Abstract
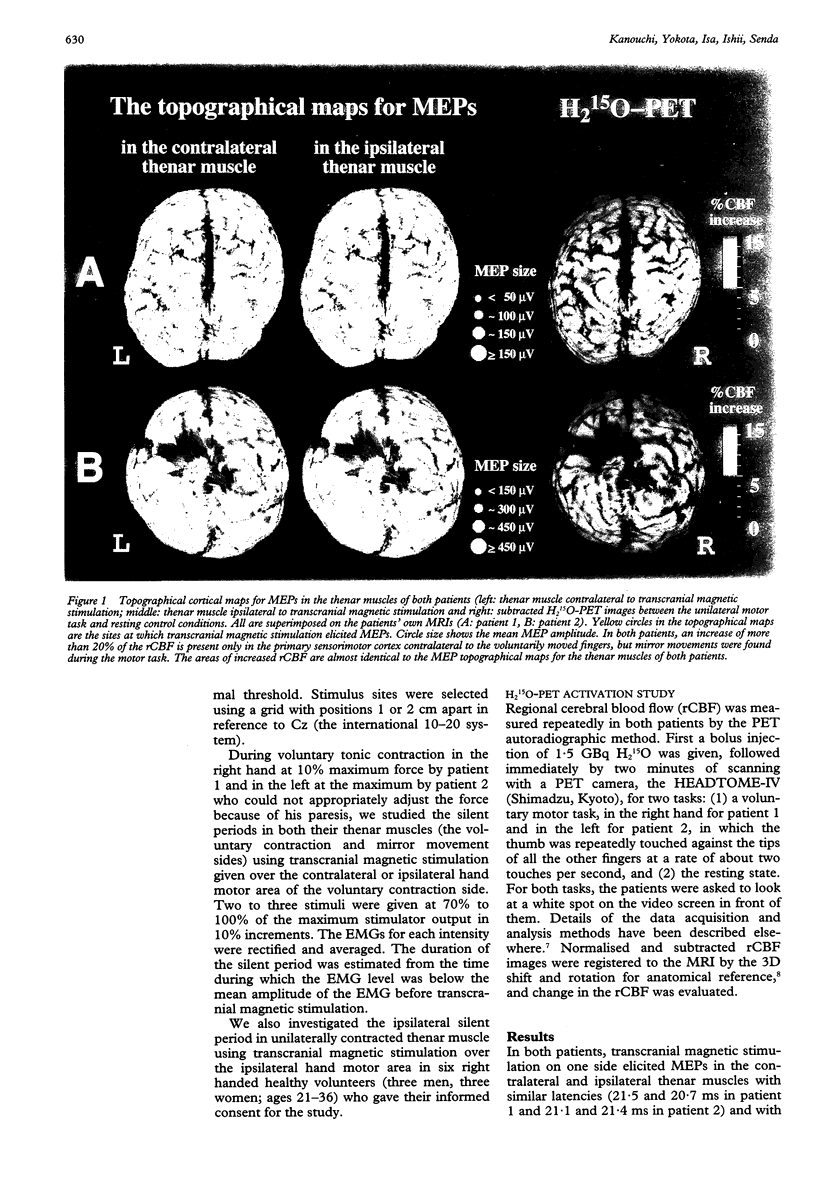
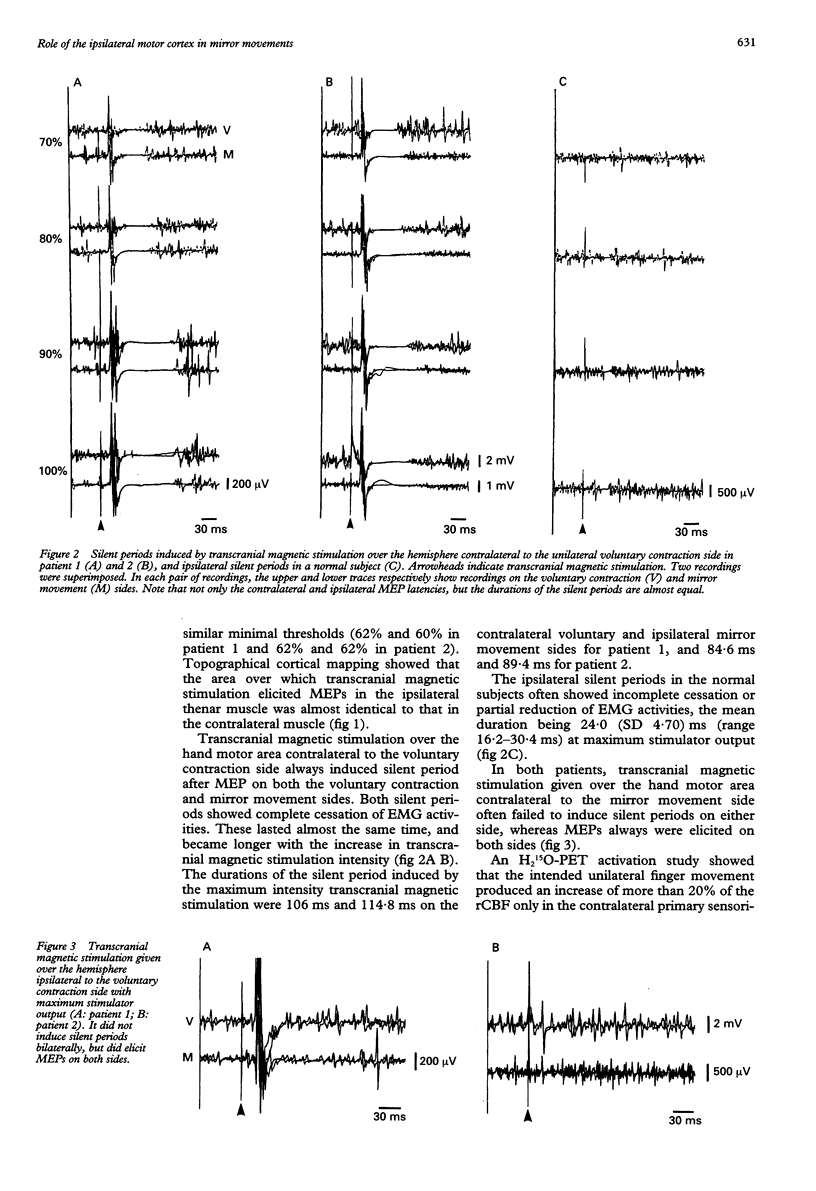
The mechanism of mirror movements in two patients was investigated; one with congenital mirror movement, the other with schizencephaly. Transcranial magnetic stimulation on one side elicited motor evoked potentials (MEPs) in their thenar muscles on both sides with almost the same latencies, minimal thresholds, and cortical topographies. During voluntary contraction of the thenar muscle on one side, contralateral transcranial magnetic stimulation induced a silent period not only on the voluntary contraction side but on the mirror movement side and of the same duration. By contrast, ipsilateral transcranial magnetic stimulation elicited MEPs without silent periods in both muscles. With intended unilateral finger movements, an H2(15)O-PET activation study showed that the regional cerebral blood flow increased predominantly in the contralateral sensorimotor cortex, as seen in normal subjects, although mirror movements occurred. It is considered that the ipsilateral motor cortex plays a major part in the generation of mirror movements, which may be induced through the ipsilateral uncrossed corticospinal tract.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britton T. C., Meyer B. U., Benecke R. Central motor pathways in patients with mirror movements. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Jun;54(6):505–510. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. G., Meer J., Tarkka I., Bierner S., Leiderman D. B., Dubinsky R. M., Sanes J. N., Jabbari B., Branscum B., Hallett M. Congenital mirror movements. Abnormal organization of motor pathways in two patients. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1B):381–403. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.1.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danek A., Heye B., Schroedter R. Cortically evoked motor responses in patients with Xp22.3-linked Kallmann's syndrome and in female gene carriers. Ann Neurol. 1992 Mar;31(3):299–304. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. F., Ingram D. A., Stephens J. A. Mirror movements studied in a patient with Klippel-Feil syndrome. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:467–484. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr P., Agostino R., Hallett M. Spinal motor neuron excitability during the silent period after cortical stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Aug;81(4):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(91)90011-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghilleri M., Berardelli A., Cruccu G., Manfredi M. Silent period evoked by transcranial stimulation of the human cortex and cervicomedullary junction. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:521–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. U., Röricht S., Gräfin von Einsiedel H., Kruggel F., Weindl A. Inhibitory and excitatory interhemispheric transfers between motor cortical areas in normal humans and patients with abnormalities of the corpus callosum. Brain. 1995 Apr;118(Pt 2):429–440. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.2.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nass R. Mirror movement asymmetries in congenital hemiparesis: the inhibition hypothesis revisited. Neurology. 1985 Jul;35(7):1059–1062. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.7.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzler A., Benecke R. The silent period after transcranial magnetic stimulation is of exclusive cortical origin: evidence from isolated cortical ischemic lesions in man. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Oct 10;180(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90909-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senda M., Kanno I., Yonekura Y., Fujita H., Ishii K., Lyshkow H., Miura S., Oda K., Sadato N., Toyama H. Comparison of anatomical standardization methods regarding the sensorimotor foci localization and between-subject variation in H2(15)O PET activation, a three-center collaboration study. Ann Nucl Med. 1994 Aug;8(3):201–207. doi: 10.1007/BF03164998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki H., Nagae K. Mirror movement: application of movement-related cortical potentials. Ann Neurol. 1984 Mar;15(3):299–302. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann E. M., Fuhr P., Cohen L. G., Hallett M. Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on ipsilateral muscles. Neurology. 1991 Nov;41(11):1795–1799. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.11.1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]