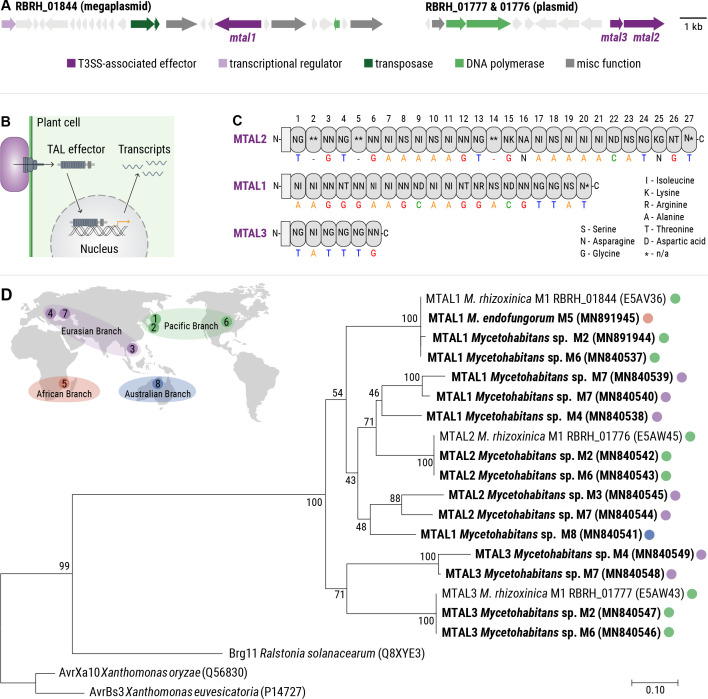
Fig 3.
Identification of predicted MTAL effectors from endofungal Mycetohabitans species. (A) Schematic illustration of the gene clusters encoding MTAL1 (RBRH_01844), MTAL2 (RBRH_01776), and MTAL3 (RBRH_01777) indicated in dark purple. (B) Mode of action of TALs from Xanthomonas sp. TALs are secreted directly into plant cells via the T3SS, translocate to the nucleus, and induce expression of target genes. (C) Schematic representation of the overall domain structure of M. rhizoxinica MTALs and the amino acid tandem repeats (top) that specify the target nucleotide sequence (bottom). Cryptic repeats that have less than 45% amino acid identity with core repeats are marked with an asterisk (*, n/a: not annotated). Modified from Lange et al. (30). (D) Phylogenetic tree of TAL proteins from eight endofungal Mycetohabitans species, and plant pathogenic R. solanacearum and Xanthomonas sp. MTAL sequences identified in this study are highlighted in bold and GenBank accession numbers are given in brackets (Table S3). The distribution of MTALs across the four Mycetohabitans branches is indicated as follows: green, Pacific branch; purple, Eurasian branch; orange, African branch; and blue, Australian branch.