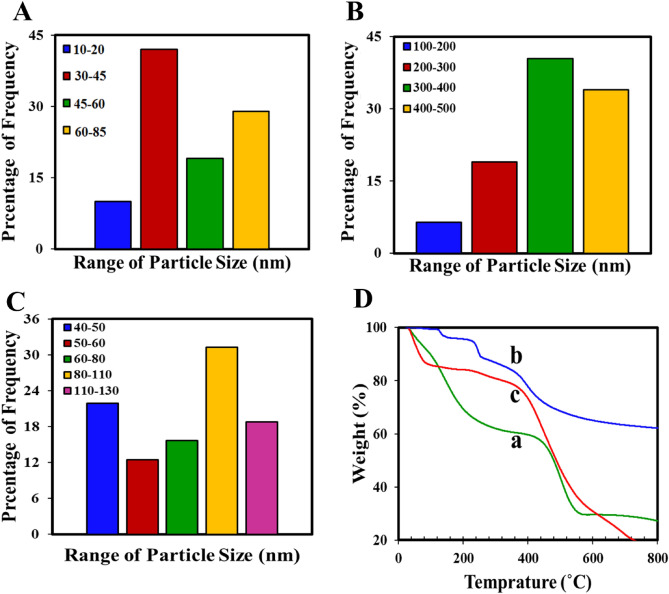
The particle size distribution (PSD) curve (Fig. 5A) shows a narrow and focused distribution of the sizes of the UIO-66 NPs pores around a specific value (the highest percentage of PSD is in the range of 30–45 nm). This is because the synthesis of these NPs usually results in a relatively uniform distribution of pore sizes, which can be used as channels for the transport of molecules or channels for the adsorption or combination of different molecular species. As evident from Fig. 5B,C, the highest percentage of PSD for Cr-MIL-101 NPs and the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is approximately 300–400 nm and 80–110 nm, respectively, which confirms that the pore sizes in the hybrid sample are almost the average pore size in Cr-MIL-101 NPs and UIO-66 NPs, and therefore, the successful preparation of the nanohybrid has resulted in a more desirable PSD and the creation of relatively smaller and uniform crystals.
Figure 5.
PSD curves of (A) UIO-66 NPs, (B) Cr-MIL-101 NPs, (C) UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; (D) TGA curves of (a) UIO-66 NPs, (b) Cr-MIL-101 NPs, (c) UIO-66@ Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
The thermal behaviors of three samples, UIO-66 NPs, Cr-MIL-101, and UiO-66@Cr-MIL-101, were studied using TGA. From the TG curves (Fig. 5D), it is evident that both UIO-66 NPs and Cr-MIL-101 NPs exhibit three weight loss stages. The first weight loss between 30 and 100 °C is due to the evaporation of absorbed water in the MOF structure, while the second weight loss stage between 100 and 320 °C is attributed to the removal of DMF molecules. The third weight-loss stage begins at 450 °C and is associated with the combustion of the organic ligand, which leads to the decomposition of both MOFs and their composite. Furthermore, the UiO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid lost 52.7% of its total weight, indicating its higher thermal stability compared to UIO-66 NPs and Cr-MIL-101, which had a total weight loss of 56.5%45.
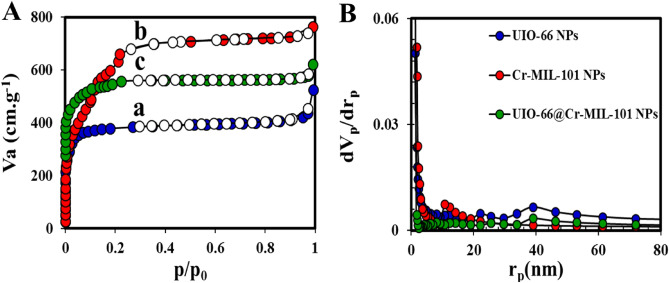
Figure 6A shows the nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms of UIO-66 NPs, Cr-MIL-101, and UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 at a temperature of 77 K. As evident from the figure, all three isotherms were of type I. As shown in Fig. 6A, for all three prepared samples, the adsorption capacity starts with relatively low pressure and rapidly increases with a gradual increase in pressure, which ends at high pressure. This behavior confirms the nature of the porous microstructure in the samples. The specific surface area of UIO-66 NPs was evaluated to be 1350.67 m2 g−1 (Table 2), which is similar to what has been evaluated in previous studies29. However, the surface area and pore volume in UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 were 1025.30 m2 g−1 and 0.4441 cm3 g−1, respectively, both slightly lower than UIO-66 NPs. This reduction could be the result of the encapsulation of Cr-MIL-101 NPs inside UIO-66 NPs. Based on the IUPAC classification, pore diameters are divided into three categories: microspore (the pore size < 2 nm), mesopore (the pore size 2–50 nm), and macrospore (the pore size > 50 nm)48–51. Since the diameter pores of the synthesized UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is about 2 nm, it has a microporous structure. Additionally, the BJH plot (Fig. 6B) also clearly shows that the pore size distribution in the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is narrower than that of Cr-MIL-101 NPs and UIO-66 NPs, and the majority of the crystal sizes are in the range of 1–20 nm with a maximum of 80 nm52.
Figure 6.
(A) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of (a) UIO-66 NPs, (b) Cr-MIL-101 NPs, (c) UIO-66@ Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; (B) BJH curves of UIO-66 NPs, Cr-MIL-101 NPs, and UIO-66@ Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
Table 2.
Textural properties parameters of UIO-66 NPs, Cr-MIL-101 and UIO-66@ Cr-MIL-101.
| Samples | BET specific surface area (m2 g−1) | Total pore volume (cm3 g−1) | Average pore diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| UIO-66 NPs | 1505 | 0.78 | 2.12 |
| Cr-MIL-101 | 3440 | 1.82 | 1.37 |
| UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 | 1921.70 | 0.56 | 2.02 |
CCRSM
The response surface methodology (RSM) is used to evaluate the correlation between experimental data and the outcomes attained. This particular method is a statistical technique that analyzes multiple variables simultaneously, aiming to enhance experimental procedures, optimize results, and minimize the need for excessive experimentation. The optimization process involves several steps, including: (1) carrying out statistically planned tests, (2) evaluating the coefficients within a mathematical model, and (3) identifying the response and assessing the model's accuracy53. Central composite design (CCD) has various applications, for example, adsorption processes54, chromatographic methods55, and spectroanalytical methods56. In this research study, the CCD method implemented through Design Expert 11.0.3.0 software is utilized to introduce randomness in the experimental runs, design the experiments, study the significant impacts of operational factors on AMX removal, and identify a combination of variables that maximize the efficiency of AMX adsorption. Randomization is essential to ensure that the outcome of each run is independent of the others, thereby obtaining accurate experimental results. To optimize the parameters, a quadratic model is employed to establish a relationship between the selected variables and the response. Equation (3) represents the quadratic equation model used in this context57.
| 3 |
In the given equation, Y (Re%) represents the response variable, while β0, βi, βii, and βij correspond to the constant coefficient, linear coefficient, quadratic coefficient, and cross-product coefficient (interaction coefficient), respectively. Additionally, Xi and Xj are coded variables, and to determine their values, one can utilize multiple regression analysis as described in Eq. (4)58:
| 4 |
where X0 and Xi (at the center point) denote the actual values of the independent variable, while δX refers to the incremental changes between the low (− 1) and high (+ 1) levels.
Optimization of adsorption of AMX onto UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid using CCRSM
In this study, four crucial factors were investigated: the loading of MIL-101 NPs on UIO-66 NPs (A = 10–30 Wt%), the initial concentration of AMX (B = 20–140 mg L−1), pH (C = 20–10), and contact time (D = 20–60 min) (refer to Table 3). Additionally, utilizing the CCRSM approach, a total of 30 experimental runs were conducted to assess the impact of these independent variables on the adsorption efficiency of AMX using the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. The average results of both experimental and predicted outcomes for this process are presented in Table 4. Furthermore, the central point parameters were also replicated six times to establish the reproducibility of the experiments and confirm the consistency of the obtained data.
Table 3.
Independent variables and levels of the process for CCRSM.
| Independent variables | Symbol | Levels of independent variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − α | − 1 | 0 | + 1 | + α | ||
| Loading (Wt%) | A | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
| Concentration (mg L−1) | B | 20 | 50 | 80 | 110 | 140 |
| pH | C | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Time (min) | D | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
Table 4.
Independent variables and levels of the process for BBRSM.
| Run | A | B | C | D | UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Re% (actual) | Re% (predicted) | |||||
| 1 | 30 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 97.31 | 96.7 |
| 2 | 10 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 78.86 | 78.38 |
| 3 | 20 | 80 | 10 | 40 | 70.8 | 72.4 |
| 4 | 15 | 50 | 4 | 50 | 95.28 | 95.27 |
| 5 | 15 | 110 | 4 | 50 | 72.06 | 72.61 |
| 6 | 15 | 110 | 8 | 50 | 59.11 | 61.78 |
| 7 | 20 | 140 | 6 | 40 | 60.67 | 57.75 |
| 8 | 20 | 80 | 2 | 40 | 82.76 | 80.07 |
| 9 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 82.76 | 81.39 |
| 10 | 15 | 110 | 8 | 30 | 66.86 | 67.48 |
| 11 | 25 | 50 | 4 | 50 | 95.49 | 95.83 |
| 12 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 79.9 | 81.39 |
| 13 | 20 | 20 | 6 | 40 | 88.2 | 90.03 |
| 14 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 81.2 | 81.39 |
| 15 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 79.12 | 81.39 |
| 16 | 25 | 110 | 4 | 30 | 79.05 | 82.83 |
| 17 | 15 | 110 | 4 | 30 | 62.32 | 61.88 |
| 18 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 60 | 92.37 | 92.46 |
| 19 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 20 | 95.23 | 94.05 |
| 20 | 15 | 50 | 4 | 30 | 84.26 | 87.33 |
| 21 | 25 | 110 | 8 | 30 | 85.1 | 85.24 |
| 22 | 15 | 50 | 8 | 50 | 88 | 85.19 |
| 23 | 25 | 50 | 8 | 30 | 94.45 | 94.86 |
| 24 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 82.76 | 81.39 |
| 25 | 20 | 80 | 6 | 40 | 82.63 | 81.39 |
| 26 | 25 | 50 | 4 | 30 | 94.24 | 91.7 |
| 27 | 15 | 50 | 8 | 30 | 95.28 | 93.69 |
| 28 | 25 | 110 | 4 | 50 | 88.03 | 89.75 |
| 29 | 25 | 50 | 8 | 50 | 81.98 | 82.55 |
| 30 | 25 | 110 | 8 | 50 | 77.82 | 75.72 |
Analysis of variant (ANOVA)
For AMX uptake using UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, different models were examined, quadratic, 2FI, linear, mean, and cubic models. The best model was quadratic to evaluate the data for UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. There is also a significant and excellent correlation between the adjusted R2 (i.e., 0.94) and predicted R2 (i.e., 0.85), which proves the compatibility of available data with new observations (Table 5). As a rule, a difference of more than 0.2 between the adjusted R2 and predicted R2 would render the model statistically insignificant. In this study, this variation is less than 0.2 for UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; thus, the chosen model has high accuracy59.
Table 5.
Model summary statistics for AMX adsorption response by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
| UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Sequential p-value | Adjusted R2 | Predicted R2 |
| Linear | < 0.0001 | 0.5681 | 0.4381 |
| 2FI | 0.0310 | 0.7218 | 0.6522 |
| Quadratic | < 0.0001 | 0.9463 | 0.8563 |
| Cubic | 0.0441 | 0.9690 | |
Significant values are in bold.
The importance of each coefficient and the degree of interaction among each independent variable can be determined by examining the p-value and F-value, respectively. In terms of the model's parameters, it is crucial for the F-value to exceed one and for the p-value to be below 0.0560. An Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was performed on the AMX adsorption using the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, and the results are presented in Table 6. The table demonstrates that the selected models employed to investigate the AMX adsorption process with the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid were statistically significant, as indicated by the low p-values (e.g., < 0.0001). Additionally, the substantial F-value further supports the validity of the model and suggests that the experimental systems can be accurately represented with minimal error (Table 6).
Table 6.
Analysis of variance for the modified quadratic.
| Source | Sum of squares | df | F-value | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 3216.95 | 9 | 55.03 | < 0.0001 | Significant |
| A | 501.00 | 1 | 77.45 | < 0.0001 | |
| B | 1441.26 | 1 | 240.71 | < 0.0001 | |
| C | 85.21 | 1 | 13.6 | 0.0015 | |
| AB | 262.82 | 1 | 42.33 | < 0.0001 | |
| CD | 265.23 | 1 | 41.61 | < 0.0001 | |
| A2 | 63.57 | 1 | 9.97 | 0.005 | |
| B2 | 97.55 | 1 | 14.86 | 0.001 | |
| C2 | 47.65 | 1 | 7.02 | 0.0154 | |
| D2 | 248.35 | 1 | 37.15 | < 0.0001 | |
| Residual | 129.9 | 20 | |||
| Lack of fit | 117.21 | 15 | 3.08 | 0.1097 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 13.00 | 5 | |||
| Cor total | 3352.79 | 29 |
The effective value of each parameter, regression coefficients, standard effect values, and standard errors are shown in Table 7.
Table 7.
The ANOVA results of the response surface modified quadratic model.
| UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Std. Dev. | 2.55 | R2 | 0.961 |
| Mean | 83.00 | Adjusted R2 | 0.943 |
| C.V. % | 3.09 | Predicted R2 | 0.9470 |
| PRESS | 340.10 | Adeq precision | 0.898 |
| − 2 Log Likelihood | 129.10 | BIC | 163.11 |
| AICc | 160.68 | ||
Diagnostic model
To validate the accuracy of the proposed model data, an alternative method involves evaluating the normality of the data, ensuring their adherence to a normal distribution.
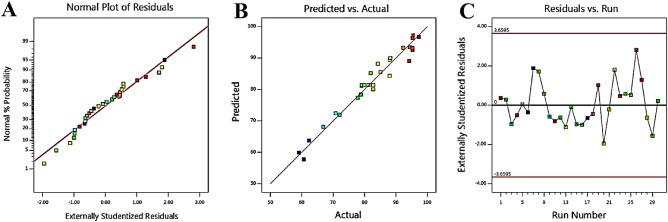
Figure 7A presents the normal values and measured statistics of the suggested model for the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. The obtained curve indicates that the collected data for the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is closely near the straight line, showing a normal distribution and further supporting the selection of the model. Furthermore, Fig. 7B includes the outcomes of the mathematical model and experimental data for AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. The obtained data validate the accuracy of the suggested model.
Figure 7.
The curve of (A) the normal probability; (B) the predicted response versus actual response; (C) analysis of residual for the response to the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
Residual analysis is employed for the identification and prediction of the suggested model's response61. The remaining equal distribution in the adsorbed value range indicates that a substantial variation in the experimental results is primarily attributed to the displacement. Consequently, the suggested model is deemed valid and successfully elucidates the adsorption process (Fig. 7C).
Response surface analysis to UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid
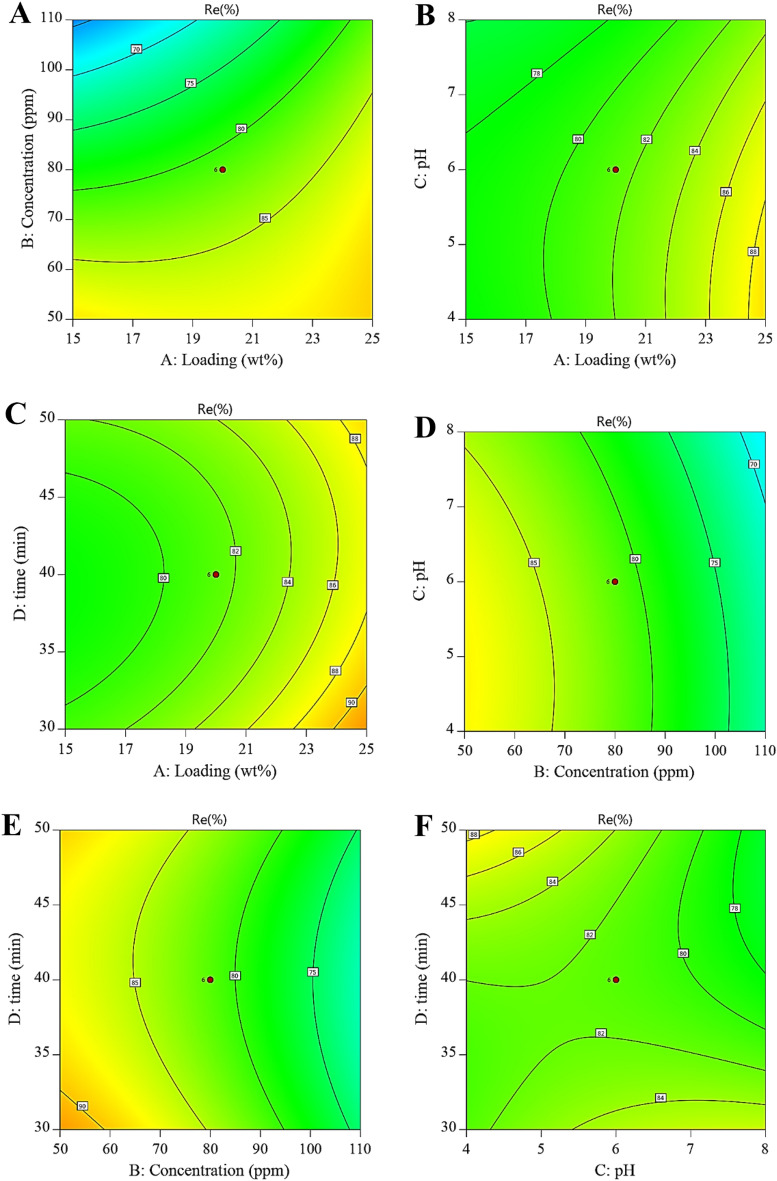
Figure 8 shows the cantour plots of the effects of the variables of Cr-MIL-101 NPs loading percentage, initial concentration of AMX, pH, and contact time against the Re%. The red region indicates where the adsorption is maximum (hot zone), graduating through yellow and green to blue zones, where the adsorption is minimal (cold zone). As can be seen from Fig. 8A,D,E, with increasing initial concentration (80 mg L−1), the Re% increases. After reaching the equilibrium point, the Re% is almost constant because at high concentrations the active sites are saturated, which leads to repulsion between the adsorbent and the AMX molecules62. Figure 8B,D,F show the effect of pH on AMX removal by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. The Re% of AMX increases slightly with increasing pH. The highest Re% of AMX was obtained at pH = 6, which related to the pHpzc of the nanohybrid (the pHpzc of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid was 4.1). In acidic pH, the surface of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid has more positive charge, so the attraction between these charges with the negative charge of AMX leads to an increase in Re%. The reduction of Re% in higher pH (as indicated by the blue region) is related to the competition between AMX anions and OH− ions on the surface of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. However, at basic pHs, the Re% of AMX is acidic due to the opposite charge of the nanohybrid surface and AMX molecules (Fig. 8)63.
Figure 8.
Cantour plots of AMX adsorption onto UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid: (A) the effect of loading and concentration; (B) the effect of loading and pH; (C) the effect of loading and time; (D) the effect of concentration and pH; (E) the effect of concentration and time; (F) the effect of pH.
The mechanism of AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid involves a combination of different factors, including: (1) electrostatic interactions: AMX is a zwitterionic molecule, meaning that it has both positive and negative charges. The metal ions in UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 can interact electrostatically with the charged groups on AMX, helping to retain the antibiotic on the MOF surface. (2) Hydrogen bonding: AMX also has several functional groups that can form hydrogen bonds with the oxygen and nitrogen atoms on the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 surface. This type of interaction is particularly important for adsorbing AMX in aqueous solutions. (3) π–π interactions: the benzene ring in amoxicillin can also interact with the aromatic rings of the organic linker molecules in UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 through π–π interactions. This type of interaction is weaker than electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding, but it can still contribute to the overall adsorption capacity of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 for AMX.
Optimization and validation
Following the adjustment of the fitting model, the CCRSM optimization target was used to determine the optimal values of the independent variables, aiming to achieve the desired Re% for AMX adsorption. Based on software predictions for the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, a Re of 99.50% could be attained under the following conditions: pH = 6, contact time of 20 min, 20% loading of MIL-101 NPs on UIO-66 NPs, and an initial concentration of AMX at 80 mg L−1. Additionally, the desirability was determined to be 1.0.
Adsorption isotherm
To analyze the experimental data from AMX removal by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, some famous adsorption isotherms were chosen, as an example, Freundlich64, Langmuir65 (Fig. 9A), Dubinin Radushkevitch (D-R)61, and Temkin66.
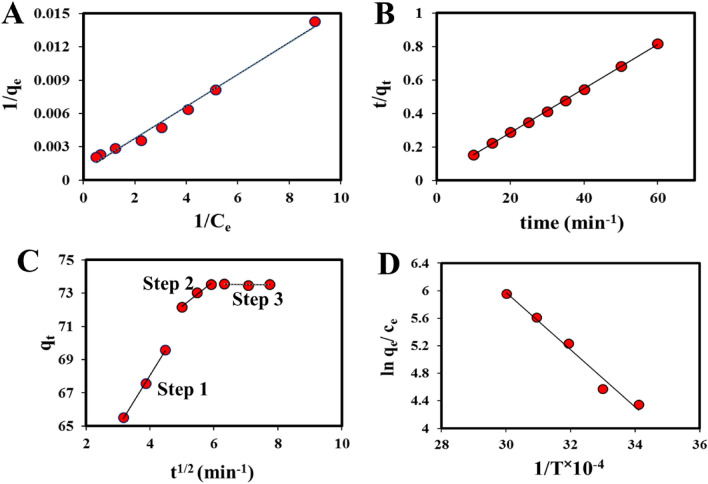
Figure 9.
(A) The plot of Ce/qe versus Ce of AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; (B) The plot of t/qt versus Ce of AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; (C) Three steps of the intraparticle diffusion model for AMX adsorption on UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid; (D) The plot of ln qe/ce versus 1/T of AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm postulates that the adsorption process follows a monolayer mechanism, with adsorption sites assumed to be homogeneous21. The linear equation representing this model is provided as follows (Eq. 5).
| 5 |
where and (mg g−1) is the equilibrium adsorption capacity of gas and the maximum theoretical adsorption capacity, respectively. KL (L mg−1) represents Langmuir adsorption constant and Ce represents equilibrium concentration (mg L−1) presented in Table 8. The Langmuir model exhibited a high correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.98, indicating a good fit. Furthermore, the maximum adsorption capacity (qm) was calculated to be 1111.11 mg g−1. These findings confirm that the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is a suitable candidate for AMX removal, as supported by the calculated values.
Table 8.
Isotherm constant and correlation coefficients calculated for AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
| Model | Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm (mg g−1) | Kl (L mg−1) | R2 | |
| 1111.11 | 0.64 | 0.98 | ||
| Freundlich | n | Kf (L mg−1) | R2 | |
| 1.58 | 5.9 | 0.93 | ||
| Temkin | B1 | KT (L mg−1) | R2 | |
| 259.33 | 13.01 | 0.96 | ||
| D–R | β(KJ2 mmol−2) | Qm(mg g−1) | R2 | E (KJ mmol−1) |
| 0.063 | 468.177 | 0.97 | 2.806 |
Freundlich is the other adsorption isotherm model, which is commonly used to describe the adsorption behavior of heterogeneous and non-ideal adsorbents (Eq. 6).
| 6 |
where Kf and n are the Freundlich adsorption constants and the deviation from the ideal homogenous surface, respectively61. Based on the calculations, R2 was 0.94, and the adsorption process is physical since the n value was 1.58 (n > 1) (Table 8). Moreover, the linear Temkin equation was employed to analyze the experimental adsorption data of AMX onto the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid. The corresponding linear equation for the Temkin model is as follows:
| 7 |
where and B1 represent the adsorbate’s binding energy and adsorbent and the heat of adsorption, respectively. T(K) is the absolute temperature, and R (8.314 J K−1 mol−1) is the universal gas constant (Table 8).
The D–R model is employed as the final model for analyzing the adsorption isotherm. Utilizing this model, various parameters, such as the free energy, uptake loading of the adsorbent, and the enhancement of adsorption due to porosity were calculated. Below is the equation that represents the D–R (Dubinin–Radushkevich) model.
| 8 |
The calculation of the intercept of the ln qe vs. ε2 plot and the slope, provided in Table 8, allows for the determination of the values for β and qm in the equation. To provide an explanation for the average adsorption reaction energy (E) in the D–R model, consider the following61:
| 9 |
where E (KJ mmol−1) and β (KJ2 mmol−2) are attributed to the average energy of adsorption and the energy of adsorption, respectively.
Moreover, Polanyi potential is computed by Eq. (10):
| 10 |
In this equation R denotes the ideal gas constant, Ce shows the equilibrium concentration, and T is the temperature (K).
Based on the analysis of the experimental data provided in Table 8, it is evident that the R2 value associated with the D–R isotherm model is relatively lower compared to the other isotherm models. This finding suggests that the D–R model is inadequate for accurately explaining the experimental data in the context of this specific research. Consequently, based on the data presented in Table 8, It can be concluded that the fitting degree to the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid exhibits the following order: Langmuir > D–R > Temkin > Freundlich.
The adsorption kinetic process
In order to gain a comprehensive understanding of the adsorbent's applicability and the underlying adsorption mechanism, a thorough investigation of adsorption kinetics was conducted. Various kinetic models, such as the pseudo-first-order (PFO) (Lagergren and Svenska)61, pseudo-second-order (PSO) (Ho and McKay)67, and Elovich (Elovich and Larionov)68, were employed in this study. These models were utilized to analyze the kinetic data and provide insights into the kinetic mechanisms involved in the adsorption process.
The first-order kinetic model67, represented by Eq. (11), is commonly employed to depict liquid/solid adsorption reactions.
| 11 |
where qe (mg g−1) and qt (mg g−1) represent the equilibrium and adsorption capacity at time (t), respectively, and k1 (min−1) denotes the PFO rate constant (Table 9).
Table 9.
Adsorption kinetic parameters for AMX adsorption onto UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
| Model | Parameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | R2 | K1 (min−1) | Qe,Calc (mg g−1) |
| 0.91 | 0.02 | 29.51 | |
| PSO | R2 | K2 (min−1) | Qe, Calc (mg g−1) |
| 0.99 | 0.02 | 52 | |
| Elovich | R2 | α (mg g−1 min−1) | β(mg g−1) |
| 0.87 | 1.27E + 08 | 0.203 | |
| Intraparticle | R2 | Kdif (L min−1) | C |
| Step (1) | 0.99 | 3.08 | 55.71 |
| Step (2) | 0.98 | 1.525 | 64.58 |
| Step (3) | 0.88 | − 0.023 | 73.69 |
| Qe,Exp (mg g−1) | 73 | ||
The following equation, derived from the PSO model69, is utilized to characterize the kinetic of adsorption:
| 12 |
The plot versus t computed the amount of , , and R2, the results are presented in Table 9 and Fig. 9B. Based on the reported data in Table 9, it can be inferred that the PSO model exhibits an excellent fit for the experimental results. This finding suggests that the sorption of AMX onto the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid predominantly follows the PSO kinetic model.
The Elitch kinetic model70, as represented by Eq. (13), is employed to elucidate the chemical adsorption behavior between the adsorbent and the adsorbate.
| 13 |
where [mg (g min)−1] represent the coverage of the surface and the activation energy range, the initial AMX adsorption rate (g mg−1) during any one experiment, and the AMX adsorption capacity of the adsorbent at time t, respectively. Analysis of the parameters presented in Table 9 leads to the conclusion that the Elovich model was inadequate in describing the kinetics of the adsorption process.
The kinetic model employed in this study to examine the kinetics of AMX adsorption by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is the intraparticle diffusion model proposed by Yang et al.71. This model elucidates the adsorption mechanism by describing the transfer of the sorbate to the surface and pores of the adsorbent, which is regarded as a critical step in the overall adsorption process (Fig. 9C). Particle diffusion plays a vital role in determining the rate of adsorption during this step, as outlined by Halsey72. Equation (14) represents the linear representation of this kinetic model.
| 14 |
In this equation, Kdif (mg g−1 min−0.5), and C are the rate of intraparticle diffusion controlled sorption constant and the intercept, respectively. It should be noted that while the plot of qt versus t1/2 passes through the origin, the C parameter is equalized to zero61.
The results obtained from this study suggest that the key factor governing the adsorption kinetics is the diffusion model within the particle. The significant deviation observed in the R2 values (Table 9) for the adsorption of AMX in UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid indicates that the chosen model is unsuitable for interpreting the adsorption kinetics. Consequently, the involvement of a speed-restricting step in the uptake process can be rejected.
The AMX adsorption process involves a series of distinct stages, namely: (1) pore diffusion or intraparticle diffusion, (2) film diffusion, (3) mass diffusion, and (4) AMX adsorption occurring on the surface of the adsorbent73. Previous literature shows that these graphs are multi-linear74, showing the incidence of two or more stages in the process of adsorption.
The initial stage of instant adsorption and external surface adsorption.
The subsequent phase is characterized by slow adsorption, where rapid diffusion occurs within the particle.
The final equilibrium stage is marked by a gradual decrease in diffusion within the particle due to the absence of solute concentration in the mixture.
Based on the kinetic studies carried out on the adsorption of AMX by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, it is proposed that the quasi-second-order model is more suitable for fitting the experimental data. The sequence of R2 agreement with UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is described: PSO > PFO > Elovich > intraparticle diffusion.
Adsorption thermodynamics
The following equations were utilized to compute the free energy change of ln K and Gibbs in the adsorption procedure75:
| 15 |
| 16 |
where K°, R (8.3145 J mol−1 K−1), and T (K) represent constant balance, the global gas constant, and temperature, respectively. The amount of the is recognized to be negative; thus, this means that the adsorption of AMX by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is automatically procedure in the Van't Hoff equation (Eq. 21). It should be noted that the computation of standard enthalpy changes (∆H°) and entropy changes (∆S°) for absorption involves determining the intercept of lnK° versus 1/T and the slope (Fig. 9D)66.
| 17 |
Also, it should be noted that the adsorption in this system is exothermic since the amount of the for UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is negative (Table 10)76.
Table 10.
Thermodynamic parameters for AMX adsorption onto UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
| Adsorbent | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 | 293.15 | 303.15 | 313.15 | 323.15 | 333.15 | |
| K° | 4.347 | 4.575 | 5.236 | 5.612 | 5.955 | |
| ΔG° (kJ mol−1) | − 1.596 | − 1.153 | − 1.363 | − 1.508 | − 1.649 | |
| ΔH° (kJ mol−1) | − 0.526 | |||||
| ΔS° (kJ mol−1) | 0.216 | |||||
Furthermore, as the temperature increases, there is a noticeable reduction in the magnitude of ΔG°, indicating a declining trend in the AMX uptake on the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid at elevated temperatures. Additionally, the positive value of ΔS° leads to an increase in the degrees of freedom for adsorbed molecules on the surface, resulting in an enhancement of the interconnection between the solution and solid during the adsorption process by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid.
Comparison of the qm of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid of this work with other adsorbents
In this study, a very inexpensive adsorbent with easy and rapid synthesis was used to remove AMX. The results showed a significant amount of qm for the removal of AMX by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid compared to other adsorbents in the literature (Table 11).
Table 11.
Comparison of the qm of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid found in the literature for AMX removal.
| Sorbent | Kinetic | Isotherm | qm (mg g−1) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 | PSO | Langmuir | 1111.11 | This work |
| UIO-66 | PSO | Langmuir | 723 | 77 |
| MOF-5 | PSO | Freundlich | 662 | 78 |
| MIL-53(Al) | PSO | Langmuir | 467 | 79 |
| PCN-124-stu(CU) | Redlich-P | Langmuir | 198 | 80 |
| ZIF-8 derived NPC | PSO | Freundlich | 416 | 81 |
| [Zn6(IDC)4(OH)2(Hprz)2]n (IDC ¼ planar imidazole-4,5-dicarboxylate; prz ¼ piperazine) | PFO | Langmuir | 185 | 82 |
Study of regeneration
The stability and reusability of sorbents are important factors for the widespread application of them83. Thus, in order to analyze the durability of the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid, the adsorption–desorption recycling test was employed (Fig. 10). After each cycle of adsorbent application, AMX desorption from UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid was performed by being washed with ethanol and utilized for the following cycle. As can be seen, there is negligible loss of adsorption sites even after undergoing eight cycles. This remarkable level of stability and durability exhibited by the UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid highlights its potential for various applications in adsorption processes, all while maintaining environmental integrity. The exceptional repeatability demonstrated by the nanohybrid highlights its potential for diverse applications in adsorption processes. Its environmentally friendly nature further contributes to minimizing pollution, making it an attractive solution for sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
Figure 10.
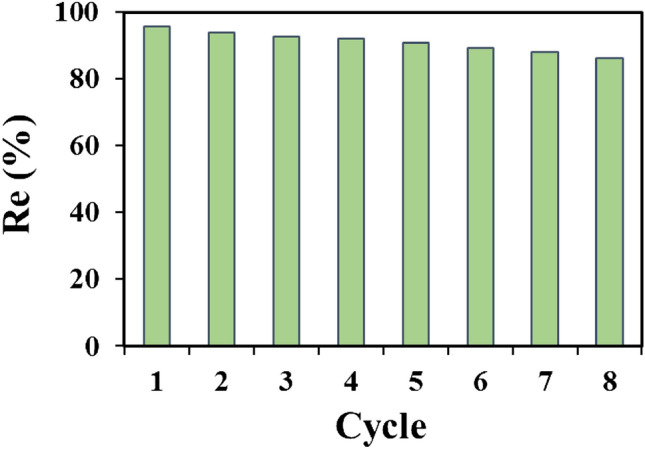
Reusability of UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid by adsorption/desorption process for eight consecutive cycles.
Conclusion
In this study, the removal of AMX antibiotic from wastewater was investigated by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid (through adsorption process), and it was observed that this nanoadsorbent has an excellent adsorption capacity to remove this AMX (1111.11 mg g−1). CCRSM was used to optimize four parameters: loading percentage Cr-MIL-101 NPs, initial concentration of AMX, contact time, and pH parameters. The results of the study showed that it follows the quadratic model. The Re% of AMX is equal to 99.50% and was obtained under the following conditions: the loading value of 20% Wt%, the initial concentration of AMX 80 mg L−1, contact time 20 min, and pH = 6. Also, the study of adsorption isotherm and kinetics shows that the Langmuir isotherm model and PSO kinetics successfully describe the equilibrium adsorption data. Investigation of thermodynamics of adsorption showed that the adsorption of AMX by UIO-66@Cr-MIL-101 nanohybrid is spontaneous and exothermic under optimal experimental conditions. Therefore, this research shows that the synthesized nanohybrid can be considered a new and excellent adsorbent due to its high adsorption capacity and short equilibrium time.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for the financial support accepted by the research councils of the Nanotechnology Research Center, Research Institute of Petroleum Industry.
Author contributions
S.S.: Collected the data, Doing the lab work and collecting data, Contributed data or analysis tools, Performed the analysis. A.R.: Conceived and designed the analysis, Supervision, Contributed data or analysis tools, Lab work and materials, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Performed the analysis, Wrote the paper, Revised and editing the manuscript with help the other authors, Other contribution, Corresponding Author. F.T.: Conceived and designed the analysis, Supervision, Contributed data or analysis tools, Lab work and materials. F.D.: Wrote the paper, Conceived and designed the analysis. F.T.: Wrote the paper, Conceived and designed the analysis. M.B.: Wrote the paper, Conceived and designed the analysis.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Leder C, Suk M, Lorenz S, Rastogi T, Peifer C, Kietzmann M, Jonas D, Buck M, Pahl A, Kümmerer K. Reducing environmental pollution by antibiotics through design for environmental degradation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:9358–9368. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c02243. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.D. Fatta-Kassinos, K. Kümmerer. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Sources, fate, effects and risks: Springer-Verlag 2008. XXXI, 521 p. 108 illus., 8 in color, 62 tables. Hardcover. 139.05 EUR. ISBN: 978–3–540–74663–8. Online version available, Springer, 2010.
- 3.Khan NA, Khan SU, Ahmed S, Farooqi IH, Dhingra A, Hussain A, Changani F. Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2019;16:81–86. doi: 10.3233/AJW190051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fatta-Kassinos D, Meric S, Nikolaou A. Pharmaceutical residues in environmental waters and wastewater: Current state of knowledge and future research. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011;399:251–275. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-4300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nazir MA, Najam T, Shahzad K, Wattoo MA, Hussain T, Tufail MK, Shah SSA, ur Rehman A. Heterointerface engineering of water stable ZIF-8@ ZIF-67: Adsorption of rhodamine B from water. Surfaces Interfaces. 2022;34:102324. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102324. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nazir MA, Bashir MA, Najam T, Javed MS, Suleman S, Hussain S, Kumar OP, Shah SSA, ur Rehman A. Combining structurally ordered intermetallic nodes: Kinetic and isothermal studies for removal of malachite green and methyl orange with mechanistic aspects. Microchem. J. 2021;164:105973. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2021.105973. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Anum A, Ibrahim SM, Tahir AA, Nazir MA, Malik M, Shah SSA, Ehsan A, Wattoo MA, ur Rehman A. Construction of hybrid sulfur-doped MOF-235@ g-C3N4 photocatalyst for the efficient removal of nicotine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023;157:111268. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111268. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nazir MA, Bashir MS, Jamshaid M, Anum A, Najam T, Shahzad K, Imran M, Shah SSA, ur Rehman A. Synthesis of porous secondary metal-doped MOFs for removal of Rhodamine B from water: Role of secondary metal on efficiency and kinetics. Surfaces Interfaces. 2021;25:101261. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2021.101261. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nazir MA, Khan NA, Cheng C, Shah SSA, Najam T, Arshad M, Sharif A, Akhtar S, ur Rehman A. Surface induced growth of ZIF-67 at Co-layered double hydroxide: Removal of methylene blue and methyl orange from water. Applied Clay Science. 2020;190:105564. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105564. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sharafinia S, Rashidi A, Babaei B, Orooji Y. Nanoporous carbons based on coordinate organic polymers as an efficient and eco-friendly nano-sorbent for adsorption of phenol from wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2023;13:13127. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40243-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barakat M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011;4:361–377. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.07.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bezaatpour A, Askarizadeh E, Akbarpour S, Amiria M, Babaei B. Green oxidation of sulfides in solvent-free condition by reusable novel Mo (VI) complex anchored on magnetite as a high-efficiency nanocatalyst with eco-friendly aqueous H2O2. Mol. Catal. 2017;436:199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.04.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Babaei B, Bezaatpour A, Amiri M, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R. Magnetically reusable MnFe2O4 nanoparticles modified with Oxo-Peroxo Mo (VI) Schiff-Base Complexes: A High efficiency catalyst for olefin epoxidation under solvent-free conditions. ChemistrySelect. 2018;3:2877–2881. doi: 10.1002/slct.201703006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bouzari N, Bezaatpour A, Babaei B, Amiri M, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S. Modification of MnFe2O4 surface by Mo (VI) pyridylimine complex as an efficient nanocatalyst for (ep) oxidation of alkenes and sulfides. J. Mol. Liquids. 2021;330:115690. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115690. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Babaei B, Bezaatpour A, Basharnavaz H. Robust and fast oxidation of sulfides by immobilized Mo (VI) complex on magnetic nanoparticles in solvent-free condition. Polyhedron. 2020;179:114382. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2020.114382. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Daughton CG, Ruhoy IS. The afterlife of drugs and the role of pharmEcovigilance. Drug Safety. 2008;31:1069–1082. doi: 10.2165/0002018-200831120-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Santos LH, Gros M, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Delerue-Matos C, Pena A, Barceló D, Montenegro MCB. Contribution of hospital effluents to the load of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewaters: Identification of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2013;461:302–316. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Boxall AB, Rudd MA, Brooks BW, Caldwell DJ, Choi K, Hickmann S, Innes E, Ostapyk K, Staveley JP, Verslycke T. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: What are the big questions? Environ. Health Perspect. 2012;120:1221–1229. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kümmerer K. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Effects and Risks. Springer Science & Business Media; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eniola JO, Kumar R, Barakat MA. Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water over natural and modified adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019;26:34775–34788. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06641-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tabarkhoon F, Abolghasemi H, Rashidi A, Bazmi M, Alivand MS, Tabarkhoon F, Farahani MV, Esrafili MD. Synthesis of novel and tunable Micro-Mesoporous carbon nitrides for Ultra-High CO2 and H2S capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2023;456:140973. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140973. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Neha R, Adithya S, Jayaraman RS, Gopinath KP, Pandimadevi M, Praburaman L, Arun J. Nano-adsorbents an effective candidate for removal of toxic pharmaceutical compounds from aqueous environment: A critical review on emerging trends. Chemosphere. 2021;272:129852. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ezeuko AS, Ojemaye MO, Okoh OO, Okoh AI. Potentials of metallic nanoparticles for the removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021;41:102041. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Prathna T, Sharma SK, Kennedy M. Nanoparticles in household level water treatment: An overview. Separation Purif. Technol. 2018;199:260–270. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.061. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tso C-P, Zhung C-M, Shih Y-H, Tseng Y-M, Wu S-C, Doong R-A. Stability of metal oxide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2010;61:127–133. doi: 10.2166/wst.2010.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Labille J, Brant J. Stability of nanoparticles in water. Nanomedicine. 2010;5:985–998. doi: 10.2217/nnm.10.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Saeed T, Naeem A, Din IU, Farooq M, Khan IW, Hamayun M, Malik T. Synthesis of chitosan composite of metal-organic framework for the adsorption of dyes; kinetic and thermodynamic approach. J. Hazardous Mater. 2022;427:127902. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Saeed T, Naeem A, Mahmood T, Ahmad Z, Farooq M, Din I, Khan I. Comparative study for removal of cationic dye from aqueous solutions by manganese oxide and manganese oxide composite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021;18:659–672. doi: 10.1007/s13762-020-02844-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Saeed, T. et al. Synthesis and spectroscopic characteristics of chitosan composite of zinc-based metal-organic framework for rapid adsorption of organic pollutants from aqueous media. Separation Sci. Technol. 58(13), 1–16 (2023).
- 30.Khan IW, Naeem A, Farooq M, Ghazi ZA, Saeed T, Perveen F, Malik T. Biodiesel production by valorizing waste non-edible wild olive oil using heterogeneous base catalyst: Process optimization and cost estimation. Fuel. 2022;320:123828. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123828. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Saeed T, Naeem A, Mahmood T, Khan A, Ahmad Z, Hamayun M, Khan IW, Khan NH. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of polyvinyl chloride composite of manganese oxide nanosheets for the efficient removal of dye from water. Water Sci. Technol. 2021;84:851–864. doi: 10.2166/wst.2021.282. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rasheed T, Rizwan K, Bilal M, Iqbal HM. Metal-organic framework-based engineered materials—Fundamentals and applications. Molecules. 2020;25:1598. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Duan C, Liang K, Zhang Z, Li J, Chen T, Lv D, Li L, Kang L, Wang K, Hu H. Recent advances in the synthesis of nanoscale hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks. Nano Mater. Sci. 2022;4:351–365. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoms.2021.12.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zou M, Dong M, Zhao T. Advances in metal-organic frameworks MIL-101 (Cr) Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:9396. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bi W, Wang G, Hu X. Fabrication of Zn-MOF derived graphitic carbon materials with mesoporous structure for adsorptive removal of ceftazidime from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 2022;652:129758. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129758. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ahmadijokani F, Tajahmadi S, Rezakazemi M, Sehat AA, Molavi H, Aminabhavi TM, Arjmand M. Aluminum-based metal-organic frameworks for adsorptive removal of anti-cancer (methotrexate) drug from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021;277:111448. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sharafinia, S. & Rashidi. A. MIL-101 (Cr) hybrid nanoporous carbon derived MOF as a nano-adsorbent for dye removal using RSM-CCD. Arab. J. Chem.16(12), 105288 (2023).
- 38.Salam S, Hussain N, Baqar Z, Ali N, Iqbal HM. Consequences of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds and Their Removal Strategies. Elsevier; 2023. pp. 269–300. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Aghajanzadeh M, Zamani M, Molavi H, Khieri Manjili H, Danafar H, Shojaei A. Preparation of metal–organic frameworks UiO-66 for adsorptive removal of methotrexate from aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Organometallic Polym. Mater. 2018;28:177–186. doi: 10.1007/s10904-017-0709-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Katz MJ, Brown ZJ, Colón YJ, Siu PW, Scheidt KA, Snurr RQ, Hupp JT, Farha OK. A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2013;49:9449–9451. doi: 10.1039/c3cc46105j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ding J, Yang Z, He C, Tong X, Li Y, Niu X, Zhang H. UiO-66 (Zr) coupled with Bi2MoO6 as photocatalyst for visible-light promoted dye degradation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;497:126–133. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.02.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bazmi M, Askari S, Ghasemy E, Rashidi A, Ettefaghi E. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for heat transfer applications: Enhancement of conduction and convection properties of water/N-CNT nanofluid. J. Thermal Anal. Calorimetry. 2019;138:69–79. doi: 10.1007/s10973-019-08024-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Eltaweil AS, Abd El-Monaem EM, El-Subruiti GM, Abd El-Latif MM, Omer AM. Fabrication of UiO-66/MIL-101 (Fe) binary MOF/carboxylated-GO composite for adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2020;10:19008–19019. doi: 10.1039/D0RA02424D. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liu L, Cui W, Lu C, Zain A, Zhang W, Shen G, Hu S, Qian X. Analyzing the adsorptive behavior of Amoxicillin on four Zr-MOFs nanoparticles: Functional groups dependence of adsorption performance and mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2020;268:110630. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yang F, Xie S, Wang G, Yu CW, Liu H, Liu Y. Investigation of a modified metal-organic framework UiO-66 with nanoscale zero-valent iron for removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020;27:20246–20258. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.M. Bazmi, L. Mahmoudian, D. Iranshahi, A. Rashidi. Scalable synthesis of a modified micro-mesoporous MIL-101 (Cr) with favorable CO2 adsorption. in Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Nanoscience & Nanotechnology (ICNN2018), Tehran, Iran, pp. 20–23. (2018).
- 47.Zhou L, Wang S, Chen Y, Serre C. Direct synthesis of robust hcp UiO-66 (Zr) MOF using poly (ethylene terephthalate) waste as ligand source. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019;290:109674. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109674. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.S. Sharafinia, A. Rashidi, M. Rostam-Abadi, R. Maleki, R. Rahighi, Y. Orooji. Adsorption of phenol from both acidic and basic industrial waste via newly synthesized metal organic framework hybrid smart adsorbents. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 1, 1554–1565 (2023).
- 49.Sharafinia S, Farrokhnia A, Lemraski EG. Optimized safranin adsorption onto poly (vinylidene fluoride)-based nanofiber via response surface methodology. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022;276:125407. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125407. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sharafinia S, Rashidi A, Esrafili MD. Optimized adsorption of volatile organic compounds on the activated carbon prepared from mesquite grain: A combined experimental and computational study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022;10:108528. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.108528. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lemraski EG, Sharafinia S. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies of Pb2+ adsorption onto new activated carbon prepared from Persian mesquite grain. J. Mol. Liquids. 2016;219:482–492. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.03.031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Herm ZR, Swisher JA, Smit B, Krishna R, Long JR. Metal−organic frameworks as adsorbents for hydrogen purification and precombustion carbon dioxide capture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:5664–5667. doi: 10.1021/ja111411q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mourabet M, El Rhilassi A, El Boujaady H, Bennani-Ziatni M, El Hamri R, Taitai A. Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by adsorption on Apatitic tricalcium phosphate using Box-Behnken design and desirability function. Appl. Surface Sci. 2012;258:4402–4410. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.12.125. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Özdemir E, Duranoğlu D, Beker Ü, Avcı AÖ. Process optimization for Cr (VI) adsorption onto activated carbons by experimental design. Chem. Eng. J. 2011;172:207–218. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.091. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stafiej A, Pyrzynska K, Ranz A, Lankmayr E. Screening and optimization of derivatization in heating block for the determination of aliphatic aldehydes by HPLC. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods. 2006;69:15–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jbbm.2006.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.de Oliveira FS, Korn M. Spectrophotometric determination of sulphate in automotive fuel ethanol by sequential injection analysis using dimethylsulphonazo (III) reaction. Talanta. 2006;68:992–999. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2005.06.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Abbasi Z, Farrokhnia A, Garcia-Lopez EI, Zargar Shoushtari M, Aghaie E. Synthesis of ZnO–Ag2CO3–Fe3O4@rGO core–shell structure: Magnetically separable photocatalyst for degradation of MB using the Box-Behnken design. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020;31:19554–19568. doi: 10.1007/s10854-020-04484-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nam S-N, Cho H, Han J, Her N, Yoon J. Photocatalytic degradation of acesulfame K: Optimization using the Box-Behnken design (BBD) Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2018;113:10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.09.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Li J, Zhang X, Liu Y. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Ganoderma lucidum spore lipids. LWT. 2016;70:16–23. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.02.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Beakou BH, El Hassani K, Houssaini MA, Belbahloul M, Oukani E, Anouar A. Novel activated carbon from Manihot esculenta Crantz for removal of Methylene Blue. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2017;27:215–222. doi: 10.1016/j.serj.2017.06.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sharafinia S, Farrokhnia A, Lemraski EG. The adsorption of cationic dye onto ACPMG@ ZIF-8 core-shell, optimization using central composite response surface methodology (CCRSM) Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 2022;634:128039. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.128039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rotte NK, Yerramala S, Boniface J, Srikanth VV. Equilibrium and kinetics of Safranin O dye adsorption on MgO decked multi-layered graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 2014;258:412–419. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.065. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chandane V, Singh V. Adsorption of safranin dye from aqueous solutions using a low-cost agro-waste material soybean hull. Desalination Water Treatment. 2016;57:4122–4134. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2014.991758. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Freundlich H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Zeitschrift für physikalische Chemie. 1907;57:385–470. doi: 10.1515/zpch-1907-5723. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Langmuir I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916;38:2221–2295. doi: 10.1021/ja02268a002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Cerofolini G. A model which allows for the Freundlich and the Dubinin-Radushkevich adsorption isotherms. Surface Sci. 1975;51:333–335. doi: 10.1016/0039-6028(75)90260-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Lagergren S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga svenska vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar. 1898;24:1–39. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Elovich SY, Larionov O. Theory of adsorption from nonelectrolyte solutions on solid adsorbents: 2. Experimental verification of the equation for the adsorption isotherm from solutions. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Division Chem. Sci. 1962;11:198–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00908017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Weber WJ, Jr, Morris JC. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanitary Eng. Division. 1963;89:31–59. doi: 10.1061/JSEDAI.0000430. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Allen S, Mckay G, Khader K. Intraparticle diffusion of a basic dye during adsorption onto sphagnum peat. Environ. Pollut. 1989;56:39–50. doi: 10.1016/0269-7491(89)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yang J, Yu M, Chen W. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by activated carbon prepared from longan seed: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015;21:414–422. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2014.02.054. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Halsey GD. The Role of Surface Heterogeneity in Adsorption. Advances in Catalysis. Elsevier; 1952. pp. 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chen G, Hai J, Wang H, Liu W, Chen F, Wang B. Gold nanoparticles and the corresponding filter membrane as chemosensors and adsorbents for dual signal amplification detection and fast removal of mercury (II) Nanoscale. 2017;9:3315–3321. doi: 10.1039/C6NR09638G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Cheung W, Szeto Y, McKay G. Intraparticle diffusion processes during acid dye adsorption onto chitosan. Bioresource Technol. 2007;98:2897–2904. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Baghdadi M, Ghaffari E, Aminzadeh B. Removal of carbamazepine from municipal wastewater effluent using optimally synthesized magnetic activated carbon: Adsorption and sedimentation kinetic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016;4:3309–3321. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.06.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bedin KC, Martins AC, Cazetta AL, Pezoti O, Almeida VC. KOH-activated carbon prepared from sucrose spherical carbon: Adsorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for Methylene Blue removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2016;286:476–484. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.099. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Singh S, Sharma S, Umar A, Jha M, Mehta SK, Kansal SK. Nanocuboidal-shaped zirconium based metal organic framework for the enhanced adsorptive removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, ketorolac tromethamine, from aqueous phase. N. J. Chem. 2018;42:1921–1930. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ03851H. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Gadipelly CR, Marathe KV, Rathod VK. Effective adsorption of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from aqueous solutions using metal-organic framework. Separation Sci. Technol. 2018;53:2826–2832. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2018.1474225. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Peng Y, Zhang Y, Huang H, Zhong C. Flexibility induced high-performance MOF-based adsorbent for nitroimidazole antibiotics capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2018;333:678–685. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.138. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Du C, Zhang Z, Yu G, Wu H, Chen H, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Su Y, Tan S, Yang L. A review of metal organic framework (MOFs)-based materials for antibiotics removal via adsorption and photocatalysis. Chemosphere. 2021;272:129501. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Li S, Zhang X, Huang Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 derived nanoporous carbon as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics from water. J. Hazardous Mater. 2017;321:711–719. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Abazari R, Mahjoub AR, Shariati J. Synthesis of a nanostructured pillar MOF with high adsorption capacity towards antibiotics pollutants from aqueous solution. J. Hazardous Mater. 2019;366:439–451. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.D.M. Maklavany, Z. Rouzitalab, M. Bazmi, M. Askarieh, A. Nabavi-Pelesaraei. Eco-environmental analysis of different routes for the synthesis of MIL-53 (Fe): An integrated life cycle assessment and life cycle cost approaches. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 11(26), 9816–9832 (2023).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.