Abstract
OBJECTIVES: Previous studies of small numbers of patients have shown that antisulphatide autoantibodies are associated with polyneuropathies having a prominent sensory component. However, clinical and electrodiagnostic features are variable. The range of clinical and electrodiagnostic findings in 19 patients with polyneuropathies and high titre (> 4500) serum IgM antisulphatide antibodies is described, together with testing for serum monoclonal (M) proteins. METHODS: About 20000 serum samples that were referred to the clinical laboratory from 1990 to the end of 1994 were screened by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for specific high titre antisulphatide antibodies. The clinical and electrodiagnostic data in 23 patients with positive results were reviewed. IgM binding to peripheral nerve structures was also evaluated in these patients. RESULTS: Nineteen patients had predominantly distal, symmetric pansensory loss. Patients with IgM antisulphatide antibodies and no serum M protein usually had clinical syndromes that included: (1) neuropathic pain or dysaesthesiae, (2) no functionally significant weakness, and (3) an axonal neuropathy on electrodiagnostic testing. On immunocytochemical studies serum IgM from the patients without M proteins usually (nine of 10; 90%) bound to peripheral nerve axons, but never to myelin. Patients with antisulphatide antibodies and a serum M protein, usually IgM, were more likely than patients without a serum M protein, to have syndromes with: (1) no pain or dysaesthesiae, (2) motor abnormalities, and (3) a demyelinating polyneuropathy by electrodiagnostic criteria. In immunocytochemical studies serum IgM most often bound to either peripheral nerve myelin or endoneurial structures. CONCLUSION: Patients with polyneuropathy and high titre serum IgM antisulphatide antibodies can be classified into subgroups according to the presence or absence of a serum M protein. Patients without an M protein are more likely to have pure sensory syndromes, pain, an axonal neuropathy, and serum IgM binding to axons. Patients with a serum M protein commonly had syndromes with prominent motor involvement, no pain, and a demyelinating neuropathy.
Full text
PDF

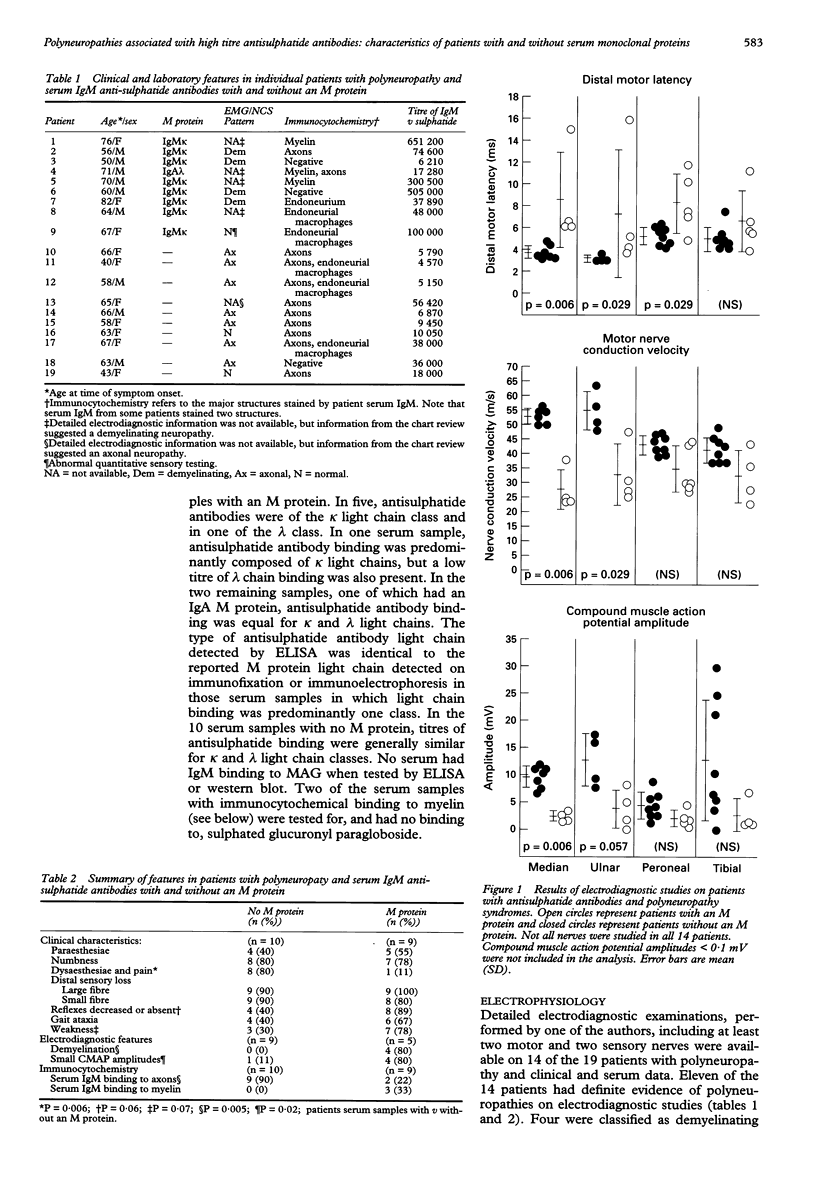

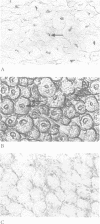
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fredman P., Lycke J., Andersen O., Vrethem M., Ernerudh J., Svennerholm L. Peripheral neuropathy associated with monoclonal IgM antibody to glycolipids with a terminal glucuronyl-3-sulfate epitope. J Neurol. 1993 Jun;240(6):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00839972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer J. A., O'Shannessy D. J., De Leon M., Gould R., Zand D., Daune G., Quarles R. H. Immunoreactivity of PMP-22, P0, and other 19 to 28 kDa glycoproteins in peripheral nerve myelin of mammals and fish with HNK1 and related antibodies. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Aug 1;35(5):546–558. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas A. A., Cook S. D., Dalakas M. C., Mithen F. A. Anti-MAG IgM paraproteins from some patients with polyneuropathy associated with IgM paraproteinemia also react with sulfatide. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90158-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaku D. A., England J. D., Sumner A. J. Distal accentuation of conduction slowing in polyneuropathy associated with antibodies to myelin-associated glycoprotein and sulphated glucuronyl paragloboside. Brain. 1994 Oct;117(Pt 5):941–947. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.5.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Jr The electrodiagnostic findings in polyneuropathies associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathies. Muscle Nerve. 1990 Dec;13(12):1113–1117. doi: 10.1002/mus.880131205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Sumner A. J. The electrodiagnostic distinctions between chronic familial and acquired demyelinative neuropathies. Neurology. 1982 Jun;32(6):592–596. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.6.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemni R., Fazio R., Quattrini A., Lorenzetti I., Mamoli D., Canal N. Antibodies to sulfatide and to chondroitin sulfate C in patients with chronic sensory neuropathy. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Mar;43(1-2):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90077-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobile-Orazio E., Manfredini E., Carpo M., Meucci N., Monaco S., Ferrari S., Bonetti B., Cavaletti G., Gemignani F., Durelli L. Frequency and clinical correlates of anti-neural IgM antibodies in neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy. Ann Neurol. 1994 Sep;36(3):416–424. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Choksi R., Bieser K., Goldstein J. M., Adler C. H., Caselli R. J., George E. B. Treatable gait disorder and polyneuropathy associated with high titer serum IgM binding to antigens that copurify with myelin-associated glycoprotein. Muscle Nerve. 1994 Nov;17(11):1293–1300. doi: 10.1002/mus.880171108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Li F., Bieser K., Choksi R., Whitton A., Kornberg A. J., Goldstein J. M., Yee W. C. Anti-MAG antibodies: major effects of antigen purity and antibody cross-reactivity on ELISA results and clinical correlation. Neurology. 1994 Jun;44(6):1131–1137. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.6.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quattrini A., Corbo M., Dhaliwal S. K., Sadiq S. A., Lugaresi A., Oliveira A., Uncini A., Abouzahr K., Miller J. R., Lewis L. Anti-sulfatide antibodies in neurological disease: binding to rat dorsal root ganglia neurons. J Neurol Sci. 1992 Oct;112(1-2):152–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90145-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons Z., Albers J. W., Bromberg M. B., Feldman E. L. Presentation and initial clinical course in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: comparison of patients without and with monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology. 1993 Nov;43(11):2202–2209. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.11.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Boström K., Fredman P., Jungbjer B., Månsson J. E., Rynmark B. M. Membrane lipids of human peripheral nerve and spinal cord. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 22;1128(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90250-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg L. H., Lankamp C. L., de Jager A. E., Notermans N. C., Sodaar P., Marrink J., de Jong H. J., Bär P. R., Wokke J. H. Anti-sulphatide antibodies in peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;56(11):1164–1168. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.11.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]