Abstract
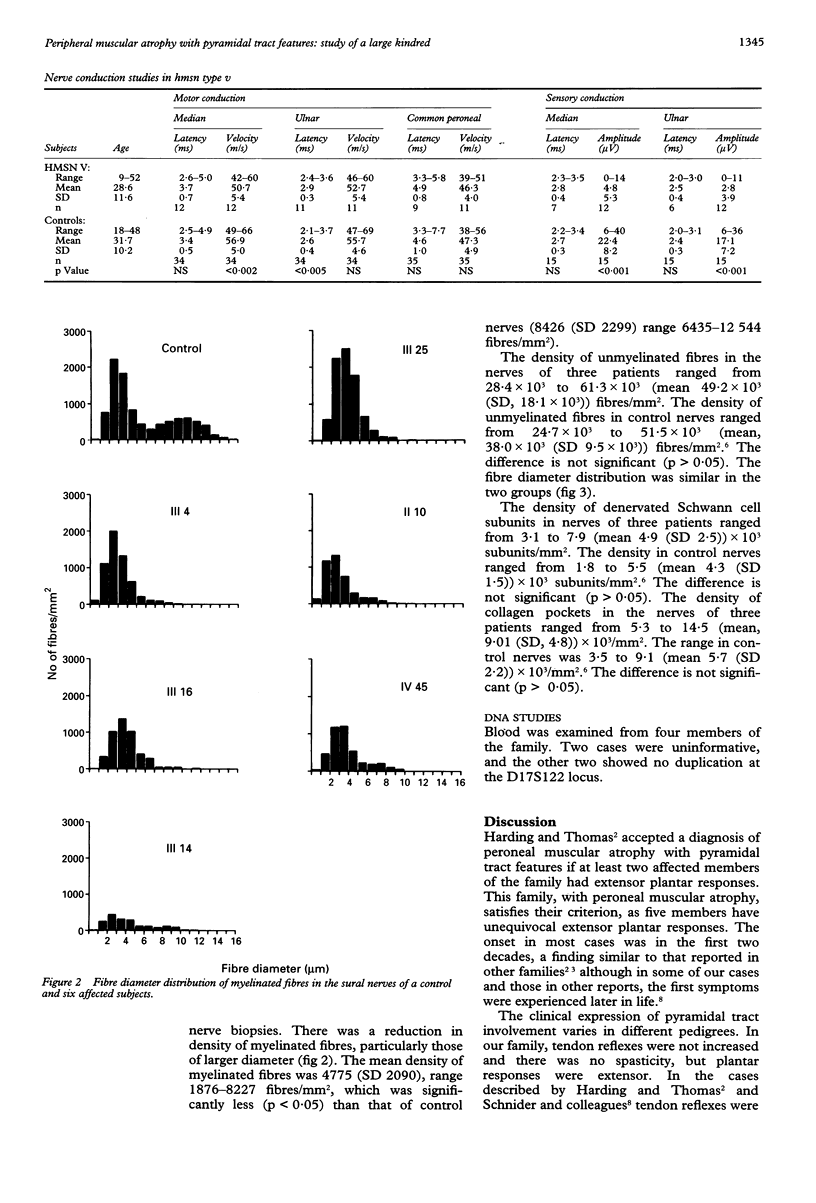
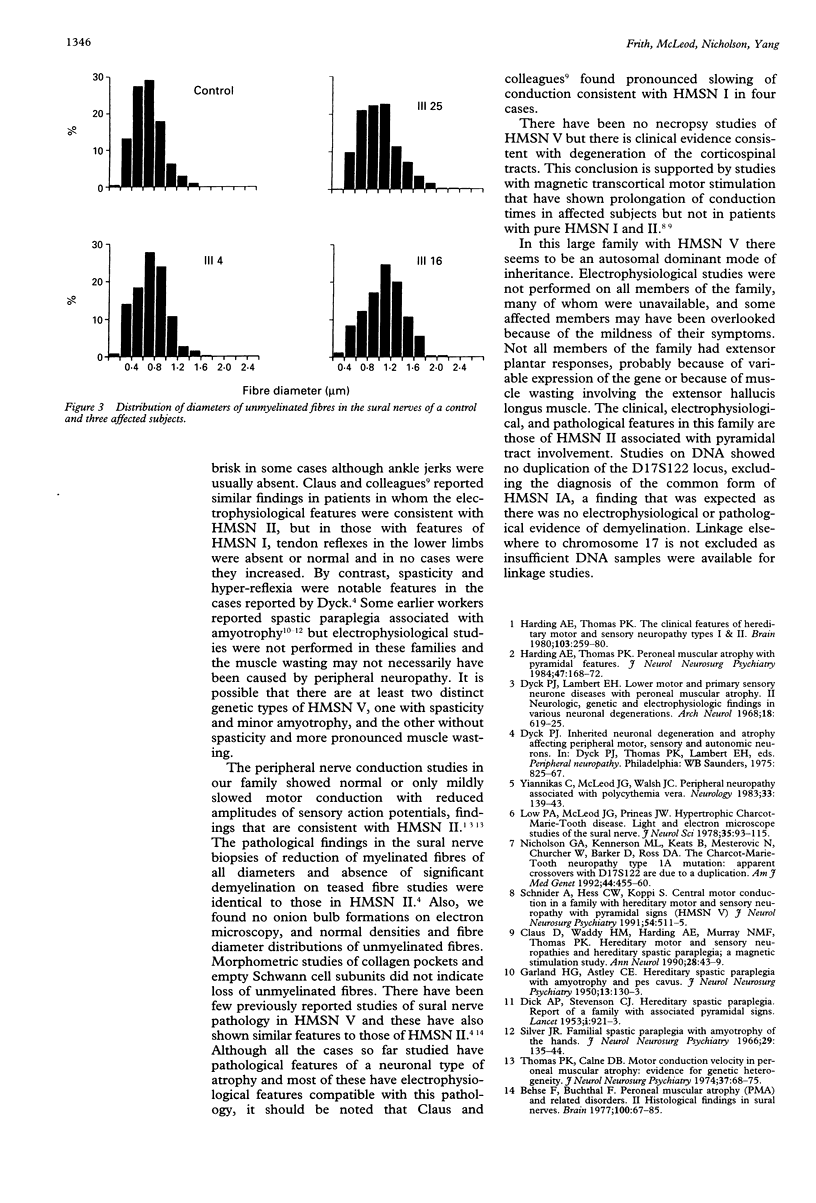
A large family with autosomal dominant inheritance of peroneal muscular atrophy, associated with extensor plantar responses in some cases, has been studied. Onset was usually in the first two decades and spasticity was not a feature. Nerve conduction studies in 21 cases and light and electron microscope findings on six sural nerve biopsies were similar to those in hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type II.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behse F., Buchthal F. Peroneal muscular atrophy (PMA) and related disorders. II. Histological findings in sural nerves. Brain. 1977 Mar;100(Pt 1):67–85. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus D., Waddy H. M., Harding A. E., Murray N. M., Thomas P. K. Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies and hereditary spastic paraplegia: a magnetic stimulation study. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):43–49. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICK A. P., STEVENSON C. J. Hereditary spastic paraplegia; report of a family with associated extrapyramidal signs. Lancet. 1953 May 9;1(6767):921–923. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)92061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Lambert E. H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. II. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in various neuronal degenerations. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jun;18(6):619–625. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470360041003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARLAND H. G., ASTLEY C. E. Hereditary spastic paraplegia with amyotrophy and pes cavus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950 May;13(2):130–133. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.2.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. Peroneal muscular atrophy with pyramidal features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;47(2):168–172. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. The clinical features of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy types I and II. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):259–280. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., McLeod J. G., Prineas J. W. Hypertrophic Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Light and electron microscope studies of the sural nerve. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Jan;35(1):93–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson G. A., Kennerson M. L., Keats B. J., Mesterovic N., Churcher W., Barker D., Ross D. A. Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1A mutation: apparent crossovers with D17S122 are due to a duplication. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Nov 1;44(4):455–460. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnider A., Hess C. W., Koppi S. Central motor conduction in a family with hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with pyramidal signs (HMSN V). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Jun;54(6):511–515. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.6.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. K., Calne D. B. Motor nerve conduction velocity in peroneal muscular atrophy: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jan;37(1):68–75. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yiannikas C., McLeod J. G., Walsh J. C. Peripheral neuropathy associated with polycythemia vera. Neurology. 1983 Feb;33(2):139–143. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


