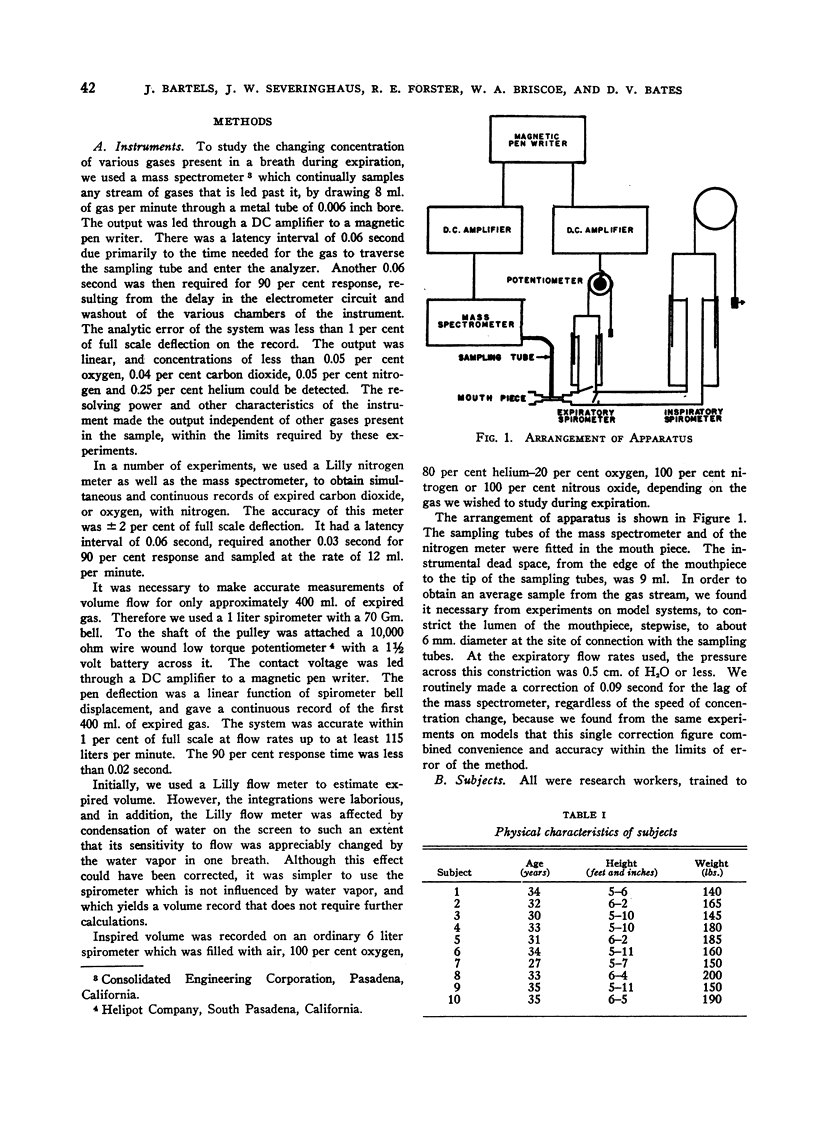
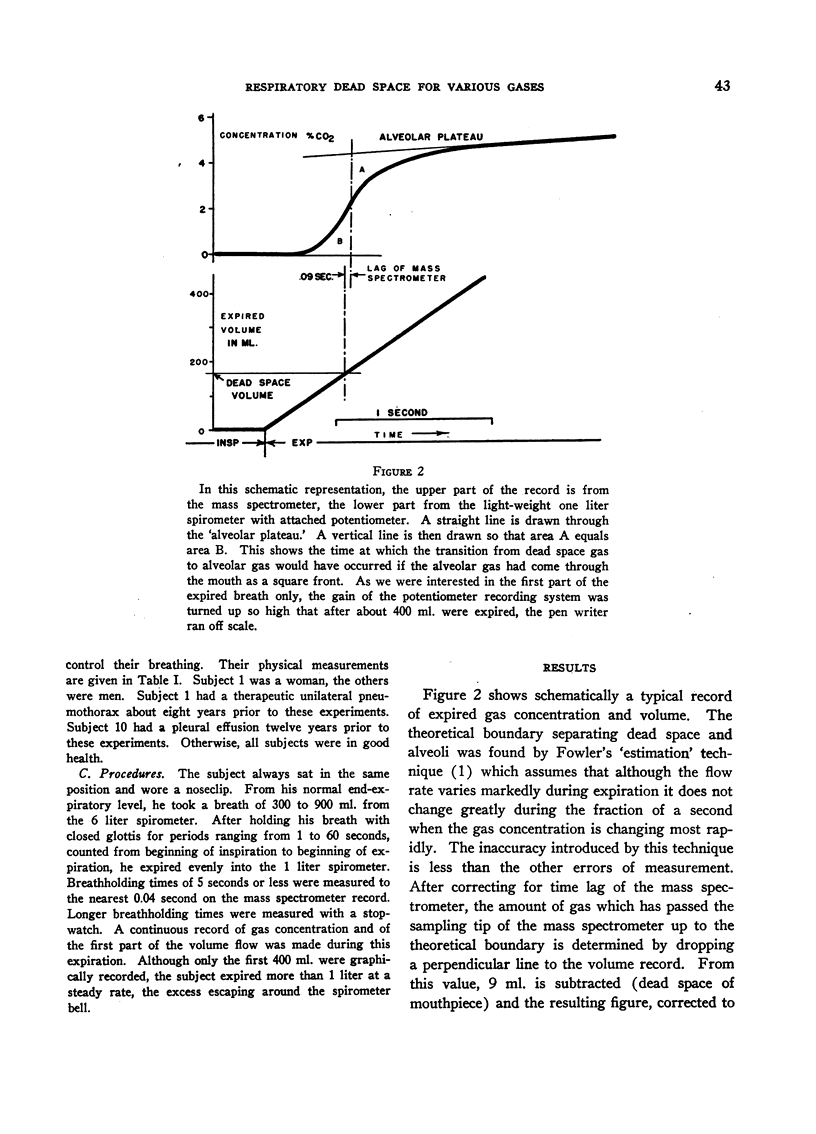
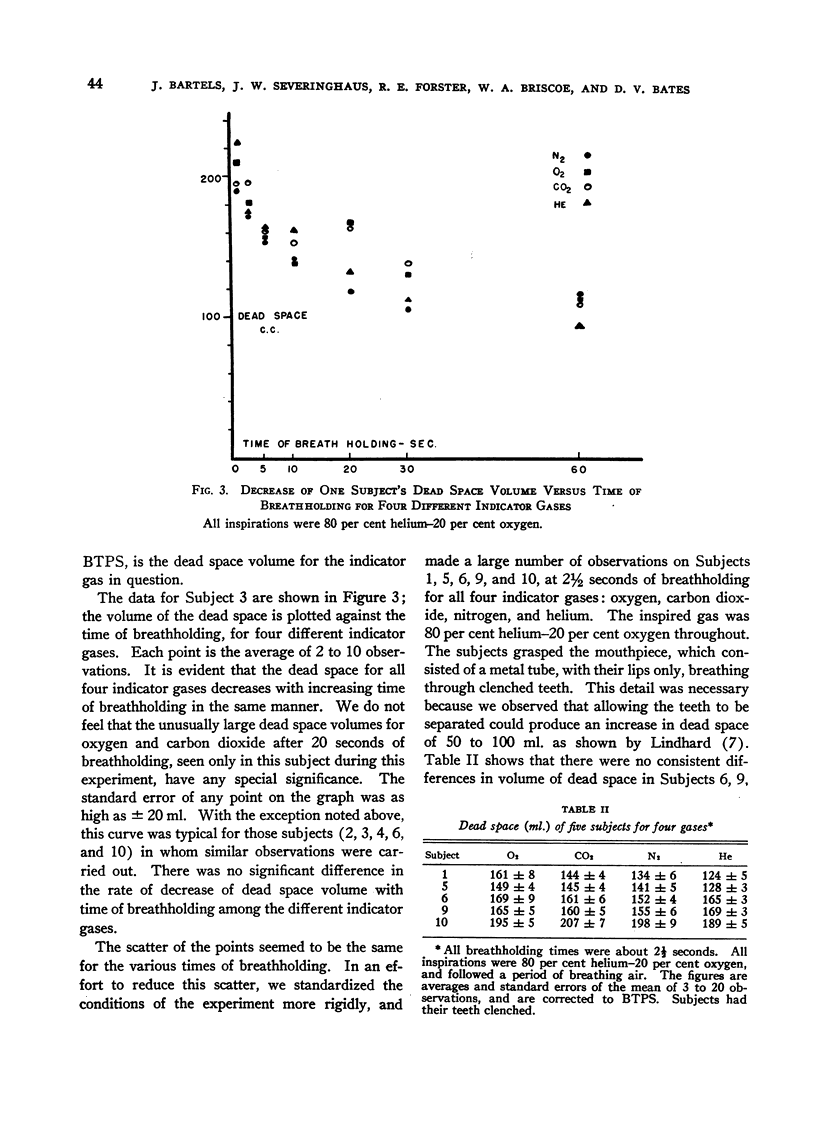
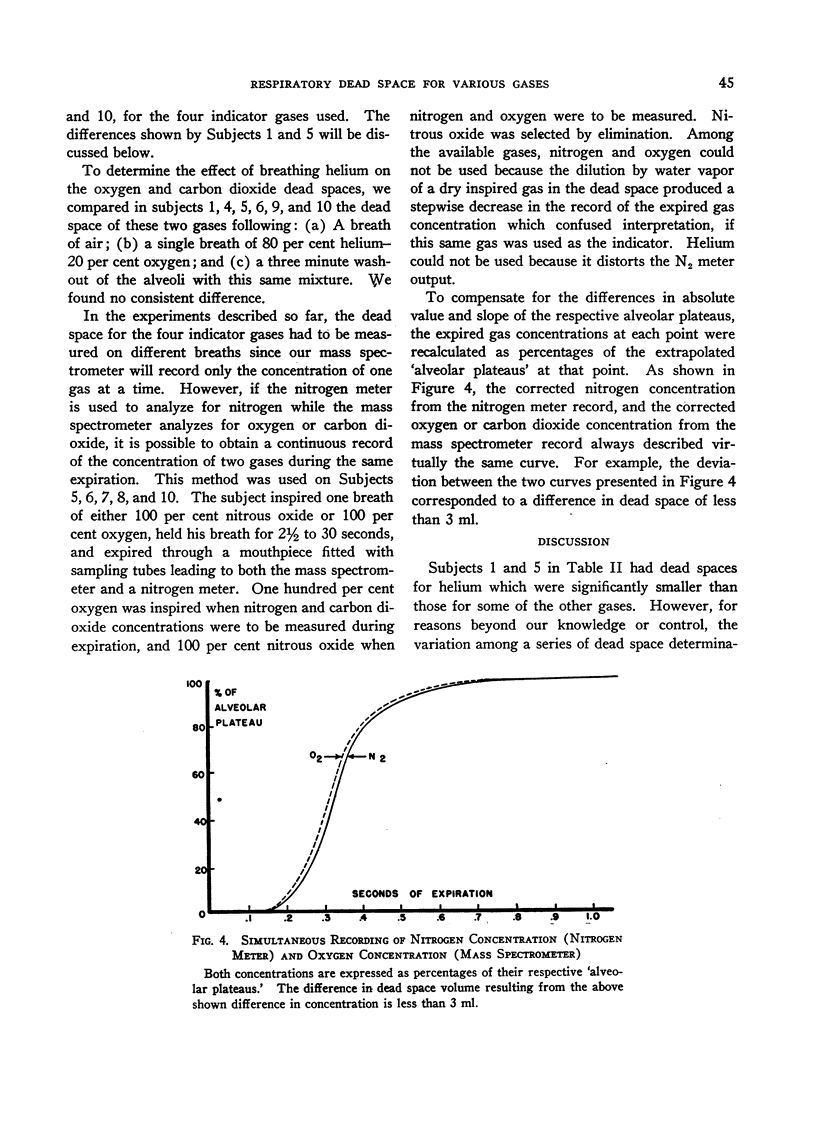
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DUBOIS A. B., FOWLER R. C., SOFFER A., FENN W. O. Alveolar CO2 measured by expiration into the rapid infrared gas analyzer. J Appl Physiol. 1952 Jan;4(7):526–534. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.7.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. G., Haldane J. S. The capacity of the air passages under varying physiological conditions. J Physiol. 1912 Oct 22;45(4):235–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWLER W. S. Lung function studies; uneven pulmonary ventilation in normal subjects and in patients with pulmonary disease. J Appl Physiol. 1949 Dec;2(6):283–299. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1949.2.6.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A., Lindhard J. On the average composition of the alveolar air and its variations during the respiratory cycle. J Physiol. 1914 Feb 27;47(6):431–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1914.sp001635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R., FISHMAN A. P., BORRERO L. M. New experimental methods for determination of effective alveolar gas composition and respiratory dead space, in the anesthetized dog and in man. J Appl Physiol. 1952 May;4(11):855–867. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.11.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


