Abstract
A prospective series of 20 patients with moderate to severe intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH) was studied for the effect of intraventricular administration of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) on reduction of haematoma volume and prognosis. On the day of haemorrhage ventriculostomy was performed and 2 to 5 mg of rt-PA were injected via the external ventricular drainage, followed by drainage closure for two hours. In 14 patients rt-PA treatment was repeated. Computed tomography showed complete clot lysis or substantial reduction of intraventricular haematoma volume in 19 patients within 96 hours; the clearance of the third and fourth ventricle preceded the clearance of the lateral ventricles. Decrease of ventricular enlargement was seen in all but one patient with initial ventricular dilatation. Increase of haematoma volume and ventricular size was found in one patient. Outcome was minor or no neurological deficit in nine patients, disabling neurological deficit in six patients, and vegetative status in four patients. One patient did not survive the IVH. Intraventricular treatment with rt-PA seems effective in rapid lysis of intraventricular haematoma and normalisation of impaired CSF circulation. This treatment may contribute to an improvement in prognosis of moderate to severe IVH.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
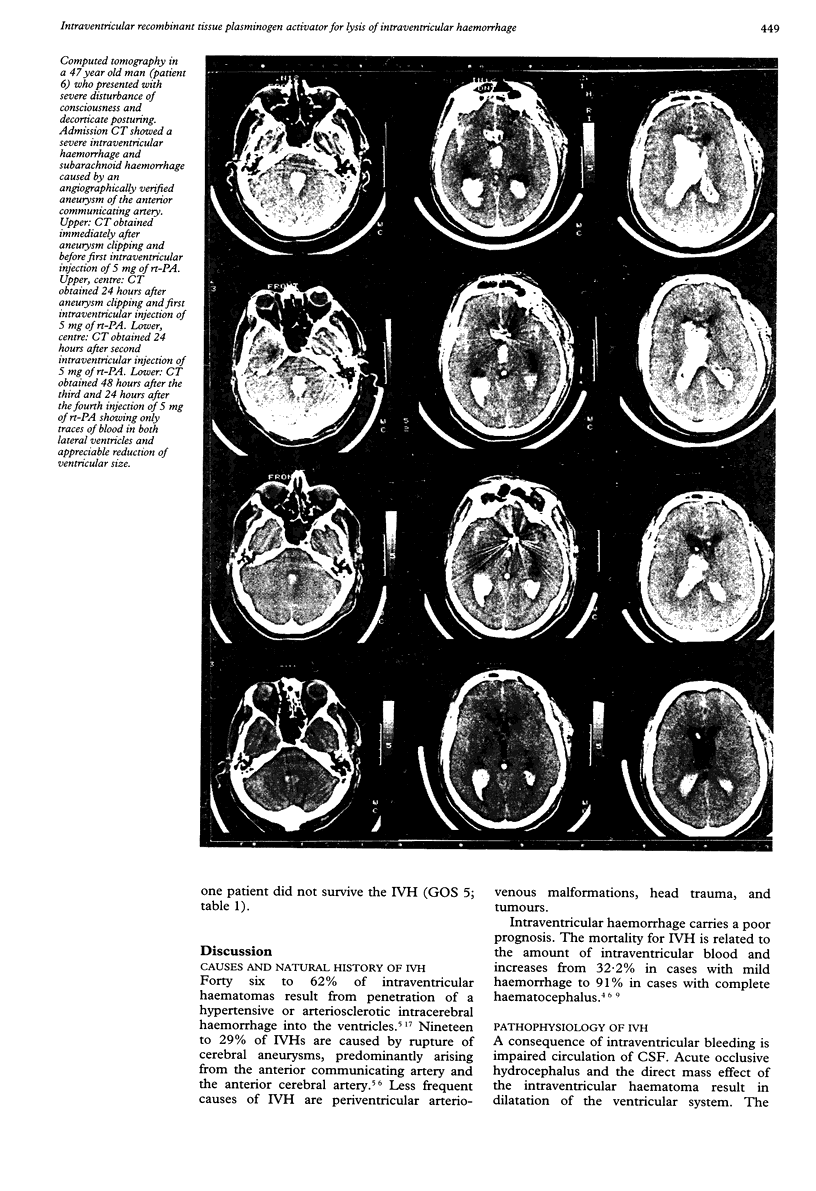
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimoto H., Maki Y. [Serial CT study of intracerebral hemorrhage (author's transl)]. No Shinkei Geka. 1979 May;7(5):455–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. H., Mann K. S. Intraventricular haematoma: management of comatose patients with valve regulated external ventricular drainage. Br J Neurosurg. 1988;2(4):465–469. doi: 10.3109/02688698809029600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donauer E., Reif J., al-Khalaf B., Mengedoht E. F., Faubert C. Intraventricular haemorrhage caused by aneurysms and angiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1993;122(1-2):23–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01446982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. M., Grace M. G., Weir B. K. Treatment of intraventricular hemorrhage with tissue plasminogen activator. Neurosurgery. 1993 Jun;32(6):941–947. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199306000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. M., Weir B. K., Kassell N. F., Disney L. B., Grace M. G. Intracisternal recombinant tissue plasminogen activator after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1991 Aug;75(2):181–188. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.2.0181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeb D. A., Robertson W. D., Lapointe J. S., Nugent R. A., Harrison P. B. Computed tomographic diagnosis of intraventricular hemorrhage. Etiology and prognosis. Radiology. 1982 Apr;143(1):91–96. doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.6977795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariton G. B., Findlay J. M., Weir B. K., Kasuya H., Grace M. G., Mielke B. W. Comparison of intrathecal administration of urokinase and tissue plasminogen activator on subarachnoid clot and chronic vasospasm in a primate model. Neurosurgery. 1993 Oct;33(4):691–697. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199310000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helweg-Larsen S., Sommer W., Strange P., Lester J., Boysen G. Prognosis for patients treated conservatively for spontaneous intracerebral hematomas. Stroke. 1984 Nov-Dec;15(6):1045–1048. doi: 10.1161/01.str.15.6.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett B., Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet. 1975 Mar 1;1(7905):480–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Blomquist G. A., Jr, Ethier R. Intraventricular hemorrhage in adults. Surg Neurol. 1977 Sep;8(3):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfrank L., Lippitz B., Groth M., Bertalanffy H., Gilsbach J. M. Effect of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on clot lysis and ventricular dilatation in the treatment of severe intraventricular haemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1993;122(1-2):32–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01446983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoi K., Yoshimoto T., Takahashi A., Fujiwara S., Koshu K., Sugawara T. Prospective study on the prevention of cerebral vasospasm by intrathecal fibrinolytic therapy with tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Neurosurg. 1993 Mar;78(3):430–437. doi: 10.3171/jns.1993.78.3.0430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr G., Ferguson G., Khan M., Malloy D., Watts R., Benoit B., Weir B. Intraventricular hemorrhage from ruptured aneurysm. Retrospective analysis of 91 cases. J Neurosurg. 1983 Apr;58(4):482–487. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.58.4.0482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman J., Servo A., Heiskanen O. Effect of intrathecal fibrinolytic therapy on clot lysis and vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1991 Aug;75(2):197–201. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.2.0197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D., Sclabassi R. J., Horton J. A. Lysis of intraventricular blood clot with urokinase in a canine model: Part 3. Effects of intraventricular urokinase on clot lysis and posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 1986 Oct;19(4):553–572. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198610000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Ohta T., Kikuchi H., Takakura K., Usui M., Ohnishi H., Kondo A., Tanabe H., Nakamura J., Yamada K. A phase II clinical trial of recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator against cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 1994 Oct;35(4):597–605. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199410000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P. H., Matsuoka Y., Kawajiri K., Kanai M., Hoda K., Yamamoto S., Nishimura S. Treatment of intraventricular hemorrhage using urokinase. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1990 May;30(5):329–333. doi: 10.2176/nmc.30.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale G., Jennett B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):81–84. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91639-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilouthis J., Richardson A. E. Ventricular dilatation and communicating hydrocephalus following spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1979 Sep;51(3):341–351. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.3.0341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins W. S., Moody D. M., Toole J. F., Laster D. W., Ball M. R. Clinical and computerized tomographic study of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Arch Neurol. 1978 Dec;35(12):832–833. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500360056011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabramski J. M., Spetzler R. F., Lee K. S., Papadopoulos S. M., Bovill E., Zimmerman R. S., Bederson J. B. Phase I trial of tissue plasminogen activator for the prevention of vasospasm in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1991 Aug;75(2):189–196. doi: 10.3171/jns.1991.75.2.0189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman R., Gürsoy A., Horn A., Harenberg J., Diehm C., Kübler W. Fibrinolytic therapy of deep vein thrombosis with continuous intravenous infusion of a recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jan;17(1):48–54. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]