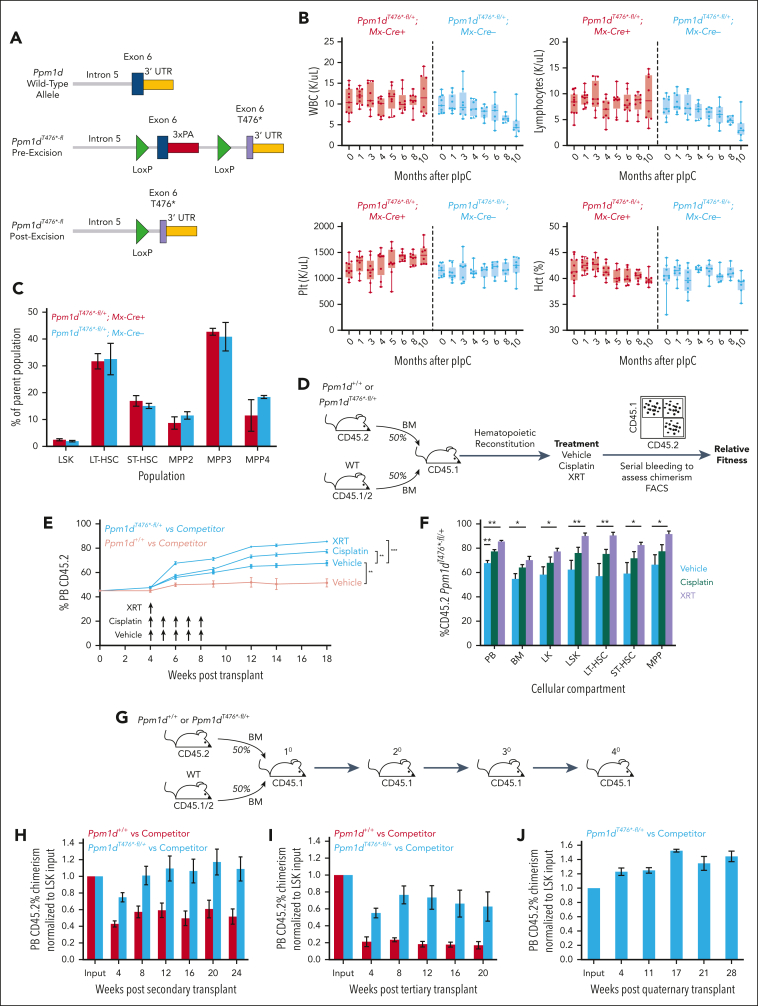
Figure 1.
Truncating mutations in Ppm1d enhance HSC fitness. (A) Schematic of engineered locus in Ppm1dT476∗-fl mice. (B) Peripheral blood white blood cell (WBC), lymphocyte, platelet (Plt) counts, and hematocrit (Hct) of Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;MxCre+ or Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;MxCre− mice treated with pIpC at age 10 weeks. (C) Bone marrow stem cell analysis of Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;MxCre+ or Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;MxCre− mice approximately 1 year after pIpC treatment. (D) Schematic of competition experiment between Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;Vav-Cre+;Cd45.2 or Ppm1d+/+;Vav-Cre+;Cd45.2 and wild-type (WT) Vav-Cre+;Cd45.1/2 control bone marrow cells transplanted into lethally irradiated Cd45.1 recipients. Cisplatin was dosed intraperitoneally at 4 mg/kg and sublethal irradiation was dosed at 2.5 Gy. (E-F) Peripheral blood (E) and bone marrow (F) CD45.2 chimerism of recipient mice from Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;Vav-Cre+;Cd45.2 and WT Cd45.1/2 competition experiment outlined in panel D. (G) Schematic of serial transplantation of the bone marrow from the vehicle control mice outline in panel D. (H-J) Peripheral blood Cd45.2 chimerism of secondary (H), tertiary (I), and quaternary (J) mice serially transplanted with Ppm1d+/+;Vav-Cre+;Cd45.2 and WT Vav-Cre+;Cd45.1/2 (gray) or Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;Vav-Cre+;Cd45.2 and WT Vav-Cre+;Cd45.1/2 (black). Note that in the quaternary transplant only Ppm1dT476∗-fl/+;Vav-Cre+;Cd45.2 were present. Error bars show standard error of the mean (SEM), ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001.