Abstract
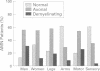
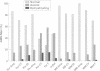
OBJECTIVE--Adrenomyeloneuropathy (AMN) is an X linked metabolic disorder presenting with progressive spastic paraparesis in the third to fifth decade of life. Although peripheral neuropathy is also present in most patients, prominent pyramidal signs may make its clinical recognition difficult. The objective was to characterise the peripheral neuropathy in patients with AMN by nerve conduction studies. METHODS--Nerve conduction studies were performed in 99 men known to have AMN and in 38 heterozygous women, all of whom had neurological disabilities. RESULTS--Of the 13 variables obtained, at least one was abnormal in 82% of patients. The abnormalities were more common in men than in women (87% v 67%); in legs than in arms (77% v 38%); in motor than in sensory conduction (80% v 39%); and in latency (distal and F wave) and velocity compared with amplitude (80% v 29%). Twenty six patients had at least one nerve variable value in the demyelinating range. Four variables (sural velocity, peroneal amplitude, peroneal velocity, and peroneal F wave) were correlated with the expanded disability status scale; five variables (peroneal velocity, tibial H reflex, median distal latency, median conduction velocity, and median F wave latency) were correlated with serum very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs); and two variables (sural amplitude and peroneal distal latency) were more likely to be abnormal in patients with normal adrenal function than in patients with Addison's disease. CONCLUSIONS--Nerve conduction studies in patients with AMN are often abnormal and suggest a mixture of axonal loss and multifocal demyelination. Their correlation with disability status and serum VLCFAs suggests that measures from nerve conduction studies may be useful in evaluating future treatments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askanas V., McLaughlin J., Engel W. K., Adornato B. T. Abnormalities in cultured muscle and peripheral nerve of a patient with adrenomyeloneuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):588–590. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubourg P., Adamsbaum C., Lavallard-Rousseau M. C., Lemaitre A., Boureau F., Mayer M., Kalifa G. Brain MRI and electrophysiologic abnormalities in preclinical and clinical adrenomyeloneuropathy. Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1):85–91. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubourg P., Adamsbaum C., Lavallard-Rousseau M. C., Rocchiccioli F., Cartier N., Jambaqué I., Jakobezak C., Lemaitre A., Boureau F., Wolf C. A two-year trial of oleic and erucic acids ("Lorenzo's oil") as treatment for adrenomyeloneuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 9;329(11):745–752. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309093291101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkovic S. F., Zajac J. D., Warburton D. J., Merory J. R., Fellenberg A. J., Poulos A., Pollard A. C. Adrenomyeloneuropathy--clinical and biochemical diagnosis. Aust N Z J Med. 1983 Dec;13(6):594–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1983.tb02611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. J., Asbury A. K. Diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 1984 Jan;15(1):2–12. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Sluga E., Heiss W. D. Spastic paraplegia associated with Addison's disease: adult variant of adreno-leukodystrophy. J Neurol. 1976;213(3):237–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00312873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. E., Snyder R. D., Orth D. N., Nicholson W. E., Kornfeld M., Seelinger D. F. Adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy associated with partial adrenal insufficiency in three generations of a kindred. Am J Med. 1979 Feb;66(2):342–347. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90562-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elrington G. M., Bateman D. E., Jeffrey M. J., Lawton N. F. Adrenoleukodystrophy: heterogeneity in two brothers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Mar;52(3):310–313. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.3.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Goren E., Schaumburg H., Engel W. K., Loriaux L. Adrenomyeloneuropathy: a probable variant of adrenoleukodystrophy. I. Clinical and endocrinologic aspects. Neurology. 1977 Dec;27(12):1107–1113. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.12.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho J. K., Moser H., Kishimoto Y., Hamilton J. A. Interactions of a very long chain fatty acid with model membranes and serum albumin. Implications for the pathogenesis of adrenoleukodystrophy. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1455–1463. doi: 10.1172/JCI118182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. W., Tusa R. J., Shankroff J., Heller J., Moser H. W. Visual evoked potentials in adrenoleukodystrophy: a trial with glycerol trioleate and Lorenzo oil. Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):169–174. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knazek R. A., Rizzo W. B., Schulman J. D., Dave J. R. Membrane microviscosity is increased in the erythrocytes of patients with adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):245–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI110963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. J., Lowenthal A., Ceuterick C., Gacoms H. Adrenomyeloneuropathy. A report on two families. J Neurol. 1982;226(4):221–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00313395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W., Bergin A., Cornblath D. Peroxisomal disorders. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;69(7):463–474. doi: 10.1139/o91-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W., Moser A. B., Naidu S., Bergin A. Clinical aspects of adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy. Dev Neurosci. 1991;13(4-5):254–261. doi: 10.1159/000112170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W., Moser A. B., Smith K. D., Bergin A., Borel J., Shankroff J., Stine O. C., Merette C., Ott J., Krivit W. Adrenoleukodystrophy: phenotypic variability and implications for therapy. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1992;15(4):645–664. doi: 10.1007/BF01799621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W., Naidu S., Kumar A. J., Rosenbaum A. E. The adrenoleukodystrophies. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1987;3(1):29–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noetzel M. J., Landau W. M., Moser H. W. Adrenoleukodystrophy carrier state presenting as a chronic nonprogressive spinal cord disorder. Arch Neurol. 1987 May;44(5):566–567. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520170092031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. M., Liu Y., Moser A. B., Moser H. W. The inflammatory myelinopathy of adreno-leukodystrophy: cells, effector molecules, and pathogenetic implications. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Nov;51(6):630–643. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199211000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Research criteria for diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Report from an Ad Hoc Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Neurology. 1991 May;41(5):617–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Koyama A., Koike R., Ohno T., Atsumi T., Miyatake T. Adrenomyeloneuropathy: report of a family and electron microscopical findings in peripheral nerve. J Neurol. 1985;232(2):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00313904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobimatsu S., Fukui R., Kato M., Kobayashi T., Kuroiwa Y. Multimodality evoked potentials in patients and carriers with adrenoleukodystrophy and adrenomyeloneuropathy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985 Jan;62(1):18–24. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(85)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercruyssen A., Martin J. J., Mercelis R. Neurophysiological studies in adrenomyeloneuropathy. A report on five cases. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov;56(2-3):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb R. W., Linehan W. M., Knazek R. A. Effects of long-chain, saturated fatty acids on membrane microviscosity and adrenocorticotropin responsiveness of human adrenocortical cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):185–188. doi: 10.1172/JCI113292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Geel B. M., Koelman J. H., Barth P. G., Ongerboer de Visser B. W. Peripheral nerve abnormalities in adrenomyeloneuropathy: a clinical and electrodiagnostic study. Neurology. 1996 Jan;46(1):112–118. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.1.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]