Abstract
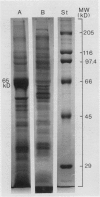
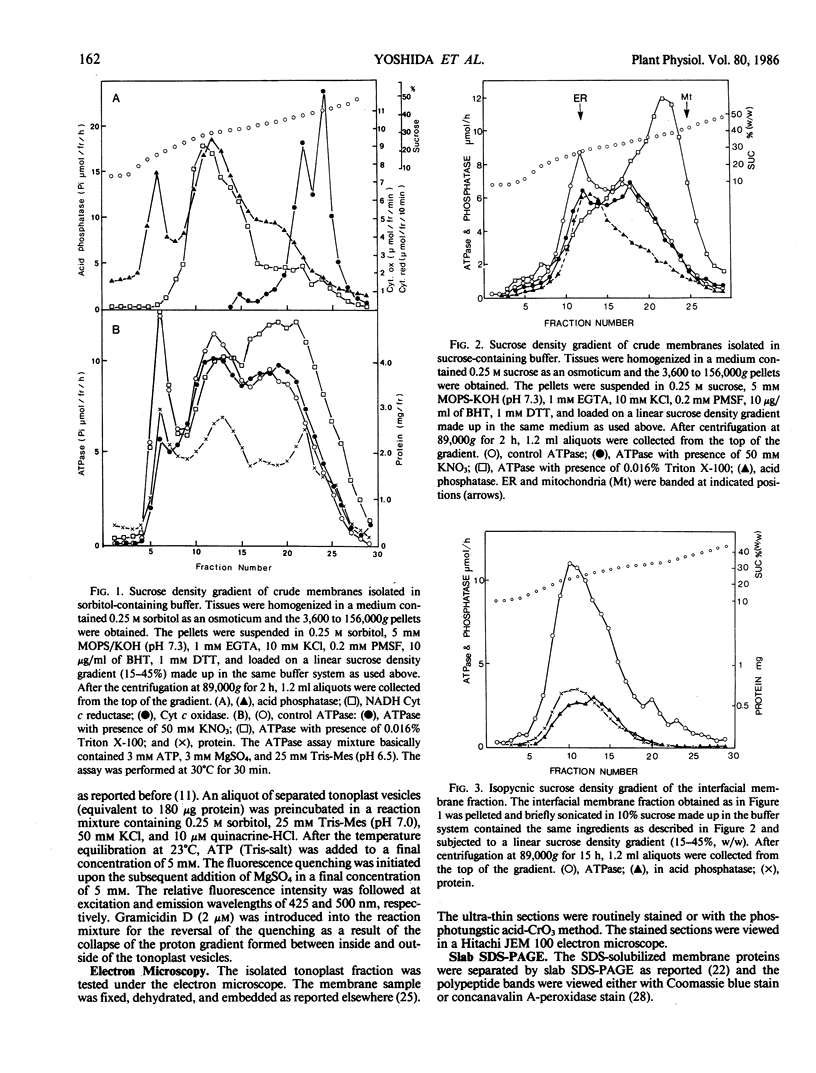
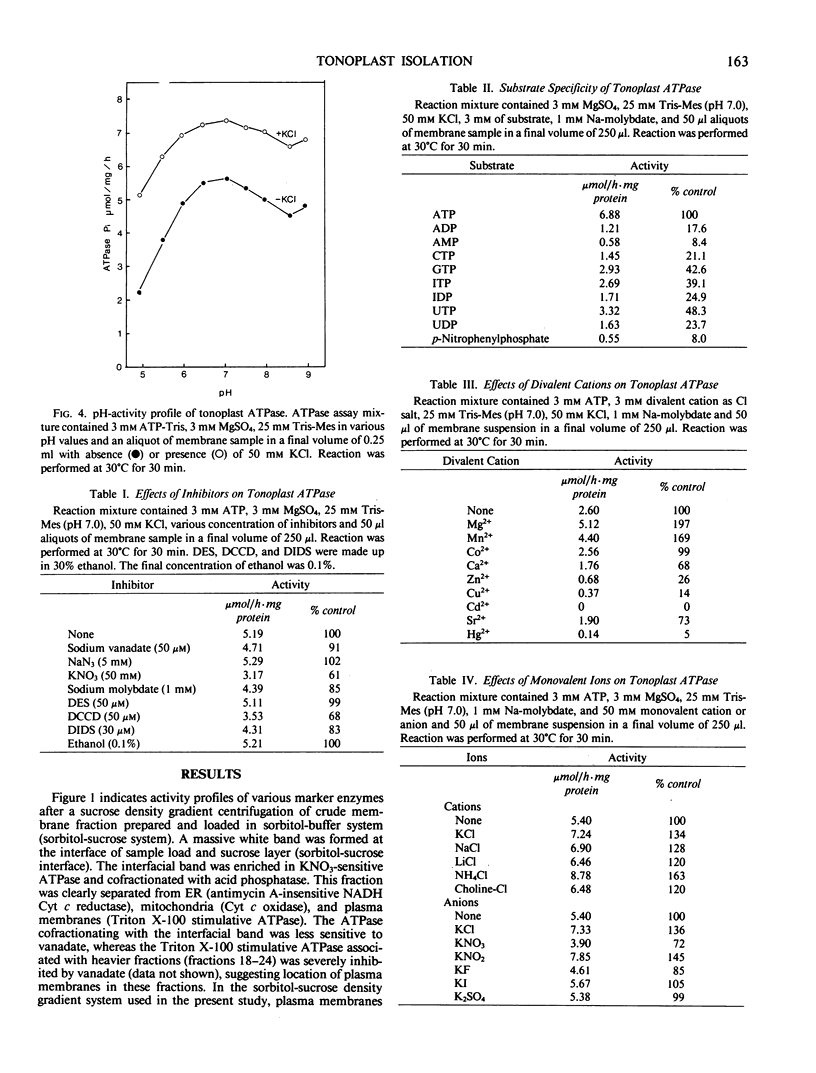
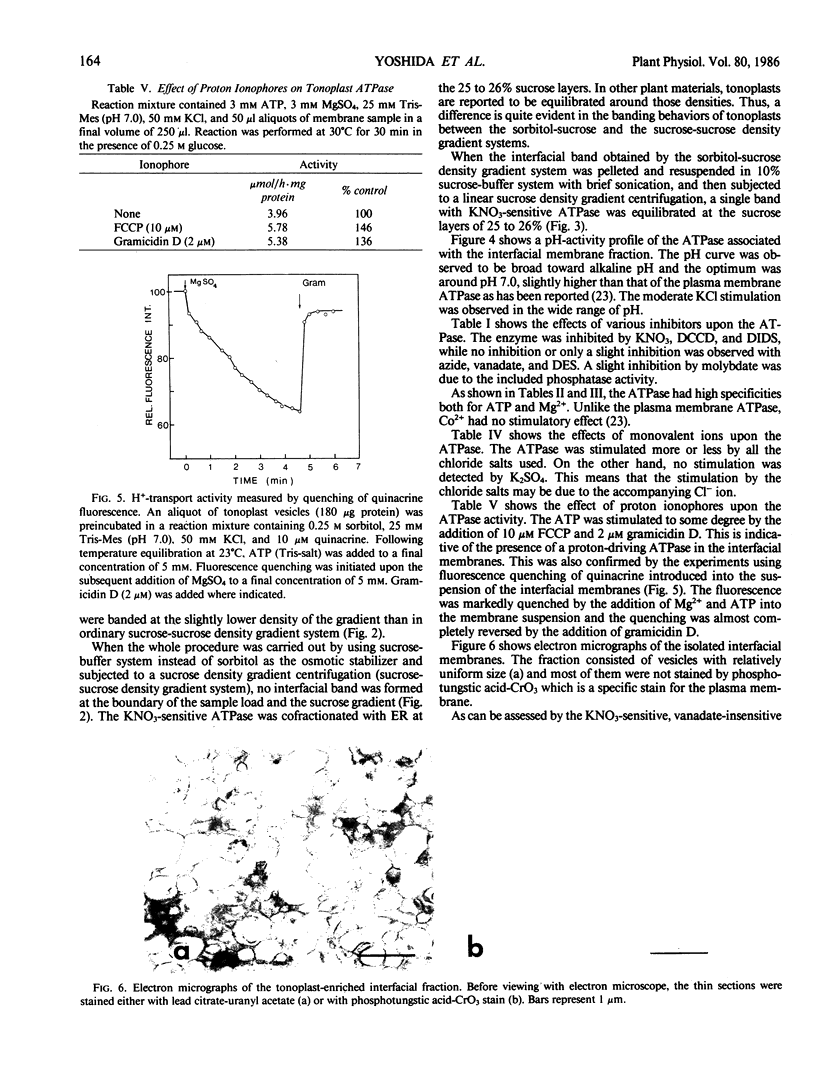
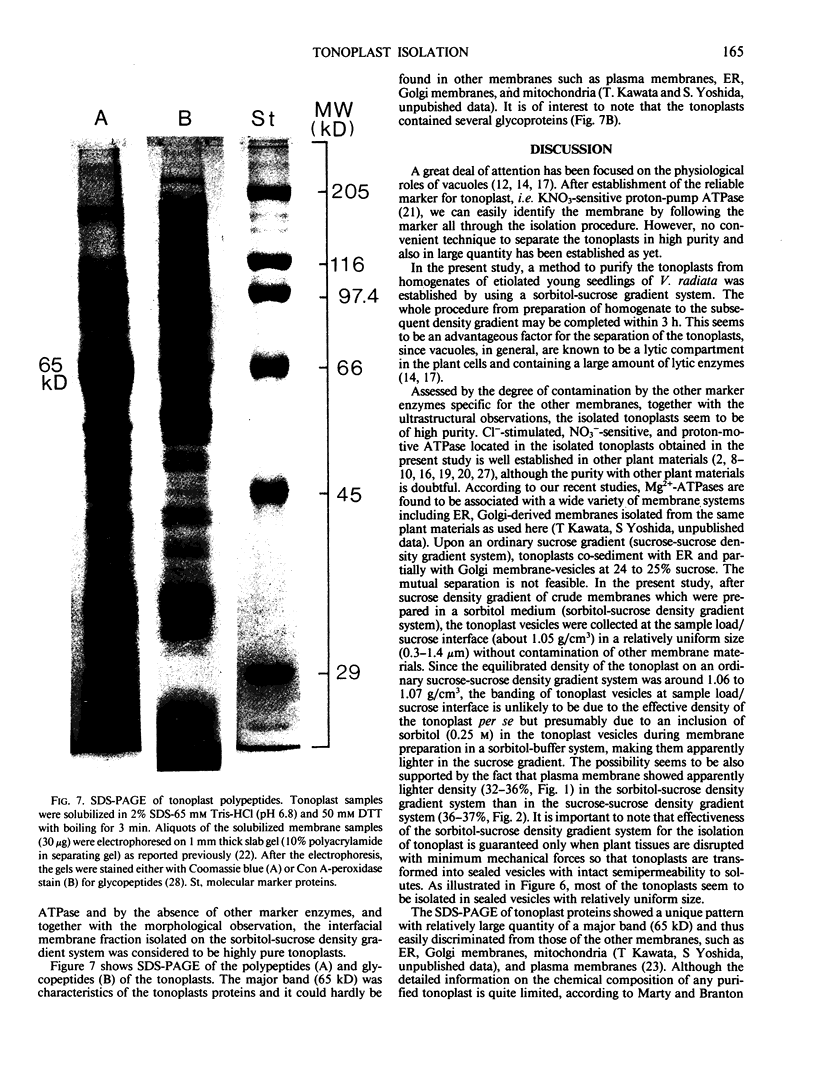
Tonoplasts were isolated in a high purity from etiolated young seedlings of Vigna radiata L. (mung bean) utilizing a sucrose density gradient system. The excised hypocotyls were homogenized in a sorbitol-buffer system and the 3,600 to 156,000g pellets obtained after the differential centrifugations were suspended in a sorbitol medium and loaded on a linear sucrose density gradient. After centrifugation at 89,000g for 2 hours, tonoplasts were banded at the sample load/sucrose interface. Assessed by electron microscopy and marker enzymes, the purity and the quantity were found to be sufficient for biochemical and biophysical analyses. The tonoplasts were associated with NO3−-sensitive and vana-date-insensitive ATPase. The tonoplast ATPase was stimulated by proton ionophores such as carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenyl-hydrazone and gramicidin D, suggesting a proton-pumping enzyme. In the presence of ATP and Mg2+, a proton gradient was formed in the isolated tonoplast vesicles as assessed by fluorescence quenching of quinacrine. The tonoplasts contained several kinds of mannosylated or glycosylated glycoproteins and a major protein (65 kilodaltons) which was unique to the membranes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A. B., O'neill S. D., Spanswick R. M. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: I. Identification and Characterization of an Anion-Sensitive H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):538–544. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckhout T. J. Characterization of Ca Transport in Purified Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Vesicles from Lepidium sativum L. Roots. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):962–967. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanson A., McNaughton E., Taiz L. Evidence for a KCl-Stimulated, Mg-ATPase on the Golgi of Corn Coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):498–507. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill K. A., Holaway B., Sze H. Separation of two types of electrogenic h-pumping ATPases from oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Dec;73(4):921–928. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill K. A., Sze H. Anion-sensitive, h-pumping ATPase in membrane vesicles from oat roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):610–617. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Bennett A. B., Spanswick R. M. Localization of a proton-translocating ATPase on sucrose gradients. Plant Physiol. 1982 Oct;70(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.4.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Giorgi D. L., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of a proton-translocating ATPase in microsomal vesicles from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1694–1699. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty F., Branton D. Analytical characterization of beetroot vacuole membrane. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):72–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. R., Keegstra K., Selman B. R. Characterization and localization of the ATPase associated with pea chloroplast envelope membranes. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):584–588. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettler I. J., Mandala S., Taiz L. Characterization of in vitro proton pumping by microsomal vesicles isolated from corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1738–1742. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze H. Nigericin-stimulated ATPase activity in microsomal vesicles of tobacco callus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5904–5908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura M., Yoshida S. Involvement of Plasma Membrane Alterations in Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):818–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Sarinana F. O. The staining of sciatic nerve glycoproteins on polyacrylamide gels with concanavalin A-peroxidase. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90597-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Kawata T., Uemura M., Niki T. Properties of Plasma Membrane Isolated from Chilling-Sensitive Etiolated Seedlings of Vigna radiata L. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):152–160. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Uemura M., Niki T., Sakai A., Gusta L. V. Partition of membrane particles in aqueous two-polymer phase system and its practical use for purification of plasma membranes from plants. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):105–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]