Abstract
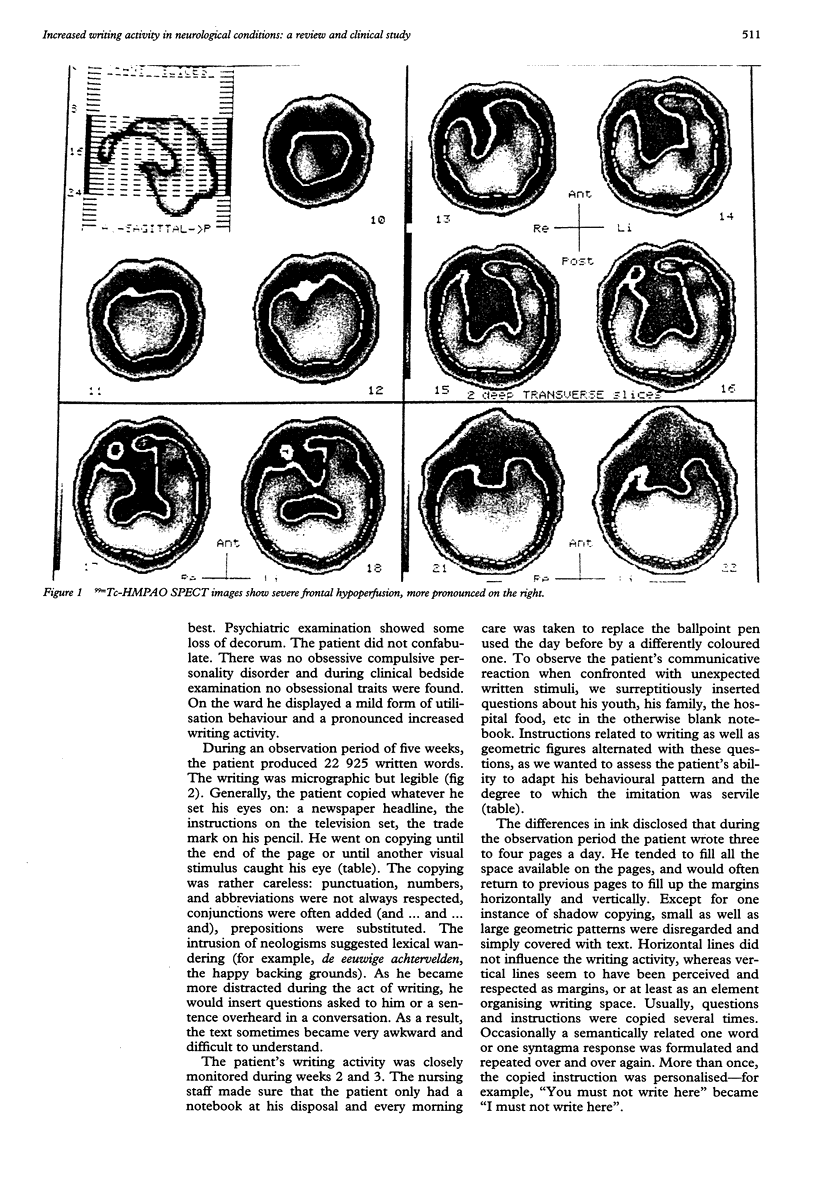
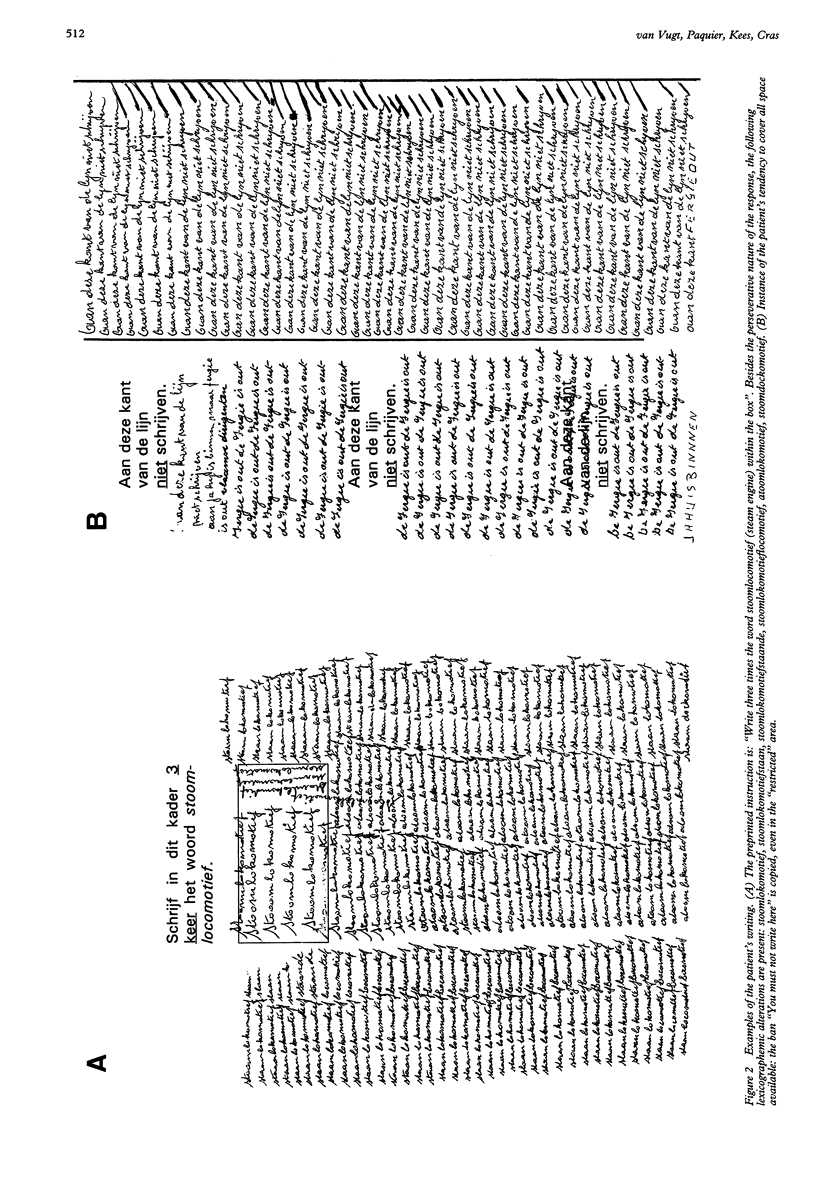
Increased writing activity in a 70 year old, right handed man presenting with a history of alcohol misuse and maturity onset diabetes is reported. Brain CT disclosed corticosubcortical atrophy and 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT disclosed severe bilateral frontal hypoperfusion more prominent on the right. The patient's neuropsychological symptomatology consisted of severe (verbal) aspontaneity, intermittent utilisation behaviour, and pronounced increased writing activity, which mainly consisted of a perseverative, micrographic written reproduction of visually or verbally perceived language fragments. Several neurological causes of increased writing activity and the equivocal terminology met in the medical literature are reviewed. A distinction between hypergraphia and automatic writing behaviour is proposed. It is concluded that our patient's increased writing activity may be characterised as automatic writing behaviour.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cambier J., Masson C., Benammou S., Robine B. La graphomanie. Activité graphique compulsive Manifestation d'un gliome fronto-calleux. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1988;144(3):158–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisoni G. B., Scuratti A., Bianchetti A., Trabucchi M. Hypergraphia and brain damage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 May;56(5):576–577. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.5.576-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil R., Neau J. P., Aubert I., Fabre C., Agbo C., Tantot A. M. Graphomimie anosognosique: variété particulière d'hypergraphie au cours d'un infarctus sylvien droit. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1995 Mar;151(3):198–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann B. P., Whitman S., Wyler A. R., Richey E. T., Dell J. The neurological, psychosocial and demographic correlates of hypergraphia in patients with epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Feb;51(2):203–208. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura T., Yamadori A., Tsuburaya K. Hypergraphia associated with a brain tumour of the right cerebral hemisphere. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Jan;55(1):25–27. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancar J., Kettle L. B. Hypergraphia and mental handicap. J Ment Defic Res. 1984 Jun;28(Pt 2):151–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1984.tb01006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph A. B. A hypergraphic syndrome of automatic writing, affective disorder, and temporal lobe epilepsy in two patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 1986 May;47(5):255–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhermitte F. 'Utilization behaviour' and its relation to lesions of the frontal lobes. Brain. 1983 Jun;106(Pt 2):237–255. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A. M. Mental illness and creative activity in female writers. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Nov;151(11):1650–1656. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.11.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Fukai M., Yamadori A., Hidari M., Asaba H., Sakai T. A clinical study of hypergraphia in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 May;56(5):556–559. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.5.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Motomura N., Asaba H., Sakai T., Fukai M., Mori E., Yamadori A. Hypergraphia in temporal lobe epilepsy--compared with stroke of the right cerebral hemisphere. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol. 1989 Sep;43(3):524–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Robertson M. M., Trimble M. R. The lateralising significance of hypergraphia in temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Feb;45(2):131–138. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamadori A., Mori E., Tabuchi M., Kudo Y., Mitani Y. Hypergraphia: a right hemisphere syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Oct;49(10):1160–1164. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.10.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]