Abstract
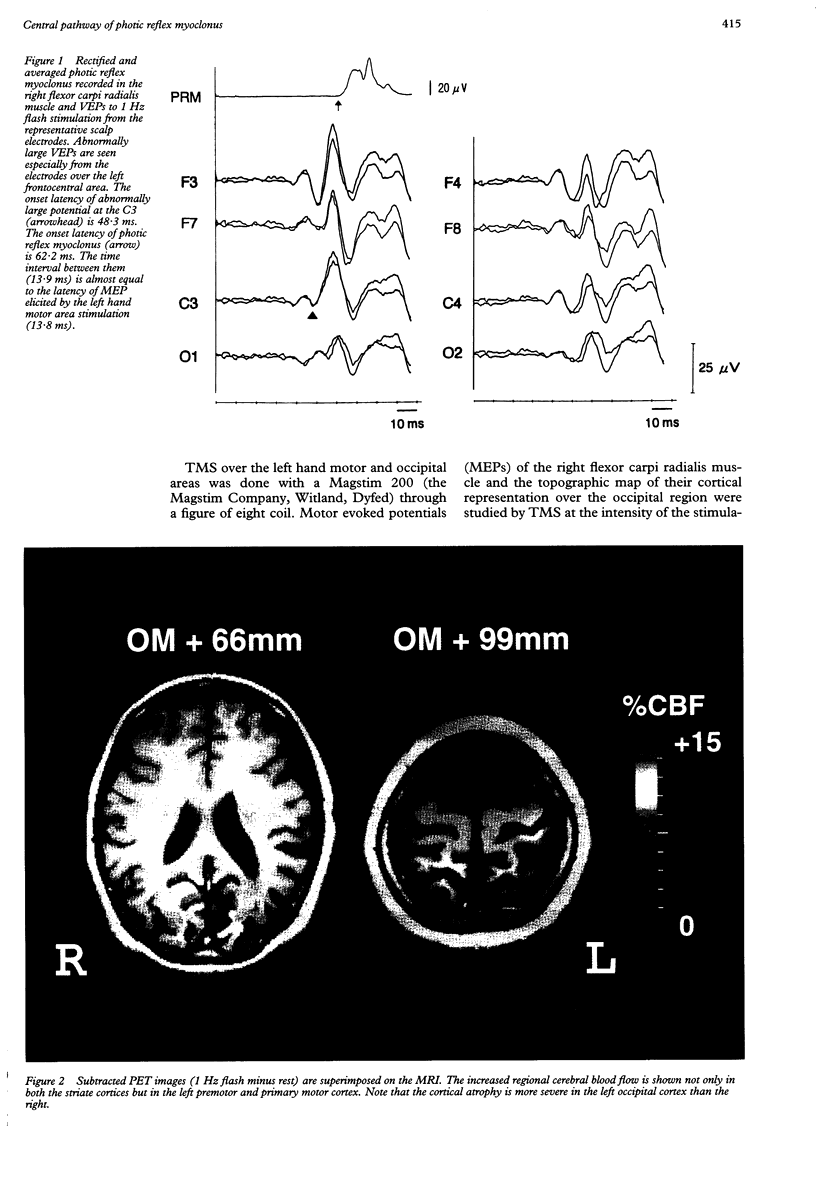
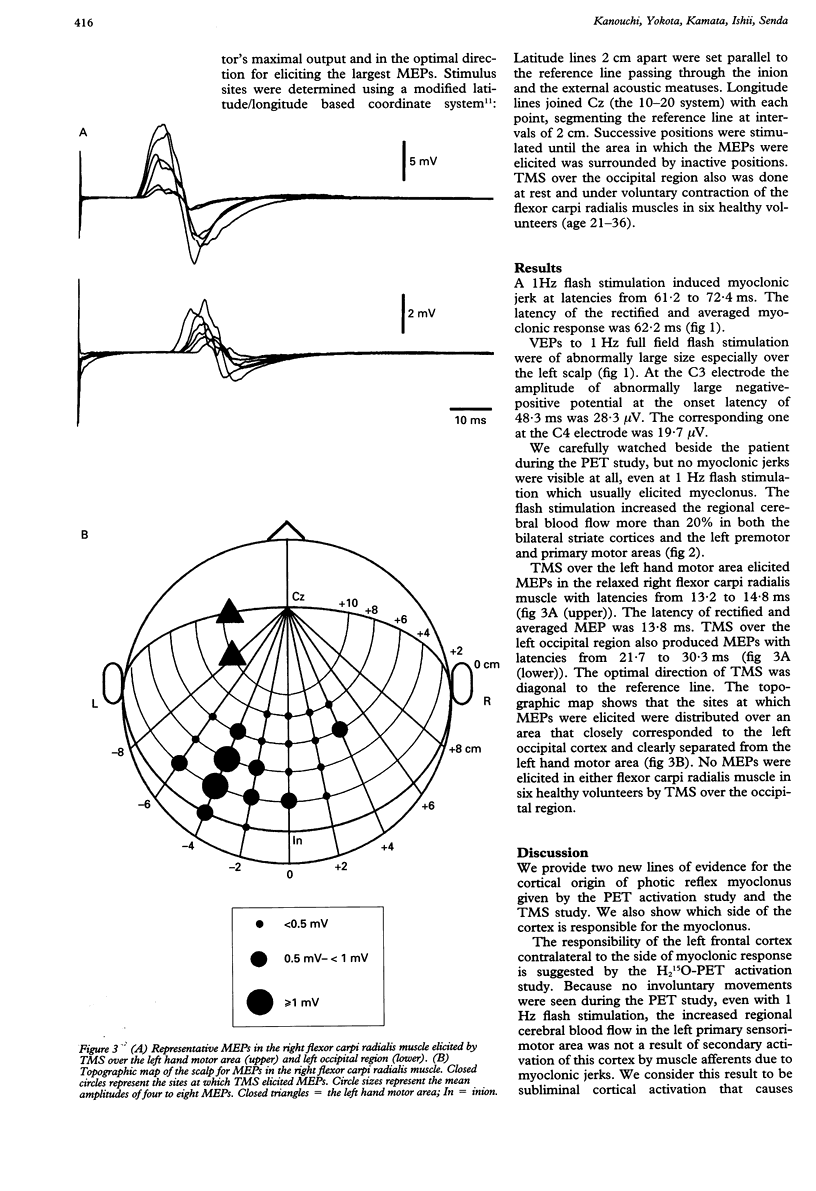
Direct, new evidence for the cortical origin of photic reflex myoclonus in a patient with "posterior cortical atrophy" is provided. Photic stimulation elicited myoclonic jerks in the right upper limb muscles. An H2(15)O-PET activation study with photic stimulation showed increased regional cerebral blood flow not only in both striate cortices but in the left premotor and primary motor areas as well. Transcranial magnetic stimulation over the area of the left occipital cortex elicited motor evoked potentials in the right upper limb muscles. It is concluded that in the central pathway of photic reflex myoclonus the contralateral occipital cortex is activated first, then the impulses propagate intrahemispherically to the primary motor cortex, to elicit myoclonic jerks.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artieda J., Obeso J. A. The pathophysiology and pharmacology of photic cortical reflex myoclonus. Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):175–184. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. F., Davis R. J., Snyder B. D. Posterior cortical atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1988 Jul;45(7):789–793. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520310107024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brailowsky S., Silva-Barrat C., Ménini C., Riche D., Naquet R. Effects of localized, chronic GABA infusions into different cortical areas of the photosensitive baboon, Papio papio. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1989 Feb;72(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(89)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER J., INGVAR D. H. Pathways mediating metrazol induced irradiation of visual impulses; an experimental study in the cat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1955 Feb;7(1):39–60. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(55)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaxma R., Kuypers H. G. Intrahemispheric cortical connexions and visual guidance of hand and finger movements in the rhusus monkey. Brain. 1975 Jun;98(2):239–260. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORENTZ DE HAAS A. M., LOMBROSO C., MERLIS J. K. Participation of the cortex in experimental reflex myoclonus. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 May;5(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandya D. N., Kuypers H. G. Cortico-cortical connections in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 1969 Mar;13(1):13–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senda M., Kanno I., Yonekura Y., Fujita H., Ishii K., Lyshkow H., Miura S., Oda K., Sadato N., Toyama H. Comparison of anatomical standardization methods regarding the sensorimotor foci localization and between-subject variation in H2(15)O PET activation, a three-center collaboration study. Ann Nucl Med. 1994 Aug;8(3):201–207. doi: 10.1007/BF03164998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki H., Neshige R. Photic cortical reflex myoclonus. Ann Neurol. 1987 Aug;22(2):252–257. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D., REMOND A. G., DOBSON R. L. Studies on the mechanism of the action of visual afferents on motor cortex excitability. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 Aug;5(3):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. A., Thickbroom G. W., Mastaglia F. L. Transcranial magnetic stimulation mapping of the motor cortex in normal subjects. The representation of two intrinsic hand muscles. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Sep;118(2):134–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



