Abstract
Bacillus subtilis, like many bacteria, will choose among several response pathways when encountering a stressful environment. Among the processes activated under growth-restricting conditions are sporulation, establishment of motility, and competence development. Recent reports implicate ComK and MecA-ClpC as part of a system that regulates both motility and competence development. MecA, while negatively controlling competence by inhibiting ComK, stimulates ςD-dependent transcription of genes that function in motility and autolysin production. Both ComK-dependent and -independent pathways have been proposed for MecA’s role in the regulation of motility. Mutations in mecA reduce the transcription of hag. encoding flagellin, and are partially suppressed by comK in both medium promoting motility and medium promoting competence. Reduced ςD levels are observed in mecA mutants grown in competence medium, but no change in ςD concentration is detected in a comK mutant. The comF operon, transcription of which requires ComK, is located immediately upstream of the operon that contains the flgM gene, encoding the ςD-specific antisigma factor. An insertion mutation that disrupts the putative comF-flgM transcription unit confers a phenotype identical to that of the comK mutant with respect to hag-lacZ expression. Expression of a flgM-lacZ operon fusion is reduced in both sigD and comK mutant cells but is abolished in the sigD comK double mutant. Reverse transcription-PCR examination of the comF-flgM transcript indicates that readthrough from comF into the flgM operon is dependent on ComK. ComK negatively controls the transcription of hag by stimulating the transcription of comF-flgM, thereby increasing the production of the FlgM antisigma factor that inhibits ςD activity. There likely exists another comK-independent mechanism of hag transcription that requires mecA and possibly affects the ςD concentration in cells undergoing competence development.
The gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium Bacillus subtilis will activate one of several developmental programs when it is confronted with a growth-restricting environment. As is the case with many bacterial species faced with nutritional stress, B. subtilis will produce several extracellular degradative enzymes and antibiotics. More elaborate responses include the establishment of motility and processes of cellular specialization such as sporulation and genetic competence. Molecular mechanisms exist which serve as switches that permit the cell to choose an appropriate developmental path in response to harsh environmental conditions (18). An example of such a mechanism is the SinR-SinI pair, which participates in the cell’s decision to undergo either sporulation or competence and motility (3, 17, 29, 42). The phosphorylation state of the response regulator DegU is another determinant of whether cells produce degradative enzymes such as proteases or undergo competence establishment and become motile (26).
Although motility and genetic competence appear to be coregulated, recent studies have shown that there likely exists another molecular switch governing the cell’s decision to choose one or the other of these pathways. Competence development is part of a complex signal transduction network influenced by the nutritional state of the environment and cell density (13, 18; Fig. 1). The key regulatory event in the establishment of genetic competence is activation of transcription factor ComK (46). ComK is required for transcription of the late competence operons (13, 35, 46) that encode, among other proteins, ComE (a DNA binding protein that functions in DNA uptake); ComGA, -B, and -C, which form a type IV pilus bundle that is thought to position ComE; and ComFA, an ATP-dependent helicase required for DNA import (6, 7, 10, 11). ComK is negatively controlled by MecA and ClpC by direct protein-protein interaction (24, 44). MecA-ClpC-dependent inhibition of ComK is overcome by ComS (9, 21, 44), a small protein encoded by the srf operon (8, 21, 36, 37, 45), which also encodes the enzyme surfactin synthetase, a peptide synthetase catalyzing the synthesis of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin (15, 32, 45, 47).
FIG. 1.
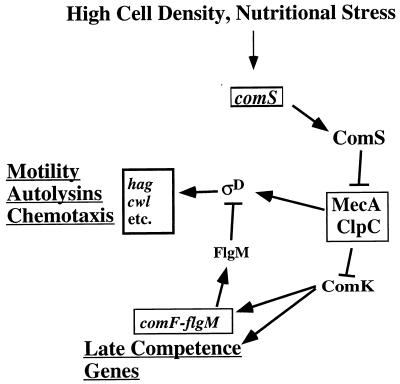
ComK-dependent and -independent MecA control of hag expression. High cell density and nutritional stress stimulate expression of the comS gene. ComS interaction with MecA-ClpC results in release of ComK, which activates comF-flgM operon transcription, as well as the expression of other late competence operons. Antisigma factor FlgM negatively controls ςD, resulting in reduced expression of hag and other genes of the ςD-regulon. MecA affects the ςD protein level, particularly in cells grown in medium that promotes competence development.
The transcription of genes that function in motility, including those that code for flagellum assembly, proteins functioning in chemotaxis, and autolysins, requires the alternative RNA polymerase sigma subunit ςD (1, 20, 27, 31, 34, 41). FlgM functions as an antisigma factor that negatively controls ςD (4, 14). MecA exerts opposite effects on competence development and motility (40, 43). MecA negatively controls the establishment of competence by interaction with ComK but is required for optimal expression of genes that are transcribed by the ςD form of RNA polymerase. Thus, MecA may serve as part of a molecular switch governing the cell’s decision to become motile or undergo genetic competence. Two independent reports provide conflicting views of how MecA-dependent positive control is exerted. Rashid et al. presented data suggesting that MecA control is independent of ComK (43), while Ogura and Tanaka proposed that ComK negatively controls ςD-dependent transcription and that the positive effect of MecA occurs solely through its interaction with ComK (40).
This report includes data showing that there exist both ComK-dependent and -independent mechanisms of MecA control of flagellar gene expression and that ComK negatively controls ςD-dependent transcription by stimulating the transcription of the flgM gene encoding the ςD-specific antisigma factor. MecA inhibits ComK but also affects the level of ςD in a ComK-independent manner.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains.
The B. subtilis strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. All of the strains constructed during this study are derivatives of B. subtilis JH642 (from J. Hoch). DNA from HB1002 cells bearing a hag-lacZ translational fusion (5; from J. D. Helmann) was used to transform JH642 competent cells with selection for erythromycin resistance (Ermr) to create strain LAB2607. To create mecA and comK mutant strains bearing a hag-lacZ translational fusion (strains LAB2722 and LAB2723, respectively), DNA from AG1312 (mecA::spc) (25) or 8G32 (comK::kan) (46) was used to transform LAB2607 competent cells with selection for spectinomycin (Spcr) or neomycin (Neor) resistance. A mecA comK double mutant bearing a hag-lacZ translational fusion (LAB2724) was constructed by transforming LAB2607 competent cells with DNA from AG1312 and 8G32 with selection for Spcr and screening for Neor.
TABLE 1.
Strains used in this study
| Strain | Genotype | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| JH642 | pheA trpC2 | J. Hoch |
| HB1002 | hag::pDM6330 hag-lacZ erm | 5 |
| HB4041 | SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | 14 |
| AG1312 (BD2092) | trpC2 mecA::spc | 25 |
| 8G32 | trpC2 comK::kan | 46 |
| CB149 | pheA trpC2 flgMΔ80 | 33 |
| LAB2607 | pheA trpC2 hag-lacZ erm | This work |
| LAB2722 | pheA trpC2 hag-lacZ erm mecA::spc | This work |
| LAB2723 | pheA trpC2 hag-lacZ erm comK::kan | This work |
| LAB2724 | pheA trpC2 hag-lacZ erm mecA::spc comK::kan | This work |
| LAB2916 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc | This work |
| LAB2917 | pheA trpC2 comK::kan | This work |
| LAB2918 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc comK::kan | This work |
| LAB2819 | pheA trpC2 SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2827 | pheA trpC2 flgMΔ80 SPβ2c2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2920 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2921 | pheA trpC2 comK::kan SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2922 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc comK::kan SPβ2cΔ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2923 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc flgMΔ80 | This work |
| LAB2924 | pheA trpC2 comK::kan flgMΔ80 | This work |
| LAB2925 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc comK::kan flgMΔ80 | This work |
| LAB2926 | pheA trpC2 flgMΔ80 mecA::spc SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2928 | pheA trpC2 comK::kan flgMΔ80 SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2929 | pheA trpC2 mecA::spc comK::kan flgMΔ80 SPβ2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phagcat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2931 | pheA trpC2 comF-flgM::pJL010 (cat) | This work |
| LAB2932 | pheA trpC2 comF-flgM::pJL010 (cat) SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan | This work |
| LAB2944 | pheA trpC2 hag-lacZ erm Δsrf::cat | This work |
| CB100 | trpC2 sigD::cat | J. D. Helmann (14) |
| LAB2994 | E. coli DH5α/pJL011 bla | This work |
| LAB2995 | trpC2 pheA1 flgM (orf139)-lacZ cat | This work |
| LAB2996 | trpC2 pheA1 flgM (orf139)-lacZ comK::neo | This work |
| LAB2997 | trpC2 pheA1 flgM (orf139)-lacZ cat sigD::erm | This work |
| LAB2998 | trpC2 pheA1 flgM (orf139)-lacZ cat comK::neo sigD::erm | This work |
The flgMΔ80 mutation is an in-frame deletion removing codons 6 through 85 of the flgM gene (34). To create a flgMΔ80 SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan strain, the transducing lysate of HB4041 [ZB307A SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan, obtained from J. D. Helmann (14)] was used to lysogenize CB149 (flgMΔ80) (34) with selection for chloramphenicol resistance (Cmr), creating strain LAB2827. Phag-cat-lacZ is a transcriptional fusion containing the promoter region of hag with the upstream UP element deleted (14). The same lysate was used to transduce strains JH642, LAB2916, LAB2917, LAB2724, LAB2923, LAB2924, and LAB2925, thereby creating the wild type (LAB2819) and mecA (LAB2920), comK (LAB2921), mecA comK (LAB2922), mecA flgMΔ80 (LAB2926), comK flgMΔ80 (LAB2928), and mecA comK flgMΔ80 (LAB2929) mutant strains bearing the phage-borne hag-lacZ transcriptional fusion, respectively. The presence of the flgMΔ80 mutation was verified by PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis of the flgM-specific PCR fragment. The forward primer (UFlgM′) used for PCR amplification was a 22-mer with the sequence GCGAATTCAGATCACTCATCTT, and the reverse primer (LFlgM′) was a 24-mer with the sequence GGGCTTTCTCCTTTTTTATTGCTT.
To create an insertion mutation at the site of PD-1 of the comF-flgM operon (34), a DNA fragment extending from 539 bp upstream to 329 bp downstream of the PD-1 transcription start site was synthesized by PCR amplification. The forward primer used to amplify the fragment was a 30-mer with the sequence ACGCGGATCCTCA ATCTGTTCATGCCGTAT, and the reverse primer was a 30-mer with the sequence TAAACTGCAGGGTATGCCAAATTAG GAAGA. The primers contained restriction sites for BamHI and PstI, respectively. These sites (underlined) were used to insert the cleaved PCR fragment into BamHI-PstI-cleaved plasmid pMMN13 (36), a pGEM4 derivative carrying a cat gene. The resulting plasmid was then introduced into wild-type strain JH642 by transformation with selection for Cmr. The lysate of the SPβc2Δ2 Tn917::Φ(Phag-cat-lacZ) kan strain was then used to lysogenize one of the transformants with selection for Neor.
Transformation and transduction.
Competent B. subtilis cells were prepared as previously described (12). Specialized transduction with SPβ was done as described by Zuber and Losick (48).
Media.
B. subtilis cells were routinely cultivated in 2XYT medium (36) to obtain cells for the preparation of DNA or to induce antibiotic resistance in transformed cells. 2XYT and one-step competence medium (CM) (12, 38) were used to culture cells for assays of lacZ fusion-encoded β-galactosidase activity. Escherichia coli cells were propagated in 2XYT medium to obtain cells for plasmid isolation. The antibiotic concentrations used for selection of drug-resistant organisms were as follows: chloramphenicol, 5 μg/ml; erythromycin in combination with lincomycin, 1 and 25 μg/ml, respectively; neomycin, 5 μg/ml; spectinomycin, 75 μg/ml; ampicillin, 25 μg/ml. The antibiotic concentrations used to induce drug resistance were as follows: chloramphenicol, 0.5 μg/ml; erythromycin, 0.1 μg/ml.
Culture conditions and β-galactosidase assay.
Cells precultured in Difco sporulation (DSM) agar plates or 2XYT broth at 37°C overnight were used to inoculate CM or 2XYT broth. Cultures were grown in 300-ml baffled sidearm flasks (MRA, Clearwater, Fla.) at 37°C in a shaking water bath. Samples were collected and assayed for β-galactosidase activity by the methods described previously (37, 49).
Protein extraction and Western immunoblot analysis.
Samples were harvested at T0 (at the end of exponential growth) and T2 (2 h after the end of exponential growth) by centrifugation at 4°C. The cells were washed once in phosphate-buffered saline, centrifuged again, and stored at −70°C. The thawed pellets were resuspended in 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)–5 mM EDTA–1 mM dithiothreitol–1.5 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Whole cell extracts were prepared with a French press, diluted in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer, and boiled for 5 min. Samples with the same protein concentrations, as determined with a Bio-Rad protein assay kit, were applied to an SDS–12% polyacrylamide gel. After electrophoresis, the proteins were electrotransferred to nitrocellulose and probed with anti-ςD antibodies (obtained from J. D. Helmann), followed by a secondary rabbit antibody conjugated with alkaline phosphatase as recommended by the manufacturer (GIBCO Bethesda Research Laboratories). The intensity of each band was determined with the NIH-Image computer program.
Construction of the flgM′-lacZ fusion.
The same PCR product as described in the construction of the comF-flgM insertion mutation was cleaved with PstI followed by T4 DNA polymerase to render the ends flush. The blunt-ended PCR fragment was digested with BamHI. The digested PCR fragment was then inserted in front of a promoterless lacZ gene in plasmid pTKlac (23), which was cut with HindIII, treated with T4 DNA polymerase to fill in the HindIII ends, and then cleaved with BamHI. The resulting plasmid (pJL011) was then introduced into JH642 competent cells by transformation. To examine the effects of mutations in comK, sigD, or both comK and sigD on the expression of flgM′-lacZ, comK mutant, sigD mutant, or comK sigD double mutant cells bearing flgM′-lacZ were constructed by transformation with DNA from the three mutant strains, using the wild-type strain carrying flgM′-lacZ as the recipient. In the case of the sigD mutation, the cat insertion marker had to be replaced with the erm marker of plasmid pCm::Er of strain ECE72 (Bacillus subtilis Genetic Stock Center, Columbus, Ohio), which was used to transform CB100 cells with selection for Ermr and screening for Cms.
Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR).
Wild-type and comK mutant cells grown in CM were harvested at T0.5 to isolate RNA. Isolation of RNA was performed as previously described (39). To ensure that no contaminating DNA was present in the RNA preparation, about 4 to 5 μg of the RNA sample (in 15 μl) was incubated at 37°C for 1 h with 30 U of RNase-free DNase and 0.5 μl (20 U) of RNase inhibitor (Promega) in a 50-μl volume. DNase-treated RNA samples still containing contaminating DNA were treated again as described above until no DNA contamination was detected by PCR. The treated RNA samples were recovered by using RNaid in accordance with the protocol recommended by the manufacturer (Bio 101, Inc.). PCR was performed to check for contaminating DNA (for the locations of the primers used, see Fig. 8). The nucleotide sequences of the downstream and upstream primers are as follows, respectively: 5′-GCACCTTTCACAAGGGTATGCAAATTAG-3′ (primer 1 [see Fig. 8]) and 5′-ACGCGGATCCTCAATCTGTTCATGCCGTAT-3′ (primer 2 [see Fig. 8]).
FIG. 8.
RT-PCR products from comF-flgM and flgM operon transcripts. At the top is a diagram of the comFC-orf139 region of the comF-flgM operon. PD1 indicates the location of the flgM promoter utilized by the ςD form of RNA polymerase. The arrows indicate the oligonucleotide primers (numbered 1 through 3) used to prime RT and to amplify cDNA and PCR products. The bottom panel is a photograph of an ethidium bromide-stained 1% agarose gel on which the PCR and RT-PCR products were resolved. In lanes 1 and 2, the template for PCR was JH642 chromosomal DNA. In lanes 3 to 6, the template for PCR and RT-PCR was RNA from strain LAB2917 (comK::neo). In lanes 7 to 10, the template for PCR and RT-PCR was from JH642 (wild-type) cells. MW, molecular weight markers. Lanes: 1, PCR product of primers 1 and 2 (no reverse transcriptase); 2, PCR product of primers 1 and 3; 3, PCR using primers 1 and 2; 4, PCR using primers 1 and 3; 5, RT-PCR using primers 1 and 2; 6, RT-PCR using primers 1 and 3; 7, PCR using primers 1 and 2; 8, PCR using primers 1 and 3; 9, RT-PCR using primers 1 and 2; 10, PCR using primers 1 and 3.
RT was conducted as described previously (2). The purified RNA was used as a template to synthesize cDNA strands by using avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase (Promega) and the antisense downstream primer shown above that was designed to anneal to orf139 mRNA. The resulting cDNA was then used as a template to create an amplified RT-PCR fragment by using Vent polymerase (New England BioLabs). The downstream and upstream primers were the same as those used as mentioned above to check for contaminating DNA, while another upstream primer with the nucleotide sequence 5′-ATGGGAGAACTGGCTAATTGTCCGAAATGCA-3′ (primer 3 [see Fig. 8]), which starts at the translational initiation codon of orf139, was used to detect both the readthrough comF-flgM operon transcript and the transcript initiating at the PD-1 promoter. The resulting RT-PCR products were identified by agarose gel electrophoresis (1%, wt/vol), while the PCR product from a template of chromosomal DNA from wild-type B. subtilis JH642 was applied as a positive control.
RESULTS
mecA, comK, and comS affect the expression of hag-lacZ.
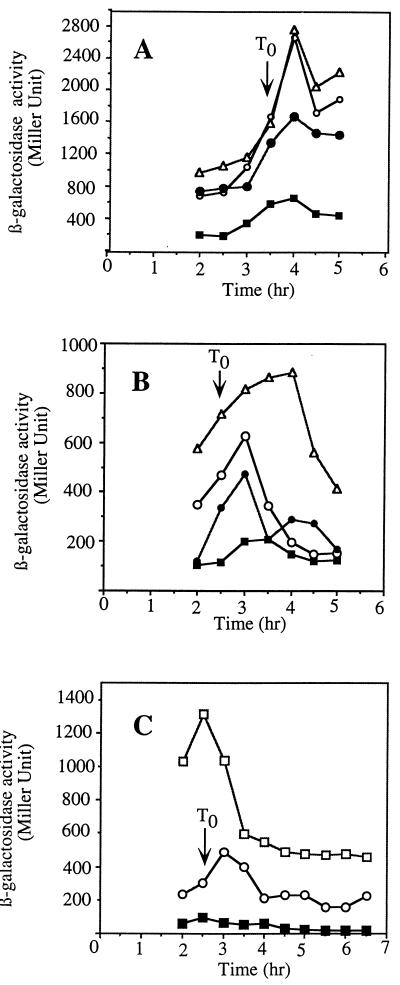
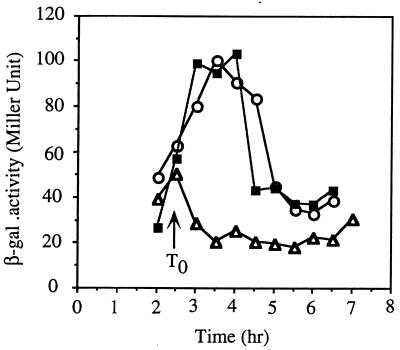
To reexamine the roles of MecA and ComK in the regulation of the ςD regulon, the mecA and comK mutations were introduced by transformation into cells bearing a translational hag-lacZ fusion plasmid integrated at the hag locus (14). A fusion-bearing strain containing both of the mecA and comK mutations was also constructed. Expression of hag in the three mutant strains was examined in cultures grown in 2XYT and in CM. Rich medium conditions, such as those existing in 2XYT, promote expression of genes of the ςD regulon but do not promote competence due to the Mec-dependent inhibition of ComK. This inhibition is relieved in CM by the comS gene product. High levels of hag-lacZ activity were observed in wild-type cells grown in 2XYT, with expression increasing as the culture reached the end of exponential growth (Fig. 2A). A mecA mutation resulted in substantially lower hag-lacZ activity throughout the growth curve. The comK mutation did not change the level of expression from that observed in wild-type cells, but introduction of a mecA mutation into the comK background resulted in a modest but reproducible decrease in expression. MecA positively influences hag-lacZ expression primarily by inhibiting ComK activity but may play some additional role in hag expression.
FIG. 2.
Expression of hag-lacZ in the wild type and mecA, comK, and mecA comK, and srf (comS) mutants. Cells of each strain were grown in 2XYT (A) or CM (B and C), and samples were collected at the indicated times. hag-directed β-galactosidase activity was determined as described in Materials and Methods and in accordance with published protocols. Symbols: ▵, LAB2723 (comK hag-lacZ); ○, LAB2607 (hag-lacZ); •, LAB2724 (comK mecA hag-lacZ); ■, LAB2722 (mecA hag-lacZ); □, LAB2944 (hag-lacZ srf).
In cells grown in CM, ComK levels are higher due to reversal of Mec-dependent inhibition by ComS (19, 28, 44). Thus, comK more profoundly influences hag-lacZ expression. As shown in Fig. 2B, the expression of hag-lacZ in a comK mutant is significantly higher than in wild-type cells. As in 2XYT medium, mecA cells exhibit low levels of hag-lacZ activity. This repression of hag is only partially reversed by the comK mutation. The repression of hag expression caused by a mecA null mutation is, in part, comK dependent, but MecA plays some other role in the positive control of hag.
As further evidence for MecA-ComK-dependent control of hag expression and the involvement of the so-called early com regulators, the expression of hag-lacZ in an srf deletion mutant lacking the comS gene was examined (Fig. 2C). Significantly higher levels of hag-lacZ expression were observed in comS mutant cells grown in CM than in wild-type cells, in accordance with the observed comK-dependent control of hag. If ComS served to release ComK from MecA-ClpC-dependent inhibition, then it, too, would be expected to exert a negative influence on hag expression.
mecA and comK mutations have little effect on ςD levels in rich medium, but mecA mutant cells grown in CM contain a reduced concentration of ςD.
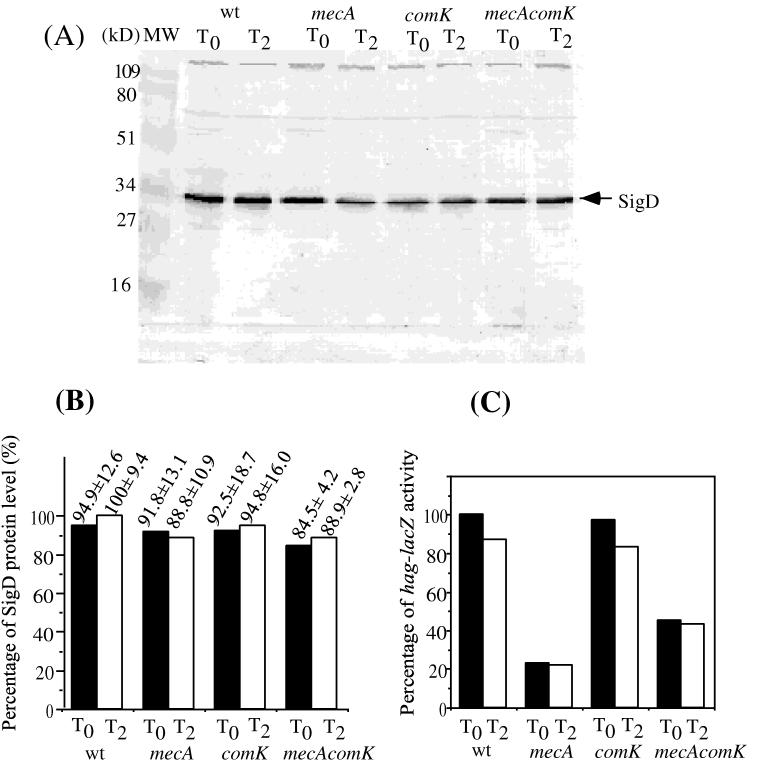
How do MecA and ComK exert their effects on the regulation of hag? As had been shown previously, expression of the class III flagellar regulon genes, such as hag, requires the ςD form of RNA polymerase (31, 33). It was conceivable, therefore, that competence regulatory factors regulate the expression of the sigD gene. Cells of the wild-type and comK, mecA, and comK mecA mutant strains bearing a translational hag-lacZ fusion (5) were grown in 2XYT medium and, in a separate experiment, CM. Samples were collected at T0 and T2 (0 and 2 h after the end of the exponential growth phase, respectively) for the measurement of ςD protein levels by immunoblot analysis, while hag expression was quantified by measuring hag-directed β-galactosidase activity. There was little significant change in the level of protein observed in the four 2XYT cultures, as shown by a computer-aided scan of the developed immunoblot (Fig. 3A and B). This is in contrast to the level of hag-lacZ expression observed in the cell culture samples. In the mecA and comK mutant cells, there was a significant difference in the level of hag-lacZ expression (Fig. 3C) but virtually identical concentrations of ςD protein. This suggested that ComK might affect the activity of ςD rather than the ςD concentration.
FIG. 3.
Level of ςD protein in the wild type (wt) and mecA, comK, and mecA comK mutants grown in rich medium. Cells precultured in 2XYT liquid medium were grown in 2XYT medium at 37°C. Samples were harvested at T0 and T2 (at the end of exponential growth and 2 h after the end of exponential growth, respectively). Cell extracts with equal protein concentrations were applied to SDS–12% polyacrylamide gels and subjected to electrophoresis. The resolved protein was electrotransferred to nitrocellulose and analyzed by the Western blotting procedures described in Materials and Methods. (A). Lane MW contained molecular size markers. The other lanes contained samples from cultures of LAB2607 (wild type), LAB2722 (mecA), LAB2723 (comK), and LAB2724 (mecA comK) cells collected at T0 and T2 of the growth curve. (B) Western blot band intensity determined by scanning of the image of the stained blot and quantification by the NIH-Image computer program. The values presented are percentages of the level of protein in the wild-type strain at T2. The standard deviation was calculated from three independent experiments. (C) Levels of hag-directed β-galactosidase in cultures used to obtain extracts for Western blot analysis.
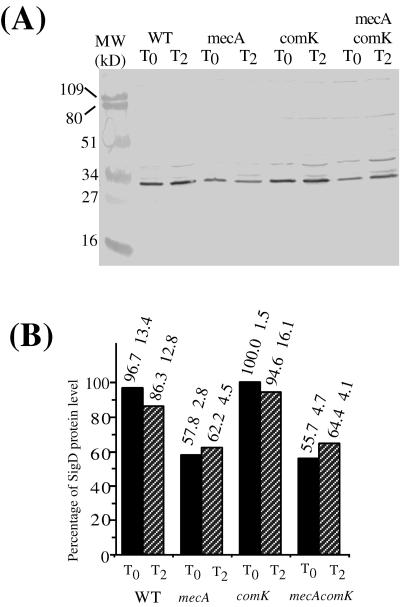
In CM, the mecA mutation modestly influenced the level of ςD protein. While wild-type and comK mutant cells contain similar concentrations of ςD protein, mecA and mecA comK mutant cells show reduced levels of ςD (Fig. 4). The ComK-independent positive control of hag expression exerted by MecA could be directed, at least in part, at the concentration of ςD protein.
FIG. 4.
Levels of ςD protein in the wild type (WT) and mecA, comK, and mecA comK mutants grown in CM. Cells precultured in DSM agar plates were grown in CM at 37°C. Samples were harvested at the same time points as in Fig. 3. Analysis of the protein extracts was conducted as described in the legend to Fig. 3. (A) Western blot of extracts of LAB2607 (wild type [WT]), LAB2722 (mecA), LAB2723 (comK), and LAB2724 (mecA comK) cell samples collected at T0 and T2 of the growth curve. (B) Western blot band intensity determined and presented as described in the legend to Fig. 3.
A comF-flgM insertion mutation results in heightened expression of hag-lacZ.
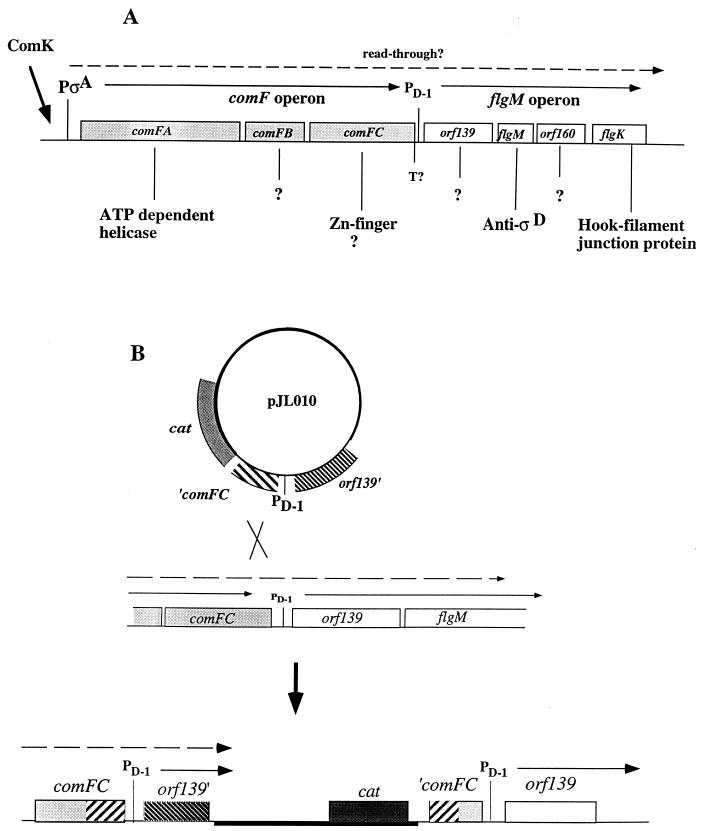
Because a mutation in comK appeared to affect the activity of ςD, it was possible that the ςD-specific antisigma factor FlgM was involved. It was noticed that the flgM operon, consisting of four genes in the order orf139 flgM orf160 fliK (31, 34), resides immediately downstream of comF, a late competence operon, transcription of which requires ComK (30, 46). We reasoned that comF and flgM could lie in the same transcription unit and that ComK functions in the negative control of hag by stimulating the transcription of flgM, thereby increasing the level of the ςD-specific antisigma factor. To test this hypothesis, a plasmid insertion mutation was constructed to separate upstream ComK-dependent transcription from ςD-dependent flgM operon transcription. If comK functioned in the negative control of hag by activating comF-flgM transcription, then the disruption of ComK-dependent transcription of flgM by the plasmid insertion would confer the same phenotype, with respect to hag expression, as a comK mutation. An 868-bp fragment encompassing the 3′ end of comFC, the PD-1 promoter, and the 5′ end of orf139 (Fig. 4) was generated by PCR. The PD-1 promoter is utilized by the ςD form of RNA polymerase and is located between the putative transcriptional terminator of the comF operon and the start codon of orf139. The fragment was inserted into integration vector pMMN13. The resulting plasmid, pJL010, was used to transform cells of strain JH642. The transformant obtained had undergone a Campbell-type recombination event, yielding a strain bearing an integrated plasmid at the comF-flgM junction (Fig. 5). This strain was lysogenized with SPβPhag-lacZ to yield strain LAB2932. The Phag-lacZ fusion is a transcriptional fusion between a promoterless lacZ gene and a derivative of the hag promoter that lacks the upstream UP element; hence, the levels of hag-directed β-galactosidase activity are lower in strains bearing this fusion than in those carrying the translational fusion. The patterns of hag-lacZ expression in the comK and comF-flgM insertion mutants are nearly identical, with higher levels of expression in the stationary phase in CM than that observed in wild-type cells (Fig. 6).
FIG. 5.
Structure of the comF-flgM operon and construction of a comF-flgM::pJL010 insertion mutant. (A) flgM is located within an operon containing the promoter PD-1, immediately downstream of the comF operon. comF is a B. subtilis late competence operon. Transcription of comF is driven by a single ςA-type promoter, utilization of which is dependent on ComK. The flgM operon contains orf139, flgM, orf160, and flgK. (B) The mutant was constructed by insertion of a plasmid (pJL010) carrying comFC and orf139 fragments by a single-recombination mechanism into the region containing the junction between the comF and flgM operons.
FIG. 6.
Expression of hag-lacZ in wild-type and comK and comF-flgM::pJL010 mutant cells grown in CM. Cells were precultured on DSM agar plates and then grown in CM liquid at 37°C. hag-directed β-galactosidase (β-gal) specific activity of samples collected at the indicated time points was determined as described in Materials and Methods and in the legend to Fig. 3. Symbols: ▵, LAB2819 (SPβhag-lacZ); ○, LAB2921 (SPβhag-lacZ comK); ■, LAB3932 (SPβhag-lacZ comF-flgM::pJL010).
Table 2 summarizes the effects of flgMΔ80 in wild-type and comK and mecA mutant genetic background cells grown in CM. flgMΔ80 in combination with a comK mutation does not result in hag-lacZ expression higher than that observed in the flgM mutant. As with the comK mutation, the flgM deletion did not show complete suppression of mecA. The flgMΔ80 comK mecA triple mutant showed a level of hag-lacZ expression similar to that of a flgMΔ80 mecA mutant. That the suppression of mecA by flgM and comK mutations is not significantly higher than that of each mutation alone suggests that comK and flgM operate within a common genetic pathway, consistent with the hypothesis that comK regulates flgM expression. The incomplete suppression of mecA caused by a flgM mutation indicates that the comK-independent function of mecA in regulating hag expression does not involve FlgM.
TABLE 2.
Effect of flgM mutation on hag expression
| Strain | Genotype | Mean β-galactosidase activity (Miller units) ± SDa |
|---|---|---|
| LAB2819 | Wild type | 70.5 ± 3.5 |
| LAB2827 | flgMΔ80 | 127.5 ± 23.2 |
| LAB2926 | flgMΔ80 mecA | 59 ± 0.4 |
| LAB2928 | flgMΔ80 comK | 129 ± 5.7 |
| LAB2929 | flgMΔ80 mecA comK | 69.5 ± 6.4 |
| LAB2920 | mecA | 34.5 ± 6.4 |
Samples were collected at T0.5 from cultures of wild-type and mutant cells grown in CM.
Expression of the flgM operon is dependent on both sigD and comK.
The phenotype of the comF-flgM insertion mutation suggested that the transcription of the flgM operon was controlled by comK. To test this prediction, a flgM operon-lacZ transcriptional fusion was constructed by inserting the same comFC-orf139 PCR fragment used to make the insertion mutation upstream of a promoterless lacZ gene. The construction was introduced into JH642 competent cells, in which the plasmid would insert by a single recombination event into the putative comF-flgM operon. Mutant derivatives of the fusion-bearing strains were constructed by transformation with sigD and comK mutant DNA, thereby creating sigD, comK, and sigD comK mutants all carrying the flgM operon-lacZ fusion.
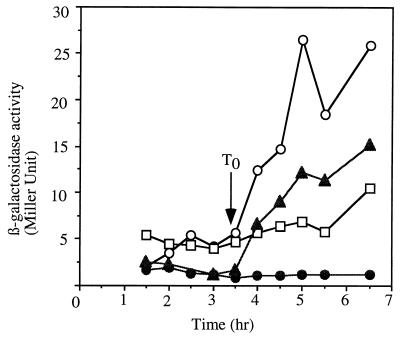
Optimal expression of the lacZ fusion was dependent on both the comK and sigD genes (Fig. 7), with the double mutant comK sigD cells exhibiting nearly undetectable levels of lacZ expression, supporting the hypothesis that flgM operon transcription is positively controlled by ComK.
FIG. 7.
flgM operon (orf139)-lacZ fusion expression in comK and sigD mutant cells. Cells of the wild-type and the comK, sigD, and comK sigD mutant strains bearing plasmid pJL011 [flgM (orf139)-lacZ] integrated at the flgM locus were grown in CM. Samples were collected at 30-min intervals for assay of β-galactosidase activity. Symbols: ○, LAB2995 [flgM (orf139)-lacZ]; ▴, LAB2997 [sigD flgM (orf139)-lacZ]; □, LAB2996 [comK flgM (orf139)-lacZ]; •, LAB2998 [sigD comK flgM (orf139)-lacZ].
RT-PCR was employed to determine if ComK-dependent readthrough transcription from comF into the flgM operon could be detected. RNA was purified from both wild-type (JH642) and comK mutant (LAB2917) cells at 30 min after the end of exponential growth. Two different RT-PCRs were assembled. Both utilized an oligonucleotide corresponding to a sequence within the orf139 open reading frame to prime reverse transcriptase-catalyzed cDNA synthesis from flgM operon RNA. In one reaction, amplification was carried out by using a primer hybridizing to comFC sequences within the cDNA to obtain an RT-PCR product of 885 bp derived from the comF-flgM readthrough transcript. The other reaction utilized a primer hybridizing to the region of the cDNA corresponding to the amino-terminal coding end of orf139, the first gene of the flgM operon. Amplification of the cDNA yields an RT-PCR product of 270 bp derived from both the readthrough transcript and the RNA synthesized from the PD-1 promoter. Control reaction mixtures containing RNA, primer, and DNA polymerase were included to determine if contaminating DNA remained in the RNA after DNase treatment.
As shown in Fig. 8, an RT-PCR product corresponding to a readthrough comF-flgM operon transcript could be detected in wild-type cells (lane 9) but not in the comK mutant cells (lane 5), whereas the 270-bp product is observed in reaction mixtures containing either comK mutant or wild-type cellular RNA (lanes 6 and 10). The results described above confirm that comF-flgM transcription is comK dependent. More of the RT-PCR product was detected in the reaction mixture producing the 270-bp fragment than in that producing the 885-bp product derived from the comK-dependent transcript. This might be due to the possibility that the RNA was harvested before the time in the growth curve when the ComK concentration and, hence, ComK-dependent transcription, was at a maximum.
DISCUSSION
The mecA gene product is required for the optimum expression of genes that constitute the ςD regulon. It participates in both comK-dependent and comK-independent mechanisms of regulation. The expression of hag is reduced in mecA mutants grown in both 2XYT and CM. A mutation in comK has no effect on the level of hag expression in 2XYT, a rich medium that does not promote competence, but when a comK mutation is introduced into a mecA mutant, nearly complete suppression of the mecA mutation is observed. This indicates that in medium that does not promote competence, the major function of MecA in stimulating hag expression is to inhibit ComK. In CM, comK mutant cells exhibit heightened hag expression which is above that observed in wild-type cells. In this medium, as opposed to 2XYT, active ComK is produced and wild-type cells show a level of hag expression lower than that observed in 2XYT-grown cells, in which ComK is absent. A mutation in mecA causes a dramatic reduction of hag expression in CM, and it is incompletely suppressed by a comK mutation. In CM, MecA functions to inhibit ComK but also stimulates hag expression through a ComK-independent mechanism. The comS mutation has nearly the same effect a comK mutation has in CM; both cause higher-level expression of hag, supporting the conclusion that MecA stimulates hag expression, in part, by negatively controlling ComK.
The examination of ςD protein levels revealed no change in sigD expression in the comK mecA mutant and wild-type cells grown in 2XYT. In CM, little, if any, difference in the ςD protein level was observed between wild-type and comK mutant cells. This suggested that ςD activity was altered in the comK mutant. A likely target for MecA-ComK-dependent control was FlgM, the ςD-specific antisigma factor. It was noticed that the flgM operon was located downstream from the comF operon, the transcription of which had been shown to require ComK (46). Optimal flgM transcription might require readthrough from the comF operon, although a sequence resembling a factor-independent terminator was identified at the end of comFC (34). This hypothesis was tested by creating an insertion mutation that separated comF from the flgM operon by introducing a plasmid bearing the comFC-orf139 intergenic region by homologous recombination. The insertion mutation produced the same phenotype with respect to hag-lacZ expression as the comK mutation. These results strongly suggest that flgM transcription is dependent, in part, on ComK and that this is the basis of ComK-dependent negative control of hag and other genes of the ςD regulon that had been shown to require MecA for their expression. This hypothesis was further supported by data showing that flgM operon expression was positively controlled by comK and by RT-PCR data indicating the presence of a comF-flgM operon transcript. This mechanism of control operates in cells grown in CM and 2XYT, but Western blot analysis of ςD protein levels in cells grown in CM showed that MecA also affects sigD expression, by affecting either the transcription or translation of sigD or the stability of the ςD protein.
Rashid et al. reported that the MecA-ClpC-dependent control of hag was independent of comK (43) when cells were grown in a rich medium that does not promote competence. However, our results not only implicate comK in the negative control of hag but also provide a reasonable explanation for the role of comK, i.e., to activate transcription of the flgM operon. Ogura and Tanaka showed that MecA stimulated ςD-transcribed gene degR by inhibiting ComK (40), but their experiments did not examine the effect of mecA and comK mutations in cells grown in medium that promoted competence, a condition in which MecA exerts positive control of hag independently of comK.
The ComS-MecA-ComK system can be viewed as a molecular switch that is thrown in the direction favoring competence at high cell density, when the ComS peptide is present in abundance (Fig. 1). At a low cell density, when the ComS concentration is low, the switch is thrown in the other direction, that favoring motility, chemotaxis, and production of autolysins, all processes requiring the ςD form of RNA polymerase. The activation of late competence operons when motility genes are down regulated is reminiscent of the opposing controls associated with toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP) production and motility in the intestinal pathogen Vibrio cholerae (16). The expression of motility genes is repressed when tcp is expressed, a situation reflecting the motility-dependent penetration of the intestinal mucous layer followed by the TCP-dependent attachment of vibrios to the cells lining the intestine. Both the TCP protein and the B. subtilis late Com products encoded by the comG operon are of the type IV pilus family (10, 22). It is possible that the transcriptional control mechanisms activating tcp expression directly or indirectly down regulate motility gene expression, perhaps through a mechanism involving flgM and a ςD homolog. Why might there be mechanisms of control that favor type IV pilus production while suppressing the expression of motility functions? One possibility is that the two structures, the type IV pilus and the flagellum, are not compatible within the bacterial cell wall. Another explanation is based on the conditions under which the two structures are utilized. The function of the pilus, whether used in genetic exchange or in cell-cell contact, is associated with conditions of high local cell density that are conducive to cell-cell interaction, whether for genetic exchange or for coordination of the activity of a concentrated population of bacteria. Motility might be expected to be characteristic of bacteria encountering stress in a low cell density environment since individual bacteria are less likely to impact their immediate environment for the purpose of responding appropriately to stressful conditions and to utilize their mechanism of genetic exchange. Hence, their ability to relocate to a less stressful environment or one inhabited by a large population of their own species would necessitate flagellum formation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to J. D. Helmann for strains, anti-ςD serum, and advice on immunoblot procedures and to L. Hamoen and A. Grossman for providing us with strains used in this study. We also thank M. M. Nakano and M. Ogura for helpful discussions and critically reading the manuscript.
This work was supported by grant GM45898 from the National Institutes of Health.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arnosti D N, Chamberlin M J. Secondary sigma factor controls transcription of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D O, Smith J A, Seidman J G, Struhl K. PCR amplification of RNA under optimal conditions. In: Ausubel F M, et al., editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1998. pp. 15.4.1–15.4.2. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bai U, Mandic-Mulec I, Smith I. SinI modulates the activity of SinR, a developmental switch protein of Bacillus subtilis, by protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1993;7:139–148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Caramori T, Barilla D, Nessi C, Sacchi L, Galizzi A. Role of FlgM in ςD-dependent gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:3113–3118. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.11.3113-3118.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chen L, Helmann J D. The Bacillus subtilis ςD-dependent operon encoding the flagellar proteins FliD, FliS, and FliT. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:3093–3101. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.11.3093-3101.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chung Y S, Dubnau D. All seven comG open reading frames are required for DNA binding during transformation of competent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:41–45. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.1.41-45.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chung Y S, Dubnau D. ComC is required for the processing and translocation of ComGC, a pilin-like competence protein of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:543–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cosmina P, Rodriguez F, de Ferra F, Grandi G, Perego M, Venema G, van Sinderen D. Sequence and analysis of the genetic locus responsible for surfactin synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993;8:821–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.D’Souza C, Nakano M M, Zuber P. Identification of comS, a gene of the srfA operon that regulates the establishment of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:9397–9401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dubnau D. Binding and transport of transforming DNA by Bacillus subtilis: the role of type-IV pilin-like proteins—a review. Gene. 1997;192:191–198. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(96)00804-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dubnau D. Genetic exchange and homologous recombination. In: Sonenshein A L, Hoch J A, Losick R, editors. Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacteria: biochemistry, physiology, and molecular genetics. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1993. pp. 555–584. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dubnau D, Davidoff-Abelson R. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. I. Formation and properties of the donor-recipient complex. J Mol Biol. 1971;56:209–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dubnau D, Hahn J, Roggiani M, Piazza R, Weinrauch Y. Two-component regulators and genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Res Microbiol. 1994;145:403–411. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(94)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fredrick K, Helmann J D. FlgM is a primary regulator of ςD activity, and its absence restores motility to a sinR mutant. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:7010–7013. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.23.7010-7013.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Galli G, Rodriguez F, Cosmina P, Pratesi C, Nogarotto R, de Ferra F, Grandi G. Characterization of the surfactin synthetase multienzyme complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1205:19–28. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gardel C L, Mekalanos J J. Alterations in Vibrio cholerae motility phenotypes correlate with changes in virulence factor expression. Infect Immun. 1996;64:2246–2255. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.6.2246-2255.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gaur N K, Oppenheim J, Smith I. The Bacillus subtilis sin gene, a regulator of alternate developmental processes, codes for a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:678–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.678-686.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Grossman A D. Genetic networks controlling the initiation of sporulation and the development of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:477–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.29.120195.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hahn J, Luttinger A, Dubnau D. Regulatory inputs for the synthesis of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1996;21:763–775. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.371407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Haldenwang W G. The sigma factors of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1995;59:1–30. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.1.1-30.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hamoen L W, Eshuis H, Jongbloed J, Venema G. A small gene, designated comS, located within the coding region of the fourth amino acid-activating domain of srfA, is required for competence development in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kaufman M R, Shaw C E, Jones I D, Taylor R K. Biogenesis and regulation of the Vibrio cholerae toxin-coregulated pilus: analogies to other virulence factor systems. Gene. 1993;126:43–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90588-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kenney T J, Moran C P., Jr Genetic evidence for interaction of ςA with two promoters in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:3282–3290. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3282-3290.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kong L, Dubnau D. Regulation of competence-specific gene expression by Mec-mediated protein-protein interaction in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kong L, Siranosian K J, Grossman A D, Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of mecA: a negative regulator of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993;9:365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kunst F, Msadek T, Rapoport G. Signal transduction network controlling degradative enzyme synthesis and competence in Bacillus subtilis. In: Piggot P J, Moran C P Jr, Youngman P, editors. Regulation of bacterial differentiation. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1994. pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuroda A, Sekiguchi J. High-level transcription of the major Bacillus subtilis autolysin operon depends on expression of the sigma D gene and is affected by a sin (flaD) mutation. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:795–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.795-801.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lazazzera B A, Grossman A D. A regulatory switch involving a Clp ATPase. Bioessays. 1997;19:455–458. doi: 10.1002/bies.950190604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu L, Nakano M M, Lee O H, Zuber P. Plasmid-amplified comS enhances genetic competence and suppresses sinR in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:5144–5152. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.17.5144-5152.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Londono-Vallejo J A, Dubnau D. comF, a Bacillus subtilis late competence locus, encodes a protein similar to ATP-dependent RNA/DNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1993;9:119–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Márquez L M, Helmann J D, Ferrari E, Parker H M, Ordal G W, Chamberlin M J. Studies of ςD-dependent functions in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990;172:3435–3443. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3435-3443.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Menkhaus M, Ullrich C, Kluge B, Vater J, Vollenbroich D, Kamp R M. Structural and functional organization of the surfactin synthetase multienzyme system. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:7678–7684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mirel D B, Chamberlin M J. The Bacillus subtilis flagellin gene (hag) is transcribed by the ς28 form of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:3095–3101. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3095-3101.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mirel D B, Lauer P, Chamberlin M J. Identification of flagellar synthesis regulatory and structural genes in a ςD-dependent operon of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:4492–4500. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4492-4500.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mohan S, Dubnau D. Transcriptional regulation of comC: evidence for a competence-specific transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990;172:4064–4071. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4064-4071.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nakano M M, Magnuson R, Myers A, Curry J, Grossman A D, Zuber P. srfA is an operon required for surfactin production, competence development, and efficient sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:1770–1778. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1770-1778.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nakano M M, Marahiel M A, Zuber P. Identification of a genetic locus required for biosynthesis of the lipopeptide antibiotic surfactin in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1988;170:5662–5668. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5662-5668.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nakano M M, Zuber P. The primary role of comA in the establishment of the competent state in Bacillus subtilis is to activate the expression of srfA. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:7269–7274. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7269-7274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nakano M M, Xia L, Zuber P. The transcription initiation region of the srfA operon which is controlled by the comP-comA signal transduction system in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:5487–5493. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5487-5493.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ogura M, Tanaka T. Bacillus subtilis ComK negatively regulates degR gene expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1997;254:157–165. doi: 10.1007/s004380050403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ordal G W, Marquez-Magana L, Chamberlin M J. Motility and chemotaxis. In: Sonenshein A L, Hoch J A, Losick R, editors. Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacteria: biochemistry, physiology, and molecular genetics. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1993. pp. 765–784. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rashid M H, Sekiguchi J. flaD (sinR) mutations affect SigD-dependent functions at multiple points in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:6640–6643. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.22.6640-6643.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rashid M H, Tamakoshi A, Sekiguchi J. Effects of mecA and mecB (clpC) mutations on expression of sigD, which encodes an alternative sigma factor, and autolysin operons and on flagellin synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:4861–4869. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.16.4861-4869.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Turgay K, Hamoen L W, Venema G, Dubnau D. Biochemical characterization of a molecular switch involving the heat shock protein ClpC, which controls the activity of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1997;11:119–128. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.van Sinderen D, Galli G, Cosmina P, de Ferra F, Withoff S, Venema G, Grandi G. Characterization of the srfA locus of Bacillus subtilis: only the valine-activating domain of srfA is involved in the establishment of genetic competence. Mol Microbiol. 1993;8:833–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.van Sinderen D, Luttinger A, Kong L, Dubnau D, Venema G, Hamoen L. comK encodes the competence transcription factor, the key regulatory protein for competence development in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:455–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vollenbroich D, Mehta N, Zuber P, Vater J, Kamp R M. Analysis of surfactin synthetase subunits in srfA mutants of Bacillus subtilis OKB105. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:395–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.395-400.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zuber P, Losick R. Role of AbrB in the Spo0A- and Spo0B-dependent utilization of a sporulation promoter in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987;169:2223–2230. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2223-2230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zuber P, Losick R. Use of a lacZ fusion to study the role of the spo0 genes of Bacillus subtilis in developmental regulation. Cell. 1983;35:275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90230-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]