Abstract
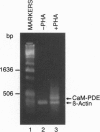
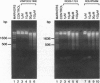
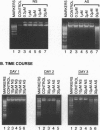
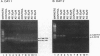
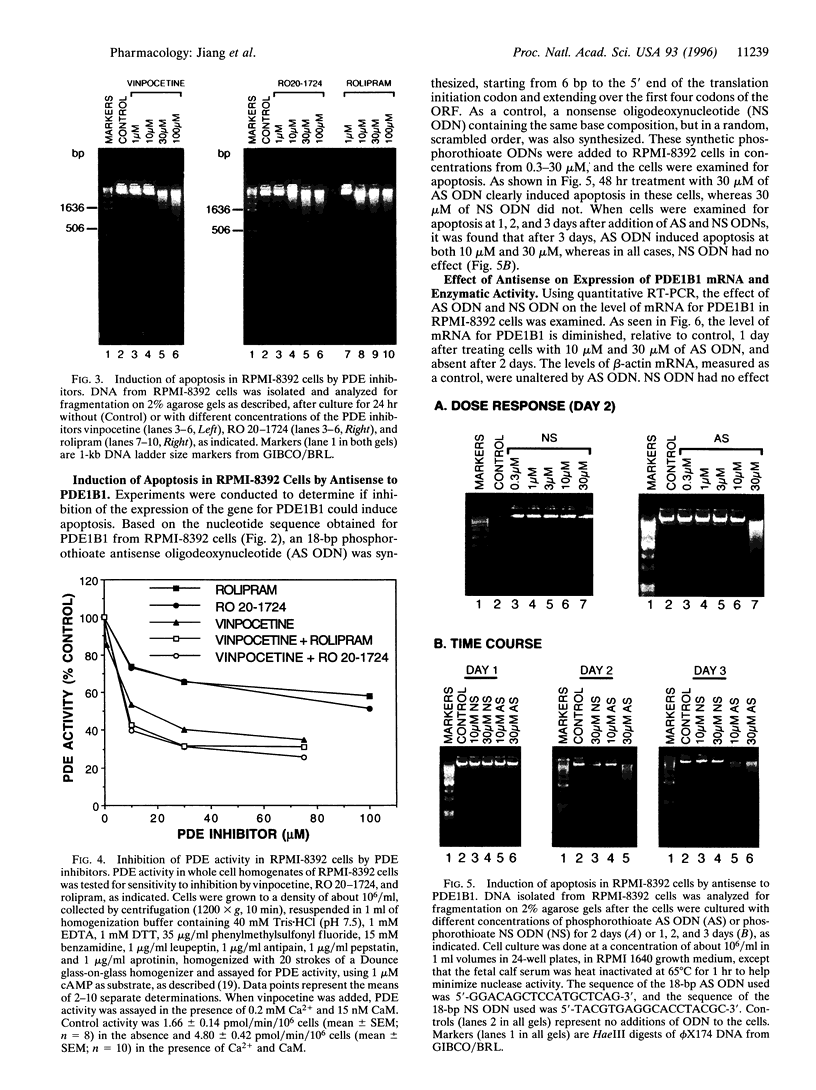
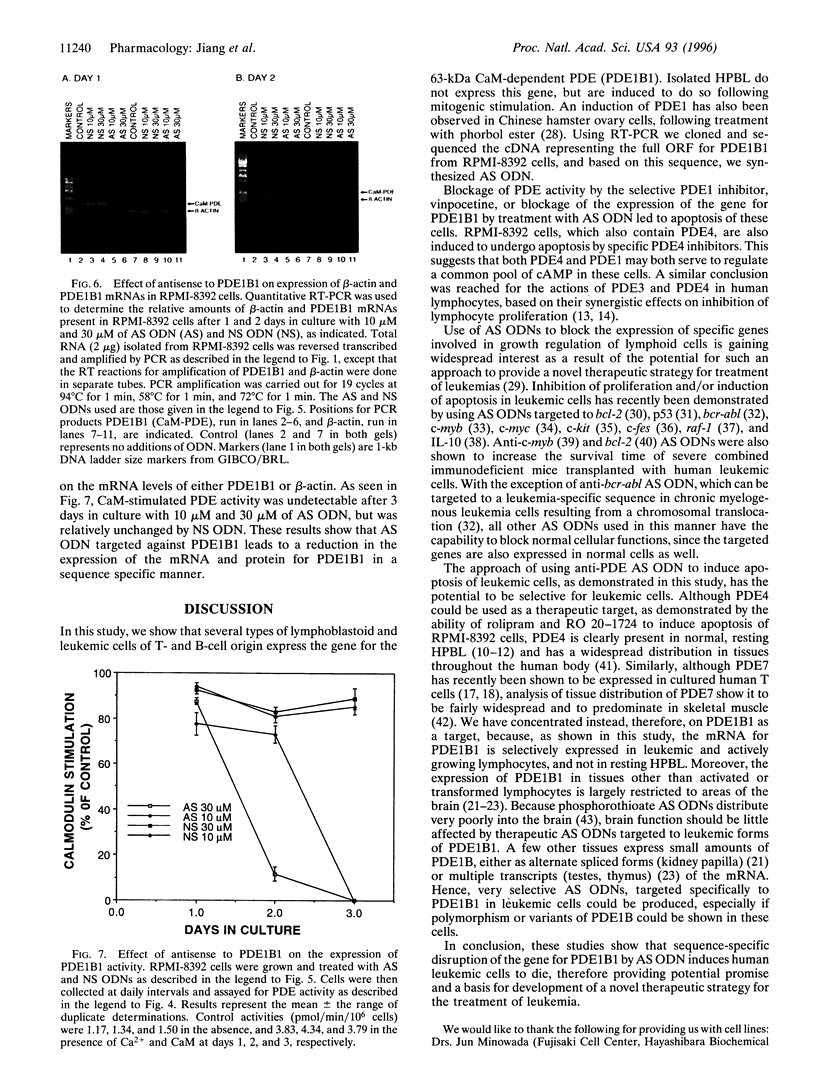
Cytosolic extracts from a human lymphoblastoid B-cell line, RPMI-8392, established from a patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia, contain two major forms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE): Ca2+-calmodulin dependent PDE (PDE1) and cAMP-specific PDE (PDE4). In contrast, normal quiescent human peripheral blood lymphocytes (HPBL) are devoid of PDE1 activity [Epstein, P. M., Moraski, S., Jr., and Hachisu, R. (1987) Biochem. J. 243, 533-539]. Using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), we show that the mRNA encoding the 63-kDa form of PDE1 (PDE1B1) is expressed in RPMI-8392 cells, but not in normal, resting HPBL. This mRNA is, however, induced in HPBL following mitogenic stimulation by phytohemagglutinin (PHA). Also using RT-PCR, the full open reading frame for human PDE1B1 cDNA was cloned from RPMI-8392 cells and it encodes a protein of 536 amino acids with 96% identity to bovine, rat, and mouse species. RT-PCR also identifies the presence of PDE1B1 in other human lymphoblastoid and leukemic cell lines of B- (RPMI-1788, Daudi) and T-(MOLT-4, NA, Jurkat) cell origin. Inhibition of PDE1 or PDE4 activity by selective inhibitors induced RPMI-8392 cells, as well as the other cell lines, to undergo apoptosis. Culture of RPMI-8392 cells with an 18-bp phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotide, targeted against the translation initiation region of the RPMI-8392 mRNA, led to a specific reduction in the amount of PDE1B1 mRNA after 1 day, and its disappearance after 2 days, and induced apoptosis in these cells in a sequence specific manner. This suggests that PDEs, particularly PDE1B1, because its expression is selective, may be useful targets for inducing the death of leukemic cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S., Temsamani J., Tang J. Y. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and stability of oligodeoxynucleotide phosphorothioates in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7595–7599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayever E., Iversen P. L., Bishop M. R., Sharp J. G., Tewary H. K., Arneson M. A., Pirruccello S. J., Ruddon R. W., Kessinger A., Zon G. Systemic administration of a phosphorothioate oligonucleotide with a sequence complementary to p53 for acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: initial results of a phase I trial. Antisense Res Dev. 1993 Winter;3(4):383–390. doi: 10.1089/ard.1993.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Conti M., Heaslip R. J. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Reifsnyder D. H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90066-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley J. K., Kadlecek A., Sherbert C. H., Seger D., Sonnenburg W. K., Charbonneau H., Novack J. P., Beavo J. A. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a "63"-kDa calmodulin-stimulated phosphodiesterase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18676–18682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Sims R. B., Valtieri M., Caracciolo D., Szczylik C., Venturelli D., Ratajczak M., Beran M., Gewirtz A. M. Normal and leukemic hematopoietic cells manifest differential sensitivity to inhibitory effects of c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotides: an in vitro study relevant to bone marrow purging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2351–2355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Bourne H. R., Tomkins G. M. Mechanism of lymphoma cell death induced by cyclic AMP. Am J Pathol. 1975 Oct;81(1):199–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Litwack G., Tomkins G. M. Induction of cytolysis of cultured lymphoma cells by adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and the isolation of resistant variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):76–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels P., Fichtel K., Lübbert H. Expression and regulation of human and rat phosphodiesterase type IV isogenes. FEBS Lett. 1994 Aug 22;350(2-3):291–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00788-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. M., Hachisu R. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase in normal and leukemic human lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;16:303–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. M., Mills J. S., Hersh E. M., Strada S. J., Thompson W. J. Activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from isolated human peripheral blood lymphocytes by mitogenic agents. Cancer Res. 1980 Feb;40(2):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. M., Mills J. S., Ross C. P., Strada S. J., Hersh E. M., Thompson W. J. Increased cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity associated with proliferation and cancer in human and murine lymphoid cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Nov;37(11):4016–4023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. M., Moraski S., Jr, Hachisu R. Identification and characterization of a Ca2+-calmodulin-sensitive cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase in a human lymphoblastoid cell line. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):533–539. doi: 10.1042/bj2430533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Manfredini R., Torelli U. Antisense strategies in leukemia. Haematologica. 1994 Mar-Apr;79(2):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz R. L., Hirsch K. M., Clark D. J., Holcombe V. N., Hurwitz M. Y. Induction of a calcium/calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase during phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocyte mitogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8901–8907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichimura M., Kase H. A new cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozyme expressed in the T-lymphocyte cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jun 30;193(3):985–990. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. The adenylate cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A pathway and regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith F. J., Bradbury D. A., Zhu Y. M., Russell N. H. Inhibition of bcl-2 with antisense oligonucleotides induces apoptosis and increases the sensitivity of AML blasts to Ara-C. Leukemia. 1995 Jan;9(1):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Maekawa T., Hirakawa K., Murakami A., Abe T. Alterations of c-myc expression by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides enhance the induction of apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Cancer Res. 1995 Mar 15;55(6):1379–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kizaki H., Suzuki K., Tadakuma T., Ishimura Y. Adenosine receptor-mediated accumulation of cyclic AMP-induced T-lymphocyte death through internucleosomal DNA cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5280–5284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanotte M., Riviere J. B., Hermouet S., Houge G., Vintermyr O. K., Gjertsen B. T., Døskeland S. O. Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is induced rapidly and with positive cooperativity by activation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-kinase I in a myeloid leukemia cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jan;146(1):73–80. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041460110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughney K., Martins T. J., Harris E. A., Sadhu K., Hicks J. B., Sonnenburg W. K., Beavo J. A., Ferguson K. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs corresponding to two human calcium, calmodulin-regulated, 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):796–806. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lømo J., Blomhoff H. K., Beiske K., Stokke T., Smeland E. B. TGF-beta 1 and cyclic AMP promote apoptosis in resting human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 15;154(4):1634–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfredini R., Grande A., Tagliafico E., Barbieri D., Zucchini P., Citro G., Zupi G., Franceschi C., Torelli U., Ferrari S. Inhibition of c-fes expression by an antisense oligomer causes apoptosis of HL60 cells induced to granulocytic differentiation. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):381–389. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcoz P., Prigent A. F., Lagarde M., Nemoz G. Modulation of rat thymocyte proliferative response through the inhibition of different cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoforms by means of selective inhibitors and cGMP-elevating agents. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;44(5):1027–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Orrenius S., Jondal M. Agents that elevate cAMP stimulate DNA fragmentation in thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1227–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meskini N., Hosni M., Nemoz G., Lagarde M., Prigent A. F. Early increase in lymphocyte cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity upon mitogenic activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jan;150(1):140–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Bloom T. J., Martins T., Loughney K., Ferguson K., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Beavo J. A., Wigler M. Isolation and characterization of a previously undetected human cAMP phosphodiesterase by complementation of cAMP phosphodiesterase-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12925–12932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obernolte R., Bhakta S., Alvarez R., Bach C., Zuppan P., Mulkins M., Jarnagin K., Shelton E. R. The cDNA of a human lymphocyte cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE IV) reveals a multigene family. Gene. 1993 Jul 30;129(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng B., Mehta N. H., Fernandes H., Chou C. C., Raveché E. Growth inhibition of malignant CD5+B (B-1) cells by antisense IL-10 oligonucleotide. Leuk Res. 1995 Mar;19(3):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(94)00129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polli J. W., Kincaid R. L. Molecular cloning of DNA encoding a calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase enriched in striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11079–11083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak M. Z., Kant J. A., Luger S. M., Hijiya N., Zhang J., Zon G., Gewirtz A. M. In vivo treatment of human leukemia in a scid mouse model with c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11823–11827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak M. Z., Luger S. M., DeRiel K., Abrahm J., Calabretta B., Gewirtz A. M. Role of the KIT protooncogene in normal and malignant human hematopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1710–1714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Swinnen J. V., Jin S. L., Van Wyk J. J., Conti M. A polymerase chain reaction strategy to identify and clone cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase cDNAs. Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding the 63-kDa calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18683–18688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robicsek S. A., Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Krzanowski J. J., Szentivanyi A., Polson J. B. Multiple high-affinity cAMP-phosphodiesterases in human T-lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robicsek S. A., Krzanowski J. J., Szentivanyi A., Polson J. B. High pressure liquid chromatography of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from purified human T-lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):554–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorski T., Nieborowska-Skorska M., Nicolaides N. C., Szczylik C., Iversen P., Iozzo R. V., Zon G., Calabretta B. Suppression of Philadelphia1 leukemia cell growth in mice by BCR-ABL antisense oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skorski T., Nieborowska-Skorska M., Szczylik C., Kanakaraj P., Perrotti D., Zon G., Gewirtz A., Perussia B., Calabretta B. C-RAF-1 serine/threonine kinase is required in BCR/ABL-dependent and normal hematopoiesis. Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 1;55(11):2275–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence S., Rena G., Sweeney G., Houslay M. D. Induction of Ca2+/calmodulin-stimulated cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE1) activity in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO) by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and by the selective overexpression of protein kinase C isoforms. Biochem J. 1995 Sep 15;310(Pt 3):975–982. doi: 10.1042/bj3100975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczylik C., Skorski T., Nicolaides N. C., Manzella L., Malaguarnera L., Venturelli D., Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. Selective inhibition of leukemia cell proliferation by BCR-ABL antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):562–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1857987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan C., Zhao A. Z., Bentley J. K., Loughney K., Ferguson K., Beavo J. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase enriched in olfactory sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9677–9681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Paskind M., Bolger G., Thompson W. J., Repaske D. R., Cutler L. S., Epstein P. M. A novel cyclic GMP stimulated phosphodiesterase from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 30;205(3):1850–1858. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]