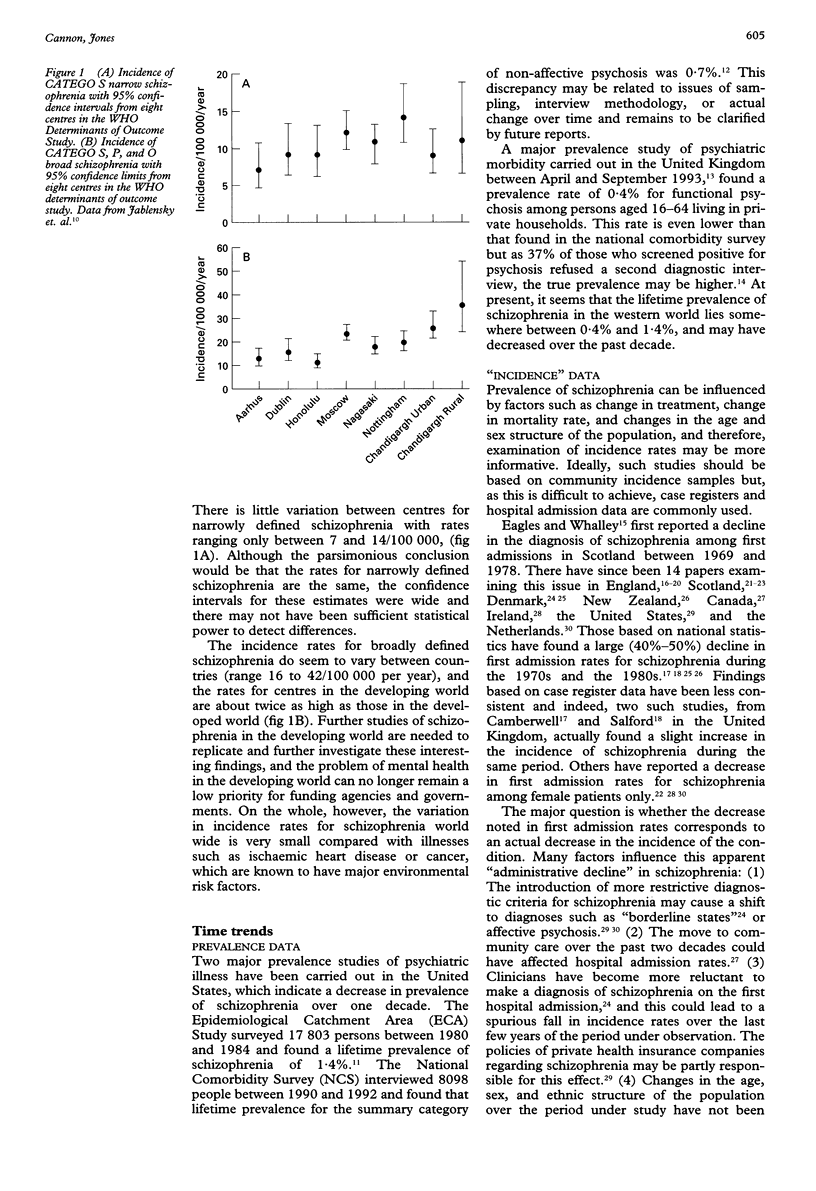
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams W., Kendell R. E., Hare E. H., Munk-Jørgensen P. Epidemiological evidence that maternal influenza contributes to the aetiology of schizophrenia. An analysis of Scottish, English, and Danish data. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Oct;163:522–534. doi: 10.1192/bjp.163.4.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen N. C. Changing concepts of schizophrenia and the ahistorical fallacy. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Oct;151(10):1405–1407. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.10.1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andréasson S., Allebeck P., Engström A., Rydberg U. Cannabis and schizophrenia. A longitudinal study of Swedish conscripts. Lancet. 1987 Dec 26;2(8574):1483–1486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92620-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aro S., Aro H., Keskimäki I. Socio-economic mobility among patients with schizophrenia or major affective disorder. A 17-year retrospective follow-up. Br J Psychiatry. 1995 Jun;166(6):759–767. doi: 10.1192/bjp.166.6.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asarnow R. F., Asarnow J. R. Childhood-onset schizophrenia: editors' introduction. Schizophr Bull. 1994;20(4):591–597. doi: 10.1093/schbul/20.4.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamrah J. S., Freeman H. L., Goldberg D. P. Epidemiology of schizophrenia in Salford, 1974-84. Changes in an urban community over ten years. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;159:802–810. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.6.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury T. N., Miller G. A. Season of birth in schizophrenia: a review of evidence, methodology, and etiology. Psychol Bull. 1985 Nov;98(3):569–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. W., Birley J. L., Wing J. K. Influence of family life on the course of schizophrenic disorders: a replication. Br J Psychiatry. 1972 Sep;121(562):241–258. doi: 10.1192/bjp.121.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buka S. L., Tsuang M. T., Lipsitt L. P. Pregnancy/delivery complications and psychiatric diagnosis. A prospective study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Feb;50(2):151–156. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820140077009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bök J. A., Wetterberg L., Modrzewska K. Schizophrenia in a North Swedish geographical isolate, 1900--1977. Epidemiology, genetics and biochemistry. Clin Genet. 1978 Dec;14(6):373–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1978.tb02105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon M., Cotter D., Coffey V. P., Sham P. C., Takei N., Larkin C., Murray R. M., O'Callaghan E. Prenatal exposure to the 1957 influenza epidemic and adult schizophrenia: a follow-up study. Br J Psychiatry. 1996 Mar;168(3):368–371. doi: 10.1192/bjp.168.3.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon T. D., Mednick S. A., Parnas J., Schulsinger F., Praestholm J., Vestergaard A. Developmental brain abnormalities in the offspring of schizophrenic mothers. I. Contributions of genetic and perinatal factors. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Jul;50(7):551–564. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820190053006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon T. D., Mednick S. A., Parnas J., Schulsinger F., Praestholm J., Vestergaard A. Developmental brain abnormalities in the offspring of schizophrenic mothers. II. Structural brain characteristics of schizophrenia and schizotypal personality disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Dec;51(12):955–962. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950120027006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon T. D., Mednick S. A. The schizophrenia high-risk project in Copenhagen: three decades of progress. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1993;370:33–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1993.tb05359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter W. T., Jr, Buchanan R. W. Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Mar 10;330(10):681–690. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199403103301006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle D. J., Murray R. M. The epidemiology of late-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1993;19(4):691–700. doi: 10.1093/schbul/19.4.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle D., Wessely S., Der G., Murray R. M. The incidence of operationally defined schizophrenia in Camberwell, 1965-84. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;159:790–794. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.6.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua S. E., McKenna P. J. Schizophrenia--a brain disease? A critical review of structural and functional cerebral abnormality in the disorder. Br J Psychiatry. 1995 May;166(5):563–582. doi: 10.1192/bjp.166.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J., Done D. J. Prenatal exposure to influenza does not cause schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Sep;161:390–393. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J. The continuum of psychosis and its genetic origins. The sixty-fifth Maudsley lecture. Br J Psychiatry. 1990 Jun;156:788–797. doi: 10.1192/bjp.156.6.788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow T. J. The search for the psychosis gene. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 May;158:611–614. doi: 10.1192/bjp.158.5.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. L., Kahn R. S., Ko G., Davidson M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: a review and reconceptualization. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 Nov;148(11):1474–1486. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.11.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der G., Gupta S., Murray R. M. Is schizophrenia disappearing? Lancet. 1990 Mar 3;335(8688):513–516. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90745-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Done D. J., Crow T. J., Johnstone E. C., Sacker A. Childhood antecedents of schizophrenia and affective illness: social adjustment at ages 7 and 11. BMJ. 1994 Sep 17;309(6956):699–703. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6956.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Done D. J., Johnstone E. C., Frith C. D., Golding J., Shepherd P. M., Crow T. J. Complications of pregnancy and delivery in relation to psychosis in adult life: data from the British perinatal mortality survey sample. BMJ. 1991 Jun 29;302(6792):1576–1580. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6792.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagles J. M., Hunter D., McCance C. Decline in the diagnosis of schizophrenia among first contacts with psychiatric services in north-east Scotland, 1969-1984. Br J Psychiatry. 1988 Jun;152:793–798. doi: 10.1192/bjp.152.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagles J. M. The relationship between schizophrenia and immigration. Are there alternatives to psychosocial hypotheses? Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;159:783–789. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagles J. M., Whalley L. J. Decline in the diagnosis of schizophrenia among first admissions to Scottish mental hospitals from 1969-78. Br J Psychiatry. 1985 Feb;146:151–154. doi: 10.1192/bjp.146.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. W. Update on the epidemiology of schizophrenia. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:320–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. W. Update on the epidemiology of schizophrenia. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:320–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlenmeyer-Kimling L., Cornblatt B. The New York High-Risk Project: a followup report. Schizophr Bull. 1987;13(3):451–461. doi: 10.1093/schbul/13.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish B., Marcus J., Hans S. L., Auerbach J. G., Perdue S. Infants at risk for schizophrenia: sequelae of a genetic neurointegrative defect. A review and replication analysis of pandysmaturation in the Jerusalem Infant Development Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Mar;49(3):221–235. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820030053007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish B. Neurobiologic antecedents of schizophrenia in children. Evidence for an inherited, congenital neurointegrative defect. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1977 Nov;34(11):1297–1313. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1977.01770230039002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. R., Black R. J., Whalley L. J., Eagles J. M. Persistence of the decline in the diagnosis of schizophrenia among first admissions to Scottish hospitals from 1969 to 1988. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;163:620–626. doi: 10.1192/bjp.163.5.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J. R., Lawrie S. M. Obstetric complications and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 1995 Dec;167(6):786–793. doi: 10.1192/bjp.167.6.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes J., Mercer G., Frith C. D., MacMillan F., Owens D. G., Johnstone E. C. Prediction of outcome following a first episode of schizophrenia. A follow-up study of Northwick Park first episode study subjects. Br J Psychiatry. 1994 Nov;165(5):664–668. doi: 10.1192/bjp.165.5.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman I. I., Bertelsen A. Confirming unexpressed genotypes for schizophrenia. Risks in the offspring of Fischer's Danish identical and fraternal discordant twins. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Oct;46(10):867–872. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810100009002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison G., Cooper J. E., Gancarczyk R. Changes in the administrative incidence of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;159:811–816. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.6.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison G., Owens D., Holton A., Neilson D., Boot D. A prospective study of severe mental disorder in Afro-Caribbean patients. Psychol Med. 1988 Aug;18(3):643–657. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700008321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegarty J. D., Baldessarini R. J., Tohen M., Waternaux C., Oepen G. One hundred years of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of the outcome literature. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Oct;151(10):1409–1416. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.10.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickling F. W. Psychiatric hospital admission rates in Jamaica, 1971 and 1988. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;159:817–821. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.6.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister J. M., Laing P., Mednick S. A. Rhesus incompatibility as a risk factor for schizophrenia in male adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1996 Jan;53(1):19–24. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1996.01830010021004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen M. O., Niskanen P. Prenatal loss of father and psychiatric disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1978 Apr;35(4):429–431. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1978.01770280039004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häfner H., Maurer K., Löffler W., Riecher-Rössler A. The influence of age and sex on the onset and early course of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Jan;162:80–86. doi: 10.1192/bjp.162.1.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablensky A. Schizophrenia: recent epidemiologic issues. Epidemiol Rev. 1995;17(1):10–20. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone E. C., Crow T. J., Johnson A. L., MacMillan J. F. The Northwick Park Study of first episodes of schizophrenia. I. Presentation of the illness and problems relating to admission. Br J Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;148:115–120. doi: 10.1192/bjp.148.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Bebbington P., Foerster A., Lewis S. W., Murray R. M., Russell A., Sham P. C., Toone B. K., Wilkins S. Premorbid social underachievement in schizophrenia. Results from the Camberwell Collaborative Psychosis Study. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Jan;162:65–71. doi: 10.1192/bjp.162.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Harvey I., Lewis S. W., Toone B. K., Van Os J., Williams M., Murray R. M. Cerebral ventricle dimensions as risk factors for schizophrenia and affective psychosis: an epidemiological approach to analysis. Psychol Med. 1994 Nov;24(4):995–1011. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700029081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P., Murray R. M. The genetics of schizophrenia is the genetics of neurodevelopment. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 May;158:615–623. doi: 10.1192/bjp.158.5.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P., Rodgers B., Murray R., Marmot M. Child development risk factors for adult schizophrenia in the British 1946 birth cohort. Lancet. 1994 Nov 19;344(8934):1398–1402. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce P. R. Changing trends in first admissions and readmissions for mania and schizophrenia in New Zealand, 1974 to 1984. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 1987 Mar;21(1):82–86. doi: 10.3109/00048678709160903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendell R. E., Malcolm D. E., Adams W. The problem of detecting changes in the incidence of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Feb;162:212–218. doi: 10.1192/bjp.162.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S. Genetic epidemiology in psychiatry. Taking both genes and environment seriously. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 Nov;52(11):895–899. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950230009003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., Gruenberg A. M., Kinney D. K. Independent diagnoses of adoptees and relatives as defined by DSM-III in the provincial and national samples of the Danish Adoption Study of Schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Jun;51(6):456–468. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950060020002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., Kessler R. C., Walters E. E., MacLean C., Neale M. C., Heath A. C., Eaves L. J. Stressful life events, genetic liability, and onset of an episode of major depression in women. Am J Psychiatry. 1995 Jun;152(6):833–842. doi: 10.1176/ajp.152.6.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., McGuire M., Gruenberg A. M., O'Hare A., Spellman M., Walsh D. The Roscommon Family Study. I. Methods, diagnosis of probands, and risk of schizophrenia in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Jul;50(7):527–540. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820190029004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., McGuire M., Gruenberg A. M., O'Hare A., Spellman M., Walsh D. The Roscommon Family Study. III. Schizophrenia-related personality disorders in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Oct;50(10):781–788. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820220033004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., McGuire M., Gruenberg A. M., O'Hare A., Spellman M., Walsh D. The Roscommon Family Study. IV. Affective illness, anxiety disorders, and alcoholism in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Dec;50(12):952–960. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820240036005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., McGuire M., Gruenberg A. M., Spellman M., O'Hare A., Walsh D. The Roscommon Family Study. II. The risk of nonschizophrenic nonaffective psychoses in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Aug;50(8):645–652. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820200059006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendler K. S., McGuire M., Gruenberg A. M., Walsh D. Schizotypal symptoms and signs in the Roscommon Family Study. Their factor structure and familial relationship with psychotic and affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995 Apr;52(4):296–303. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1995.03950160046009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. C., McGonagle K. A., Zhao S., Nelson C. B., Hughes M., Eshleman S., Wittchen H. U., Kendler K. S. Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Jan;51(1):8–19. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950010008002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Wender P. H., Jacobsen B., Ingraham L. J., Jansson L., Faber B., Kinney D. K. Mental illness in the biological and adoptive relatives of schizophrenic adoptees. Replication of the Copenhagen Study in the rest of Denmark. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Jun;51(6):442–455. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950060006001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury M. J., Beaty T. H., Newill C. A., Bryant S., Cohen B. H. Genetic-environmental interactions in chronic airways obstruction. Int J Epidemiol. 1986 Mar;15(1):65–72. doi: 10.1093/ije/15.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M., Coker E., Leavey G., Hoare A., Johnson-Sabine E. Incidence of psychotic illness in London: comparison of ethnic groups. BMJ. 1994 Oct 29;309(6962):1115–1119. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6962.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff J., Kuipers L., Berkowitz R., Vaughn C., Sturgeon D. Life events, relatives' expressed emotion and maintenance neuroleptics in schizophrenic relapse. Psychol Med. 1983 Nov;13(4):799–806. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700051503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff J., Sartorius N., Jablensky A., Korten A., Ernberg G. The International Pilot Study of Schizophrenia: five-year follow-up findings. Psychol Med. 1992 Feb;22(1):131–145. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700032797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff J., Wig N. N., Bedi H., Menon D. K., Kuipers L., Korten A., Ernberg G., Day R., Sartorius N., Jablensky A. Relatives' expressed emotion and the course of schizophrenia in Chandigarh. A two-year follow-up of a first-contact sample. Br J Psychiatry. 1990 Mar;156:351–356. doi: 10.1192/bjp.156.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewine R. R. Sex differences in age of symptom onset and first hospitalization in schizophrenia. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1980 Apr;50(2):316–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1980.tb03293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G., David A., Andréasson S., Allebeck P. Schizophrenia and city life. Lancet. 1992 Jul 18;340(8812):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93213-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G., Pelosi A. J. The case-control study in psychiatry. Br J Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;157:197–207. doi: 10.1192/bjp.157.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linszen D. H., Dingemans P. M., Lenior M. E. Cannabis abuse and the course of recent-onset schizophrenic disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Apr;51(4):273–279. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950040017002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebel A. D., Lieberman J. A., Alvir J. M., Mayerhoff D. I., Geisler S. H., Szymanski S. R. Duration of psychosis and outcome in first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1992 Sep;149(9):1183–1188. doi: 10.1176/ajp.149.9.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loranger A. W. Sex difference in age at onset of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;41(2):157–161. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790130053007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier W., Lichtermann D., Minges J., Hallmayer J., Heun R., Benkert O., Levinson D. F. Continuity and discontinuity of affective disorders and schizophrenia. Results of a controlled family study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;50(11):871–883. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820230041004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus J., Hans S. L., Auerbach J. G., Auerbach A. G. Children at risk for schizophrenia: the Jerusalem Infant Development Study. II. Neurobehavioral deficits at school age. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Oct;50(10):797–809. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820220053006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P., Wilkinson G. The prevalence of psychiatric morbidity. OPCS survey of psychiatric morbidity in Great Britain. Br J Psychiatry. 1996 Jan;168(1):1–3. doi: 10.1192/bjp.168.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGovern D., Cope R. V. First psychiatric admission rates of first and second generation Afro Caribbeans. Soc Psychiatry. 1987;22(3):139–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00583848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuffin P., Owen M. J., Farmer A. E. Genetic basis of schizophrenia. Lancet. 1995 Sep 9;346(8976):678–682. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie K., van Os J., Fahy T., Jones P., Harvey I., Toone B., Murray R. Psychosis with good prognosis in Afro-Caribbean people now living in the United Kingdom. BMJ. 1995 Nov 18;311(7016):1325–1328. doi: 10.1136/bmj.311.7016.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky A. F., Silberman E. K., Latz A., Nagler S. Adult outcomes of high-risk children: differential effects of town and kibbutz rearing. Schizophr Bull. 1985;11(1):150–154. doi: 10.1093/schbul/11.1.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen P. B., Juel K. Mortality and causes of death in first admitted schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Aug;163:183–189. doi: 10.1192/bjp.163.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk-Jørgensen P. Decreasing first-admission rates of schizophrenia among males in Denmark from 1970 to 1984. Changing diagnostic patterns? Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1986 Jun;73(6):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1986.tb02738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk-Jørgensen P., Mortensen P. B. Incidence and other aspects of the epidemiology of schizophrenia in Denmark, 1971-87. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Oct;161:489–495. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.4.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. C., Bland R. C. Mortality in a cohort of patients with schizophrenia: a record linkage study. Can J Psychiatry. 1991 May;36(4):239–245. doi: 10.1177/070674379103600401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicole L., Lesage A., Lalonde P. Lower incidence and increased male:female ratio in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Oct;161:556–557. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.4.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan E., Sham P., Takei N., Glover G., Murray R. M. Schizophrenia after prenatal exposure to 1957 A2 influenza epidemic. Lancet. 1991 May 25;337(8752):1248–1250. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92919-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldehinkel A. J., Giel R. Time trends in the care-based incidence of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1995 Dec;167(6):777–782. doi: 10.1192/bjp.167.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas J., Cannon T. D., Jacobsen B., Schulsinger H., Schulsinger F., Mednick S. A. Lifetime DSM-III-R diagnostic outcomes in the offspring of schizophrenic mothers. Results from the Copenhagen High-Risk Study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993 Sep;50(9):707–714. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1993.01820210041005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plomin R., Owen M. J., McGuffin P. The genetic basis of complex human behaviors. Science. 1994 Jun 17;264(5166):1733–1739. doi: 10.1126/science.8209254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum F. Prospects for research on schizophrenia. 3. Neurophysiology. Neuropathological findings. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1972 Nov;10(4):384–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram R., Bromet E. J., Eaton W. W., Pato C., Schwartz J. E. The natural course of schizophrenia: a review of first-admission studies. Schizophr Bull. 1992;18(2):185–207. doi: 10.1093/schbul/18.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. Suicide in chronic schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1982 Aug;141:171–177. doi: 10.1192/bjp.141.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten J. P., Sijben N. First admission rates for schizophrenia in immigrants to The Netherlands. The Dutch National Register. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1994 Apr;29(2):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00805625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Brynjolfsson J., Petursson H., Potter M., Dudleston K., Barraclough B., Wasmuth J., Dobbs M., Gurling H. Localization of a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 5. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):164–167. doi: 10.1038/336164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll A. L., Tohen M., Baldessarini R. J., Goodwin D. C., Stein S., Katz S., Geenens D., Swinson R. P., Goethe J. W., McGlashan T. Shifts in diagnostic frequencies of schizophrenia and major affective disorders at six North American psychiatric hospitals, 1972-1988. Am J Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;150(11):1668–1673. doi: 10.1176/ajp.150.11.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., MacLean C. J., O'Neill F. A., Burke J., Murphy B., Duke F., Shinkwin R., Webb B. T., Zhang J., Walsh D. A potential vulnerability locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p24-22: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):287–293. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman P. A., Craufurd D. Schizophrenia in the Afro-Caribbean community. Br J Psychiatry. 1994 Apr;164(4):474–480. doi: 10.1192/bjp.164.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susser E. S., Lin S. P. Schizophrenia after prenatal exposure to the Dutch Hunger Winter of 1944-1945. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Dec;49(12):983–988. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820120071010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susser E., Neugebauer R., Hoek H. W., Brown A. S., Lin S., Labovitz D., Gorman J. M. Schizophrenia after prenatal famine. Further evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1996 Jan;53(1):25–31. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1996.01830010027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. S., Stone K., Osborn M., Thomas P. F., Fisher M. Psychiatric morbidity and compulsory admission among UK-born Europeans, Afro-Caribbeans and Asians in central Manchester. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Jul;163:91–99. doi: 10.1192/bjp.163.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien A. Y., Eaton W. W. Psychopathologic precursors and sociodemographic risk factors for the schizophrenia syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Jan;49(1):37–46. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820010037005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tienari P. Interaction between genetic vulnerability and family environment: the Finnish adoptive family study of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1991 Nov;84(5):460–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1991.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohen M., Stoll A. L., Strakowski S. M., Faedda G. L., Mayer P. V., Goodwin D. C., Kolbrener M. L., Madigan A. M. The McLean First-Episode Psychosis Project: six-month recovery and recurrence outcome. Schizophr Bull. 1992;18(2):273–282. doi: 10.1093/schbul/18.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrey E. F. Prevalence studies in schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1987 May;150:598–608. doi: 10.1192/bjp.150.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallada H. P., Gill M., Sham P., Lim L. C., Nanko S., Asherson P., Murray R. M., McGuffin P., Owen M., Collier D. Linkage studies on chromosome 22 in familial schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet. 1995 Apr 24;60(2):139–146. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van OS J., Castle D. J., Takei N., Der G., Murray R. M. Psychotic illness in ethnic minorities: clarification from the 1991 census. Psychol Med. 1996 Jan;26(1):203–208. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700033845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddington J. L., Youssef H. A. Evidence for a gender-specific decline in the rate of schizophrenia in rural Ireland over a 50-year period. Br J Psychiatry. 1994 Feb;164(2):171–176. doi: 10.1192/bjp.164.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E., Lewine R. J. Prediction of adult-onset schizophrenia from childhood home movies of the patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1990 Aug;147(8):1052–1056. doi: 10.1176/ajp.147.8.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner R. Time trends in schizophrenia: changes in obstetric risk factors with industrialization. Schizophr Bull. 1995;21(3):483–500. doi: 10.1093/schbul/21.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger D. R. From neuropathology to neurodevelopment. Lancet. 1995 Aug 26;346(8974):552–557. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessely S., Castle D., Der G., Murray R. Schizophrenia and Afro-Caribbeans. A case-control study. Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;159:795–801. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.6.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. J. Neuroleptics and the natural course of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1991;17(2):325–351. doi: 10.1093/schbul/17.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Os J., Fahy T. A., Bebbington P., Jones P., Wilkins S., Sham P., Russell A., Gilvarry K., Lewis S., Toone B. The influence of life events on the subsequent course of psychotic illness. A prospective follow-up of the Camberwell Collaborative Psychosis Study. Psychol Med. 1994 May;24(2):503–513. doi: 10.1017/s003329170002746x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Os J., Howard R., Takei N., Murray R. Increasing age is a risk factor for psychosis in the elderly. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 1995 Jul;30(4):161–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00790654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


