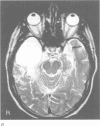
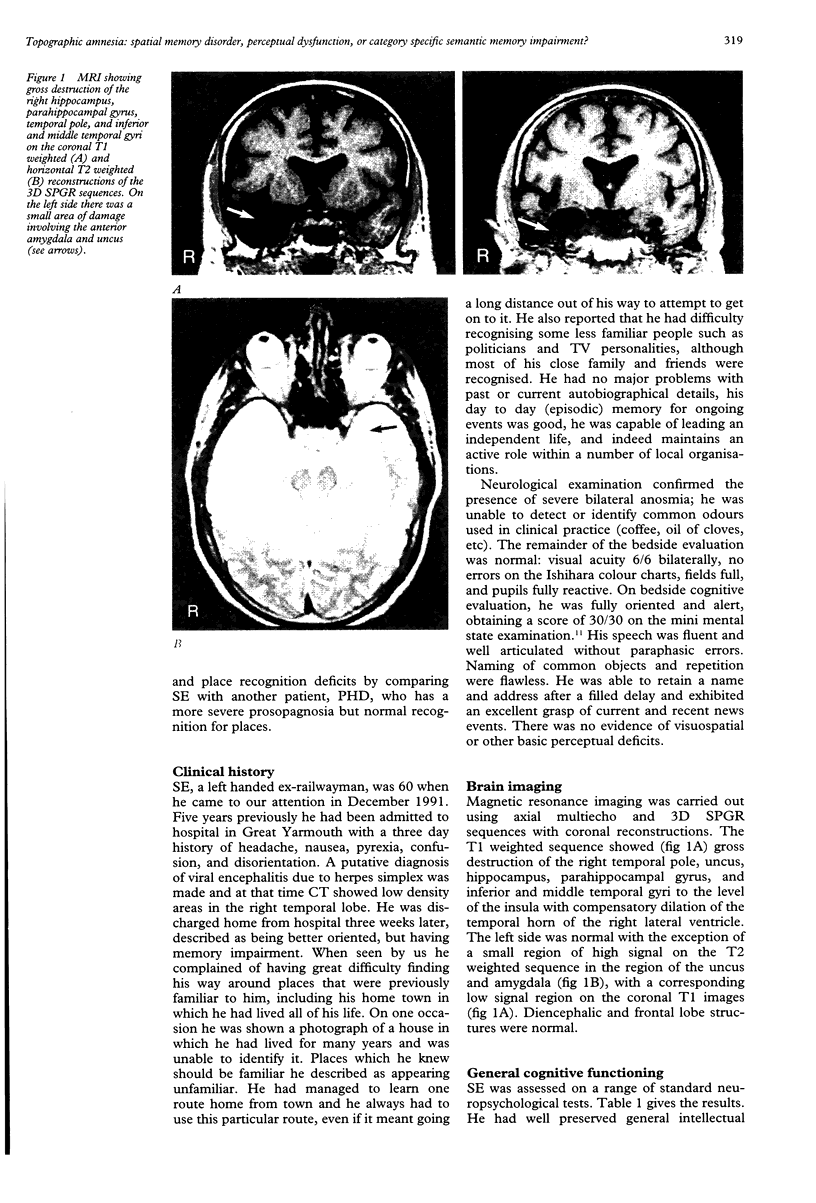
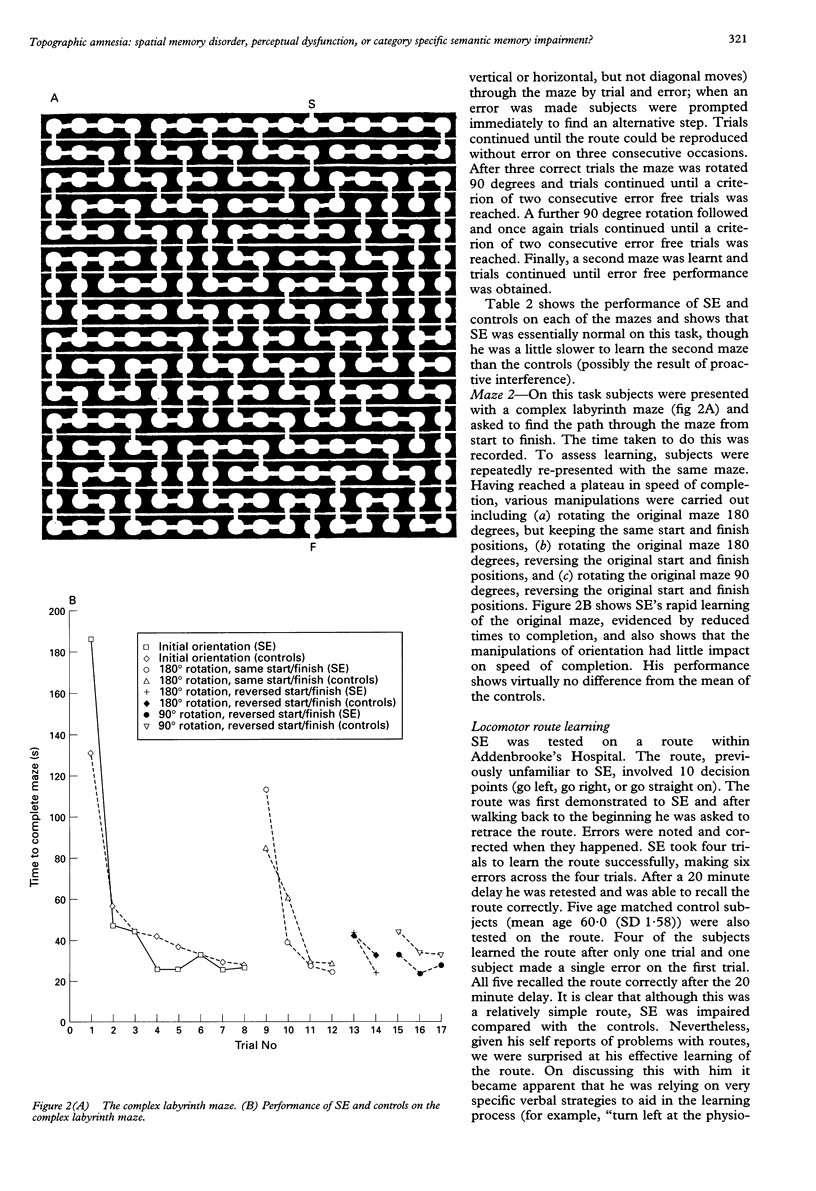
Abstract
A 60 year old patient, SE, who presented with a severe difficulty in finding his way around previously familiar environments and a mild prosopagnosia is described. SE had herpes simplex encephalitis resulting in selective right temporal lobe damage. He showed normal spatial learning, but was severely imparied in his ability to recognise pictures of buildings and landmarks. The disorder was not confined to the visual modality, but rather involved a loss of knowledge about famous buildings and landmarks when tested from their spoken name. SE was contrasted with a more severely prosopagnosic patient, PHD, who showed normal ability to recognise buildings and landmarks, indicating that recognition of people dissociates from recognition of buildings/landmarks. It is concluded that SE's failure of place knowledge represents a category specific supramodal semantic memory impairment.
Full text
PDF

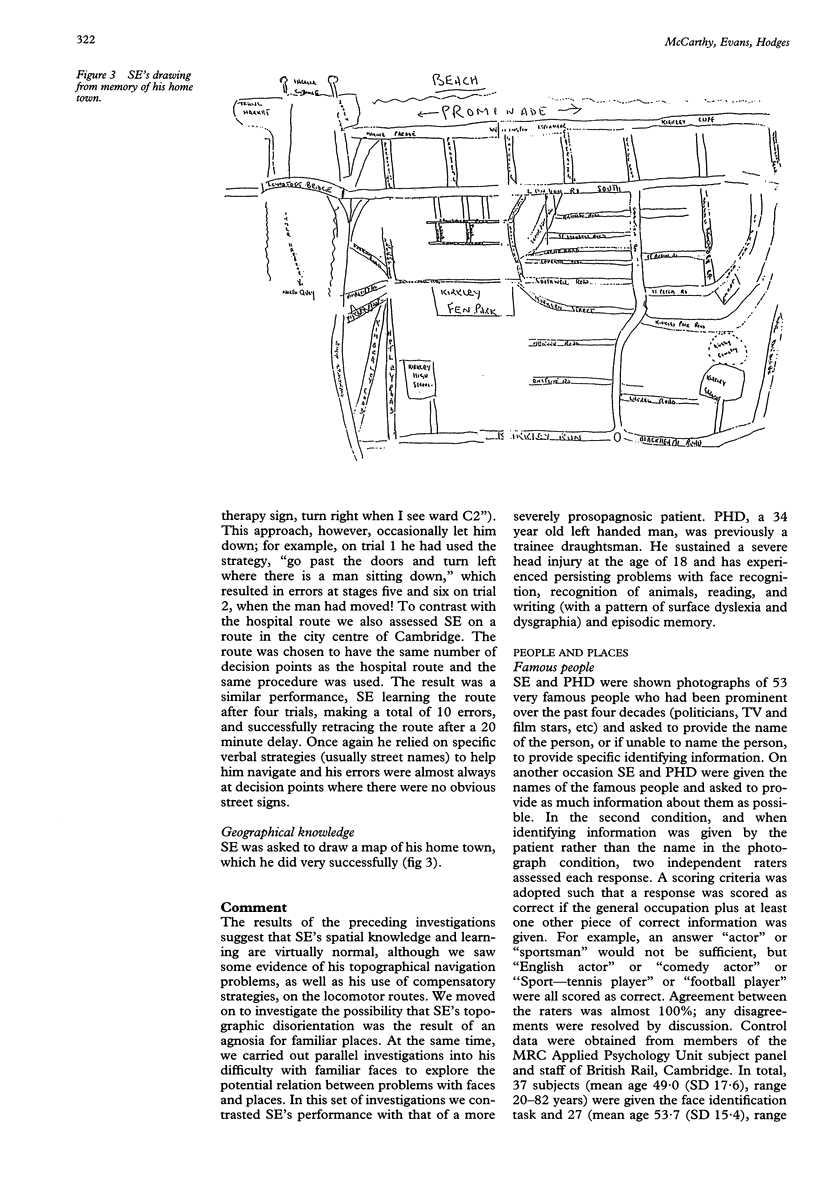
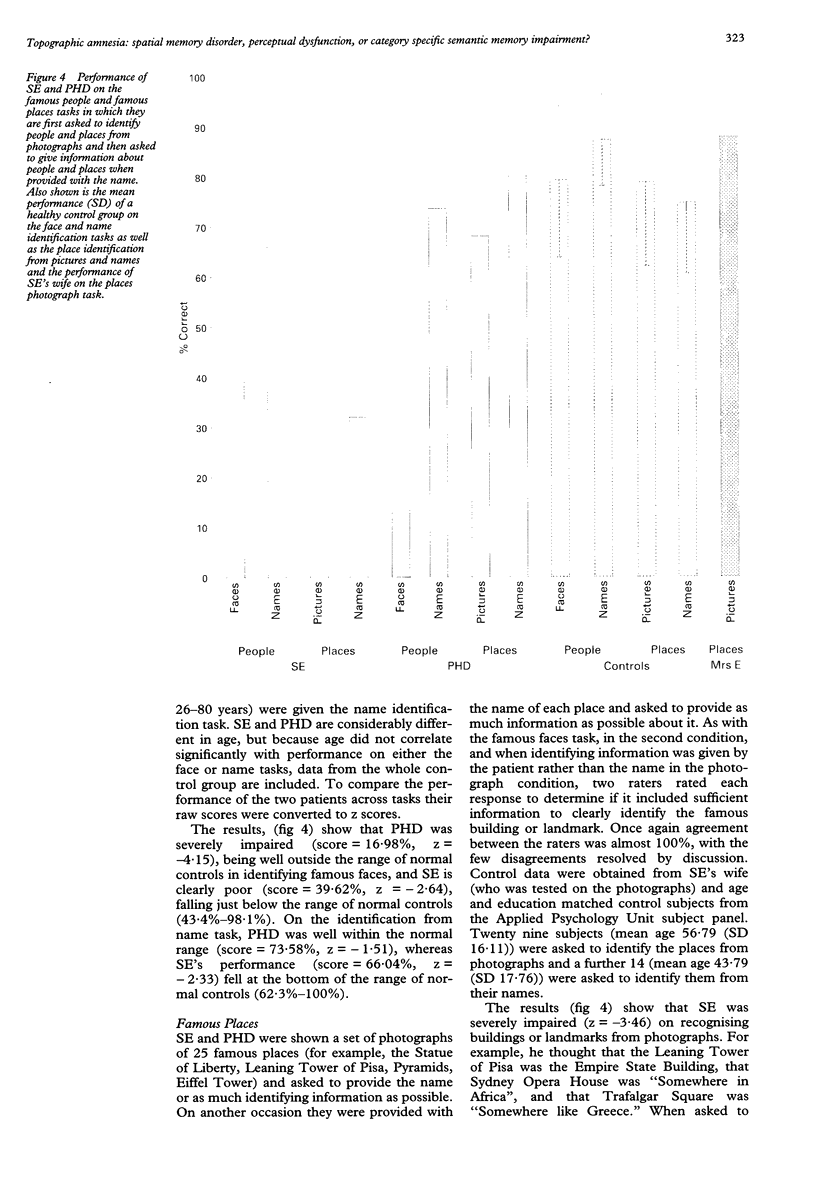


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assal G., Favre C., Anderes J. P. Non-reconnaissance d'animaux familiers chez un paysan. Zoo-agnosie ou prosopagnosie pour les animaux. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1984;140(10):580–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruyer R., Laterre C., Seron X., Feyereisen P., Strypstein E., Pierrard E., Rectem D. A case of prosopagnosia with some preserved covert remembrance of familiar faces. Brain Cogn. 1983 Jul;2(3):257–284. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(83)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio A. R., Tranel D., Damasio H. Face agnosia and the neural substrates of memory. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:89–109. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Haan E. H., Young A. W., Newcombe F. Covert and overt recognition in prosopagnosia. Brain. 1991 Dec;114(Pt 6):2575–2591. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.6.2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Haan E. H., Young A., Newcombe F. Faces interfere with name classification in a prosopagnosic patient. Cortex. 1987 Jun;23(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(87)80041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Renzi E., Faglioni P., Villa P. Topographical amnesia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 May;40(5):498–505. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.5.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis A. W., Young A. W., Critchley E. M. Loss of memory for people following temporal lobe damage. Brain. 1989 Dec;112(Pt 6):1469–1483. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.6.1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. J., Heggs A. J., Antoun N., Hodges J. R. Progressive prosopagnosia associated with selective right temporal lobe atrophy. A new syndrome? Brain. 1995 Feb;118(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Oxbury S. M. Persistent memory impairment following transient global amnesia. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1990 Dec;12(6):904–920. doi: 10.1080/01688639008401030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Patterson K., Oxbury S., Funnell E. Semantic dementia. Progressive fluent aphasia with temporal lobe atrophy. Brain. 1992 Dec;115(Pt 6):1783–1806. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.6.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. R., Salmon D. P., Butters N. Semantic memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease: failure of access or degraded knowledge? Neuropsychologia. 1992 Apr;30(4):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(92)90104-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laws K. R., Evans J. J., Hodges J. R., McCarthy R. A. Naming without knowing and appearance without associations: evidence for constructive processes in semantic memory? Memory. 1995 Sep-Dec;3(3-4):409–433. doi: 10.1080/09658219508253159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy R. A., Warrington E. K. Disorders of semantic memory. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994 Oct 29;346(1315):89–96. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1994.0132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe J., Speakman A. Single unit activity in the rat hippocampus during a spatial memory task. Exp Brain Res. 1987;68(1):1–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00255230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALLIS C. A. Impaired identification of faces and places with agnosia for colours; report of a case due to cerebral embolism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1955 Aug;18(3):218–224. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.18.3.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley A. M., Warrington E. K. Selective impairment of topographical memory: a single case study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Jun;41(6):575–578. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.6.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]