Abstract
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (Fru2,6P2) appears to function as a regulator metabolite in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in animal tissues, yeast, and the photosynthetic cells of leaves. We have investigated the role of Fru2,6P2 in guard-cell protoplasts from Vicia faba L. and Pisum sativum L. (Argenteum mutant), and in epidermal strips purified by sonication from all cells except for the guard cells. Guard-cell protoplasts were separated into fractions enriched in cytosol and in chloroplasts by passing them through a nylon net, followed by silicone oil centrifugation. The cytosol contained a pyrophosphate: fructose 6-phosphate phosphotransferase (involved in glycolysis) which was strongly stimulated by Fru2,6P2. A cytosolic fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (a catalyst of gluconeogenesis) was inhibited by Fru2,6P2. There was virtually no fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase activity in guard-cell chloroplasts of V. faba. It is therefore unlikely that the starch formed in these chloroplasts originates from imported triose phosphates or phosphoglycerate.
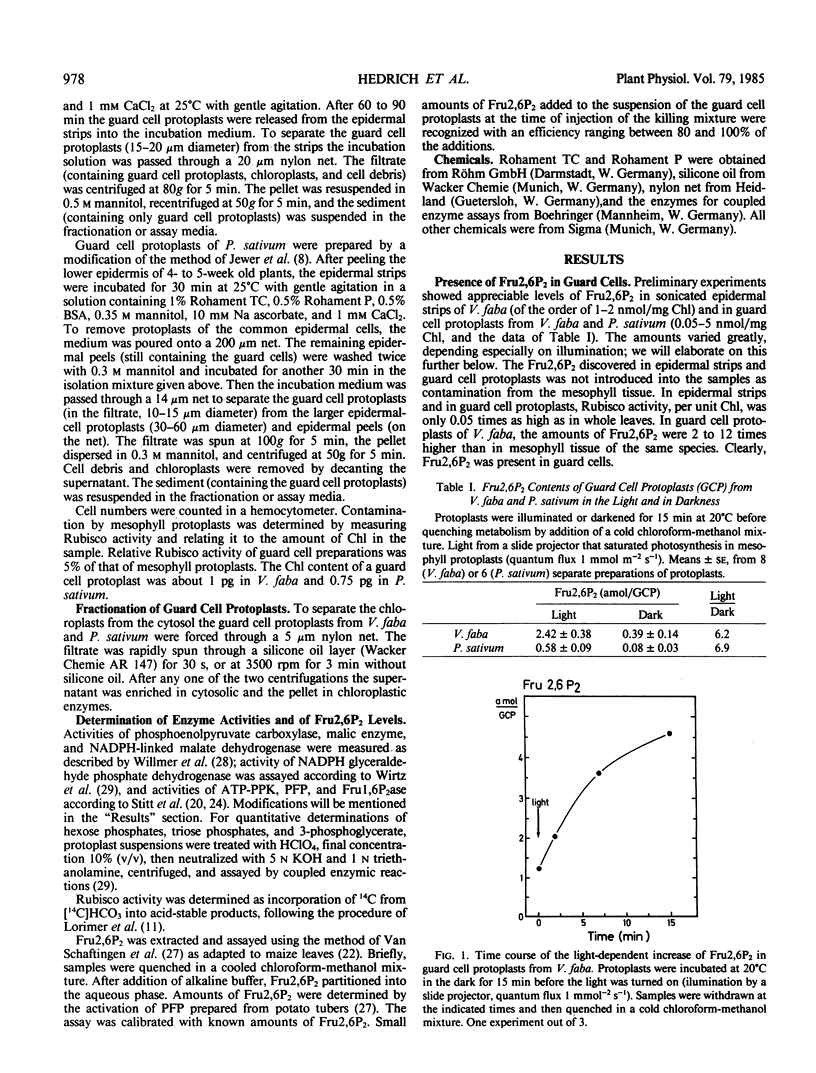
The level of Fru2,6P2 in guard-cell protoplasts and epidermal strips was about 0.1 to 1 attomole per guard cell in the dark (corresponding to 0.05 to 0.5 nanomole per milligram chlorophyll) and increased three- to tenfold within 15 minutes in the light. Within the same time span, hexose phosphate levels in guard-cell protoplasts declined to approximately one-half, indicating that acceleration of glycolysis involved stimulation of reactions using hexose phosphates. The level of Fru2,6P2 in guard cells appears to determine the direction in which carbohydrate metabolism proceeds.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cséke C., Weeden N. F., Buchanan B. B., Uyeda K. A special fructose bisphosphate functions as a cytoplasmic regulatory metabolite in green leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya E., Uyeda K. An activation factor of liver phosphofructokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5861–5864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kombrink E., Kruger N. J., Beevers H. Kinetic properties of pyrophosphate:fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from germinating castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):395–401. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo T., Kiriyama T., Kato Y., Kogame Y., Kaneko K., Hishida H., Mizuno Y., Ejiri K., Kawai K., Takeuchi A. [Clinical reliability and limitation of 99m Tc-pyrophosphate myocardial scintigraphy for the assessment of acute myocardial infarction--with special reference to evaluation of the area affected by infarction]. Kaku Igaku. 1982 Jul;19(6):871–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger N. J., Beevers H. Effect of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate on the kinetic properties of cytoplasmic fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase from germinating castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):49–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Improved methods for the activation and assay of catalytic activities. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw W. H., Manchester J., Dicamelli C. A., Randall D. D., Rapp B., Veith G. M. Photosynthetic carbon reduction pathway is absent in chloroplasts of Vicia faba guard cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6371–6375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Bulpin P. V., ap Rees T. Pathway of starch breakdown in photosynthetic tissues of Pisum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 15;544(1):200–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Gerhardt R., Kürzel B., Heldt H. W. A role for fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in the regulation of sucrose synthesis in spinach leaves. Plant Physiol. 1983 Aug;72(4):1139–1141. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.4.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Herzog B., Heldt H. W. Control of Photosynthetic Sucrose Synthesis by Fructose 2,6-Bisphosphate : I. Coordination of CO(2) Fixation and Sucrose Synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):548–553. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kirk C. A., Raschke K. Release of Malate from Epidermal Strips during Stomatal Closure. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):474–475. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Lederer B., Bartrons R., Hers H. G. A kinetic study of pyrophosphate: fructose-6-phosphate phosphotransferase from potato tubers. Application to a microassay of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):191–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07039.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmer C. M., Pallas J. E., Black C. C. Carbon dioxide metabolism in leaf epidermal tissue. Plant Physiol. 1973 Nov;52(5):448–452. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.5.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz W., Stitt M., Heldt H. W. Enzymic determination of metabolites in the subcellular compartments of spinach protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jul;66(1):187–193. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


