Abstract
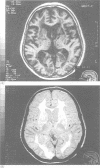
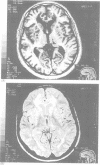
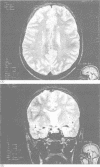
A survey was carried out on a large family presenting the symptoms of familial arteriopathy (CADASIL) recently mapped to chromosome 19. This is characterised clinically by recurrent subcortical infarcts developing into pseudobulbar palsy and subcortical dementia, and radiologically by early MRI abnormalities. To characterise this familial condition, 43 members older than 20 years and spreading over four generations were studied clinically (31 living, 12 deceased), genetically, and radiologically by MRI (n = 31). Twenty out of 43 were found to be clinically symptomatic and of these 13 out of 31 had MRI abnormalities. Genetic studies mapped this condition to the locus of CADASIL (lod score > 3). The natural history suggests a chronological clinicoradiological staging of this phenotype of CADASIL: stage I between 20 and 40 years with frequent migraine-like episodes and well delineated lesions of the white matter; stage II between 40 and 60 years with stroke-like episodes, bipolar or monopolar-like psychotic disorders, coalescent lesions of the white matter, and well delineated lesions of the basal ganglia; and stage III over 60 years with subcortical dementia, pseudobulbar palsy, diffuse leukoencephalopathy, and multiple well delineated lesions of the basal ganglia. This phenotype differs from the other two previously described by high frequency of migraine, frequency of psychotic disorders, and early neurological manifestations. The new acronym "cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts, leukoencephalopathy, and migraine" (CADASILM) is proposed to better describe this particular subvariety of CADASIL.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baudrimont M., Dubas F., Joutel A., Tournier-Lasserve E., Bousser M. G. Autosomal dominant leukoencephalopathy and subcortical ischemic stroke. A clinicopathological study. Stroke. 1993 Jan;24(1):122–125. doi: 10.1161/01.str.24.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousser M. G., Tournier-Lasserve E. Summary of the proceedings of the First International Workshop on CADASIL. Paris, May 19-21, 1993. Stroke. 1994 Mar;25(3):704–707. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.3.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler J. V., Hachinski V. Progress in the genetics of cerebrovascular disease: inherited subcortical arteriopathies. Stroke. 1994 Aug;25(8):1696–1698. doi: 10.1161/01.str.25.8.1696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabriat H., Tournier-Lasserve E., Vahedi K., Leys D., Joutel A., Nibbio A., Escaillas J. P., Iba-Zizen M. T., Bracard S., Tehindrazanarivelo A. Autosomal dominant migraine with MRI white-matter abnormalities mapping to the CADASIL locus. Neurology. 1995 Jun;45(6):1086–1091. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davous P., Fallet-Bianco C. Démence sous-corticale familiale avec leucoencéphalopathie artériopathique. Observation clinico-pathologique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1991;147(5):376–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson T. J., Engelstein M., Lee M. K., Ho E. C., Rubenfield M. J., Adams C. P., Housman D. E., Dracopoli N. C. Isolation and chromosomal assignment of 100 highly informative human simple sequence repeat polymorphisms. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90133-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joutel A., Bousser M. G., Biousse V., Labauge P., Chabriat H., Nibbio A., Maciazek J., Meyer B., Bach M. A., Weissenbach J. A gene for familial hemiplegic migraine maps to chromosome 19. Nat Genet. 1993 Sep;5(1):40–45. doi: 10.1038/ng0993-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mas J. L., Dilouya A., de Recondo J. A familial disorder with subcortical ischemic strokes, dementia, and leukoencephalopathy. Neurology. 1992 May;42(5):1015–1019. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.5.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbadini G., Francia A., Calandriello L., Di Biasi C., Trasimeni G., Gualdi G. F., Palladini G., Manfredi M., Frontali M. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leucoencephalopathy (CADASIL). Clinical, neuroimaging, pathological and genetic study of a large Italian family. Brain. 1995 Feb;118(Pt 1):207–215. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvi F., Michelucci R., Plasmati R., Parmeggiani L., Zonari P., Mascalchi M., Tassinari C. A. Slowly progressive familial dementia with recurrent strokes and white matter hypodensities on CT scan. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(2):135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02226962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonninen V., Savontaus M. L. Hereditary multi-infarct dementia. Eur Neurol. 1987;27(4):209–215. doi: 10.1159/000116158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourander P., Wälinder J. Hereditary multi-infarct dementia. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):1015–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourander P., Wålinder J. Hereditary multi-infarct dementia. Morphological and clinical studies of a new disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Aug 31;39(3):247–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00691704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkstein S. E., Mayberg H. S., Berthier M. L., Fedoroff P., Price T. R., Dannals R. F., Wagner H. N., Leiguarda R., Robinson R. G. Mania after brain injury: neuroradiological and metabolic findings. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jun;27(6):652–659. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Hewlett R. H., Brownell B. Chronic familial vascular encephalopathy. Lancet. 1977 Jun 25;1(8026):1364–1365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92576-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier-Lasserve E., Iba-Zizen M. T., Romero N., Bousser M. G. Autosomal dominant syndrome with strokelike episodes and leukoencephalopathy. Stroke. 1991 Oct;22(10):1297–1302. doi: 10.1161/01.str.22.10.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier-Lasserve E., Joutel A., Melki J., Weissenbach J., Lathrop G. M., Chabriat H., Mas J. L., Cabanis E. A., Baudrimont M., Maciazek J. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy maps to chromosome 19q12. Nat Genet. 1993 Mar;3(3):256–259. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]