Abstract
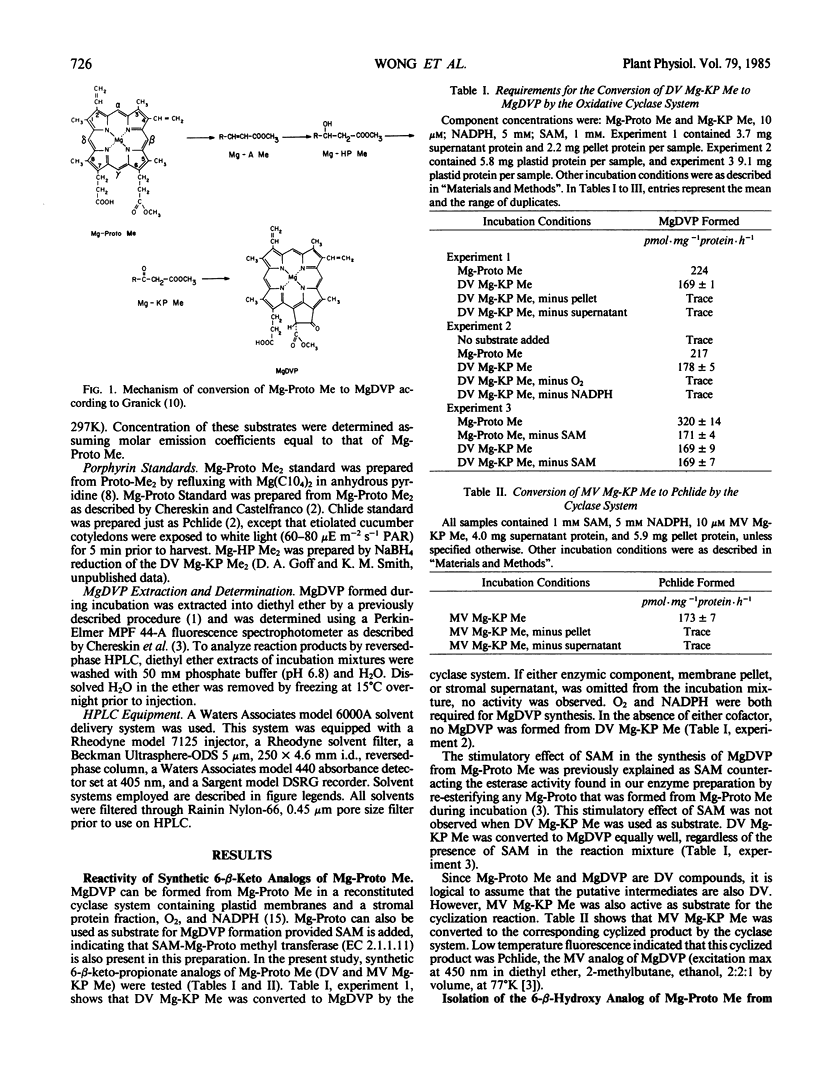
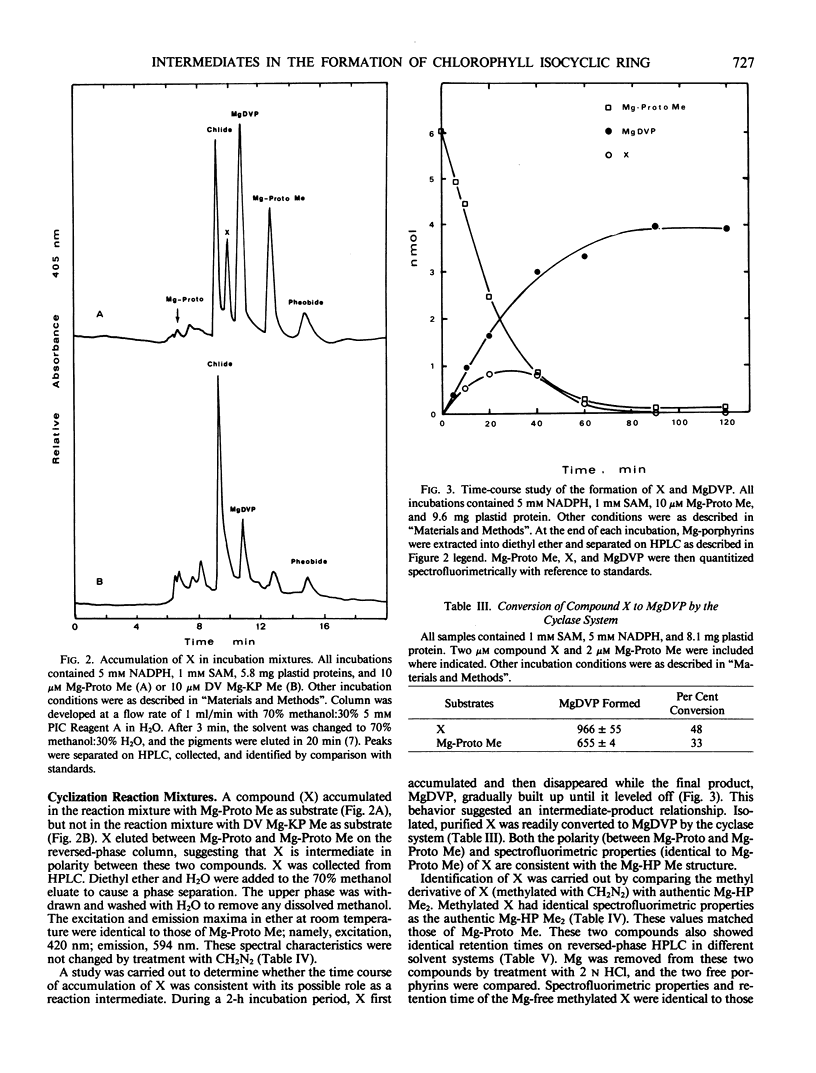
Cell-free, organelle-free synthesis of Mg-2,4-divinylpheoporphyrin a5 (MgDVP) from Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (Mg-Proto Me) has been described (Wong and Castelfranco 1984 Plant Physiol 75: 658-661). This system consists of plastid membrane and stromal fractions and requires O2, NAD(P)H and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM). The synthetic 6-methyl-β-ketopropionate analog of Mg-Proto Me was converted to MgDVP by the same catalytic system in the presence of O2 and NADPH. SAM was not required. A compound (X) displaying the kinetic behavior of an intermediate was isolated from reaction mixtures with Mg-Proto Me as the substrate, but not with the 6-methyl-β-ketopropionate analog as the substrate. X was identified as the 6-methyl-β-hydroxypropionate analog of Mg-Proto Me by conversion to the dimethyl ester with CH2N2 and comparison with authentic 6-β-hydroxydimethyl ester. X was converted to MgDVP by the same catalytic system in the presence of O2 and NADPH. We conclude that the conversion of Mg-Proto Me to MgDVP proceeds through the 6-β-hydroxy and the 6-β-ketopropionate esters in agreement with earlier suggestions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castelfranco P. A., Weinstein J. D., Schwarcz S., Pardo A. D., Wezelman B. E. The Mg insertion step in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Feb;192(2):592–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chereskin B. M., Castelfranco P. A. Effects of Iron and Oxygen on Chlorophyll Biosynthesis : II. OBSERVATIONS ON THE BIOSYNTHETIC PATHWAY IN ISOLATED ETIOCHLOROPLASTS. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jan;69(1):112–116. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chereskin B. M., Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A. In Vitro Synthesis of the Chlorophyll Isocyclic Ring : Transformation of Magnesium-Protoporphyrin IX and Magnesium-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester into Magnesium-2,4-Divinyl Pheoporphyrin A(5). Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):987–993. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. T., Jackson A. H., Kenner G. W., McCombie S. W., Smith K. M. Pyrroles and related compounds. 29. Vinylporphyrin beta-keto-esters. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1974;4:516–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R. K., Aronoff S. Investigations of the biogenesis of chlorophyll a. IV. Isolation and partial characterization of some biosynthetic intermediates between Mg-protoporphine IX monomethyl ester and Mg-vinylpheoporphine a5, obtained from Chlorella mutants. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth R. K., Aronoff S. Investigations on the biogenesis of chlorophyll a. 3. Biosynthesis of Mg-vinylpheoporphine a5 methylester from Mg-protoporphine IX monomethylester as observed in Chlorella mutants. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuesler T. P., Hanamoto C. M., Castelfranco P. A. Separation of Mg-Protoporphyrin IX and Mg-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester Synthesized de novo by Developing Cucumber Etioplasts. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):421–423. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANICK S. The structural and functional relationships between heme and chlorophyll. Harvey Lect. 1948 1949;Series 44:220–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S. I., Castelfranco P. A., Rebeiz C. A. Effect of the hypocotyl hook on greening in etiolated cucumber cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1970 Nov;46(5):705–707. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeiz C. A., Mattheis J. R., Smith B. B., Rebeiz C., Dayton D. F. Chloroplast biogenesis. Biosynthesis and accumulation of Mg-protoprophyrin IX monoester and longer wavelength metalloporphyrins by greening cotyledons. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Feb;166(2):446–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. B., Rebeiz C. A. Chloroplast biogenesis: detection of Mg-protoporphyrin chelatase in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 15;180(1):178–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A. Properties of the Mg-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester (Oxidative) Cyclase System. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):730–733. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Y. S., Castelfranco P. A. Resolution and Reconstitution of Mg-Protoporphyrin IX Monomethyl Ester (Oxidative) Cyclase, the Enzyme System Responsible for the Formation of the Chlorophyll Isocyclic Ring. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):658–661. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


