Abstract
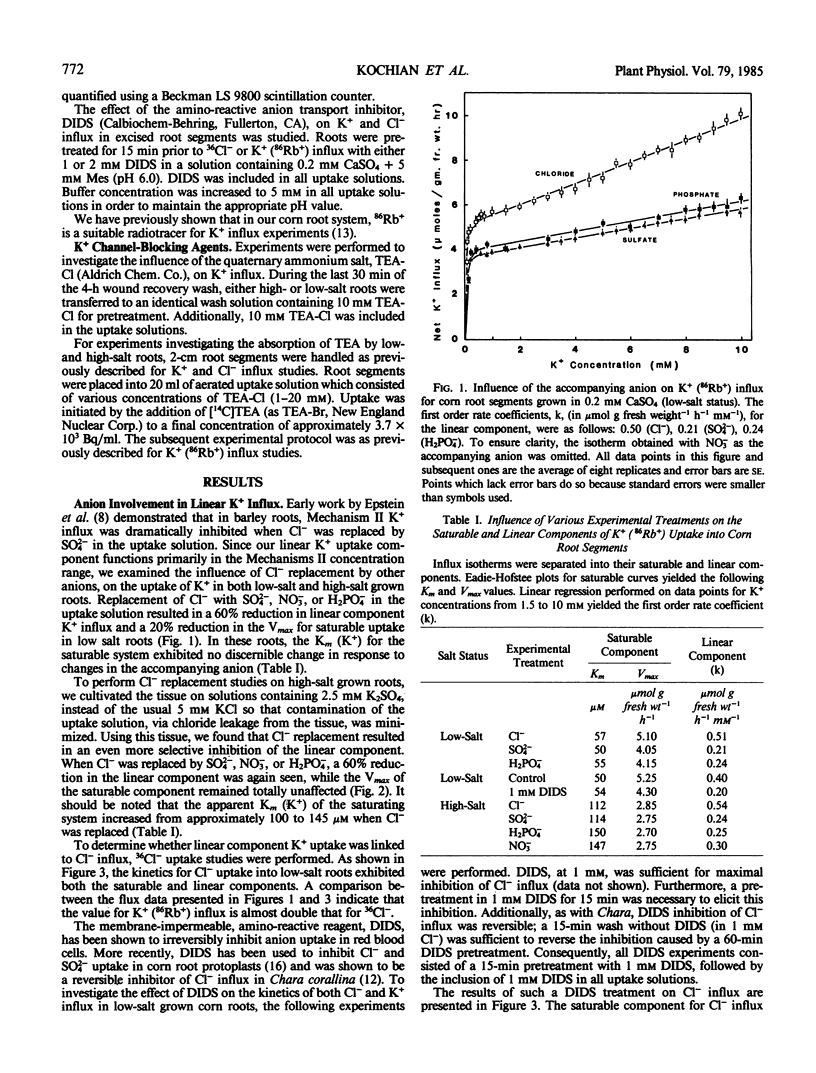
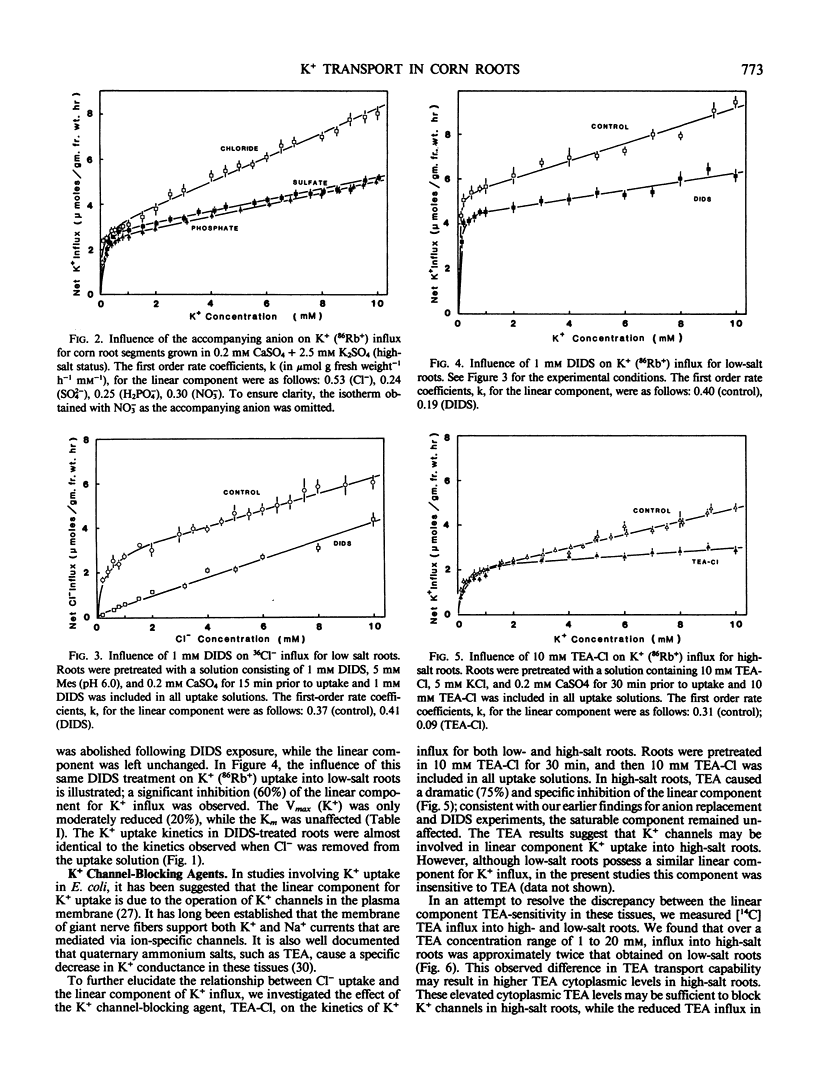
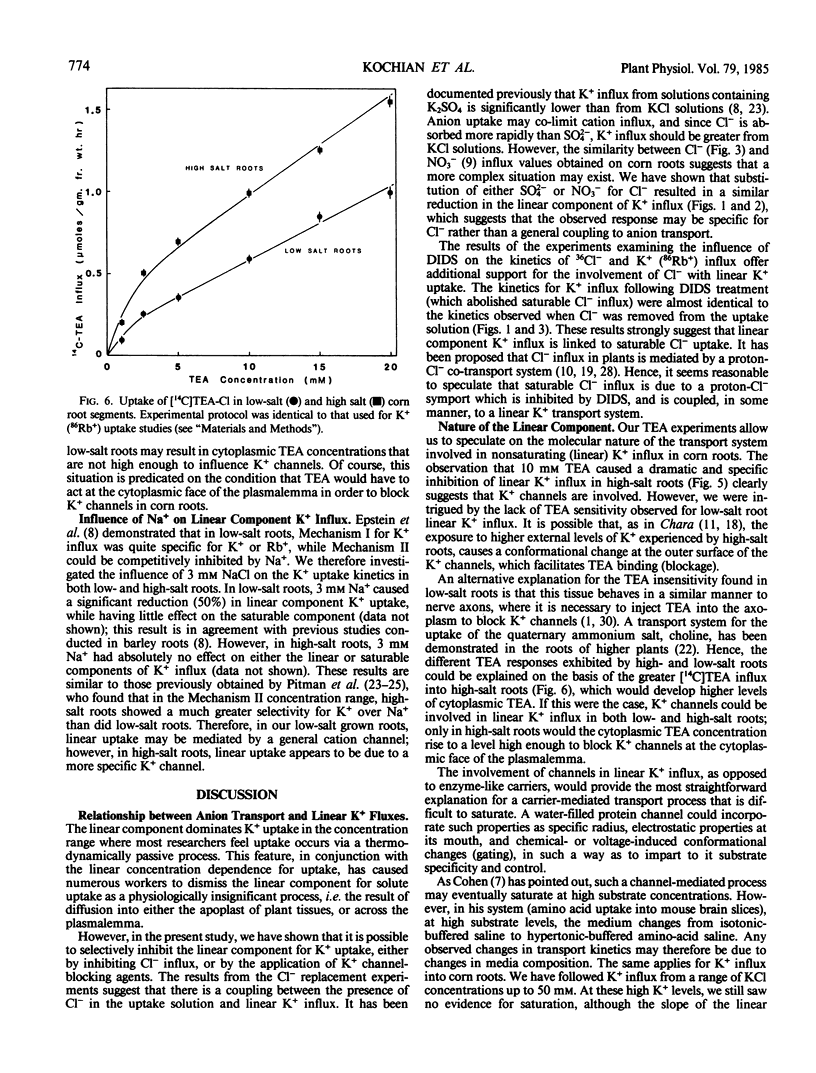
A detailed examination was conducted on the linear, or first-order kinetic component for K+(86Rb+) influx into root segments of both low- and high-salt grown corn seedlings (Zea mays [A632 × Oh 43]). In tissue from both low- and high-salt grown roots, replacement of Cl− in the uptake solution by either SO42−, H2PO4−, or NO3− caused a significant (50-60%) and specific inhibition of the linear component of K+ influx. The anion transport inhibitor, 4,4′-diisothiocyano-2,2′-disulfonic acid, was found to abolish saturable Cl− influx in corn roots while causing a significant (50-60%) and specific inhibition of the linear K+ uptake system; this inhibition was identical to that observed when Cl− was replaced by other anions in the K+ uptake solution. Additionally, the quaternary ammonium cation, tetraethylammonium, which has been shown to block K+ channels in nerve axons, also caused a dramatic (70%) and specific inhibition of the linear component of K+ influx, but this was obtained only in high-salt roots. The reasons for this difference are discussed with respect to the differing abilities of low- and high-salt roots to absorb tetraethylammonium.
Our present results indicate that the linear component of K+ influx may occur by a passive process involving transmembrane K+ channels. Fluxes through these K+ channels may be partly coupled to a saturating Cl− influx mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injection in squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):553–575. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. B., Spanswick R. M. Derepression of amino Acid-h cotransport in developing soybean embryos. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):781–786. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman J. M., Hanson J. B. Energy-linked Potassium Influx as Related to Cell Potential in Corn Roots. Plant Physiol. 1979 Nov;64(5):842–845. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.5.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman J. M., Hanson J. B. Mathematical analysis of the dependence of cell potential on external potassium in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman J. M., Lafayette P. R., Gronewald J. W., Hanson J. B. Effect of ATPase inhibitors on cell potential and k influx in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1139–1145. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Liang M. On the nature of the "non-saturable" migration of amino acids into Ehrlich cells and into rat jejunum. Bibl Laeger. 1966 Mar 14;112(3):524–531. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. R. A comparison of the rate equations, kinetic parameters, and activation energies for the initial uptake of L-lysine, L-valine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and alpha-aminoisobutyric acid by mouse brain slices. J Membr Biol. 1975 Jun 3;22(1):53–72. doi: 10.1007/BF01868163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Rains D. W., Elzam O. E. RESOLUTION OF DUAL MECHANISMS OF POTASSIUM ABSORPTION BY BARLEY ROOTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):684–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. A., Flesher D., Hageman R. H. Nitrate Uptake by Dark-grown Corn Seedlings: Some Characteristics of Apparent Induction. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):120–127. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keifer D. W., Franceschi V. R., Lucas W. J. Plasmalemma Chloride Transport in Chara corallina: Inhibition by 4,4'-Diisothiocyano-2,2'-Disulfonic Acid Stilbene. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1327–1334. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keifer D. W., Lucas W. J. Potassium Channels in Chara corallina: CONTROL AND INTERACTION WITH THE ELECTROGENIC H PUMP. Plant Physiol. 1982 Apr;69(4):781–788. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.4.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J. Potassium Transport in Corn Roots : II. The Significance of the Root Periphery. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):208–215. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J. Potassium transport in corn roots : I. Resolution of kinetics into a saturable and linear component. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1723–1731. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtner F. T., Spanswick R. M. Sucrose uptake by developing soybean cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1981 Sep;68(3):693–698. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. Inhibition of anion transport in corn root protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1981 Aug;68(2):435–438. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowendorf H. S., Slayman C. L., Slayman C. W. Phosphate transport in Neurospora. Kinetic characterization of a constitutive, low-affinity transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 24;373(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas W. J. HCO(3) Influx across the Plasmalemma of Chara corallina: Physiological and Biophysical Influence of 10 mm K. Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):487–493. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. W., Lucas W. J. A Reanalysis of the Two-Component Phloem Loading System in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1982 Mar;69(3):734–739. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.3.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. W., Lucas W. J. Sucrose and Glucose Uptake into Beta vulgaris Leaf Tissues : A Case for General (Apoplastic) Retrieval Systems. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1436–1443. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman M. G. Active H Efflux from Cells of Low-salt Barley Roots during Salt Accumulation. Plant Physiol. 1970 Jun;45(6):787–790. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.6.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A. Sugar transport in Neurospora crassa. II. A second glucose transport system. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3985–3987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


