Abstract
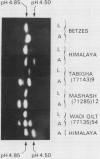
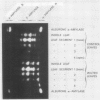
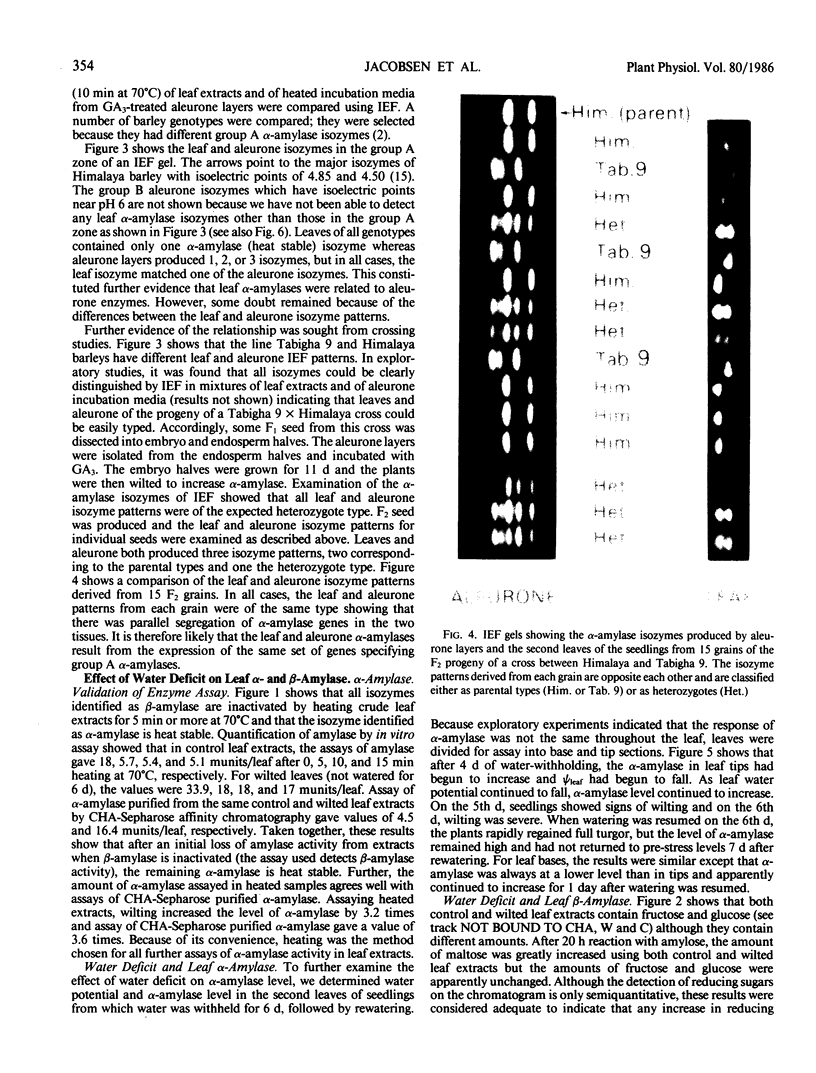
The amylases of the second leaves of barley seedlings (Hordeum vulgare L. cv Betzes) were resolved into eight isozymes by isoelectric focusing, seven of which were β-amylase and the other, α-amylase. The α-amylase had the same isoelectric point as one of the gibberellin-induced α-amylase isozymes in the aleurone layer. This and other enzyme characteristics indicated that the leaf isozyme corresponded to the type A aleurone α-amylase (low pI group). Crossing experiments indicated that leaf and type A aleurone isozymes resulted from expression of the same genes.
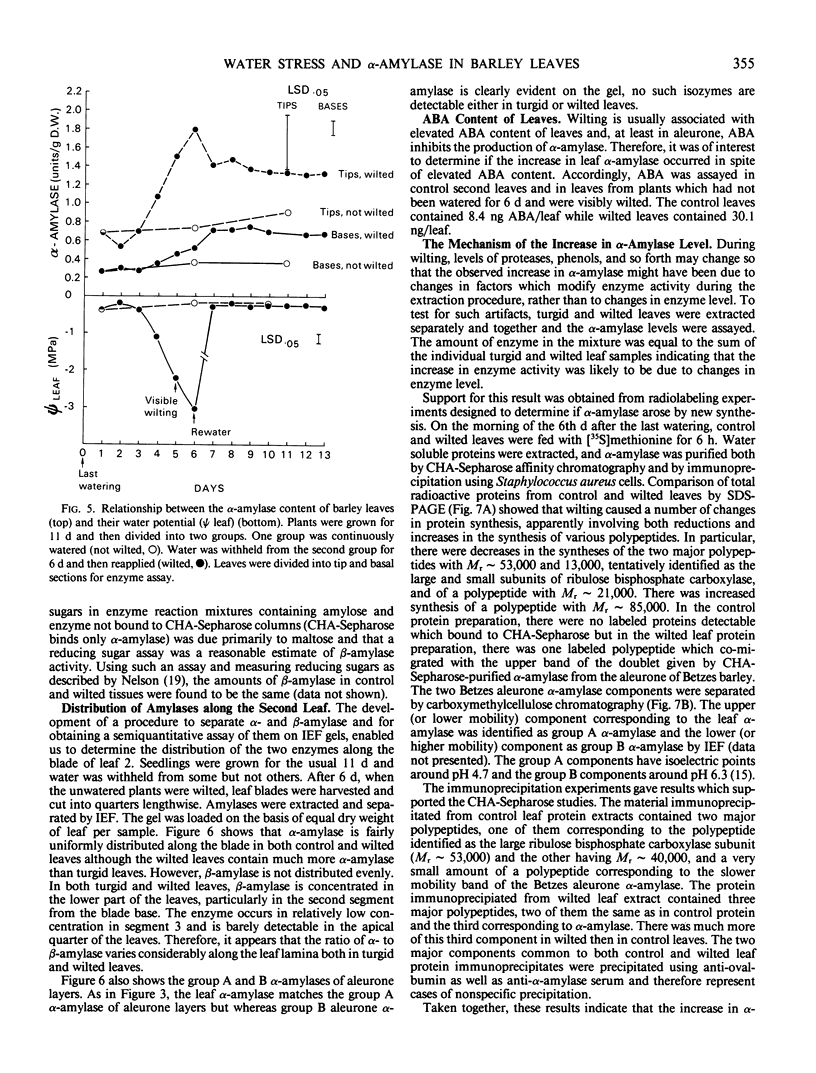
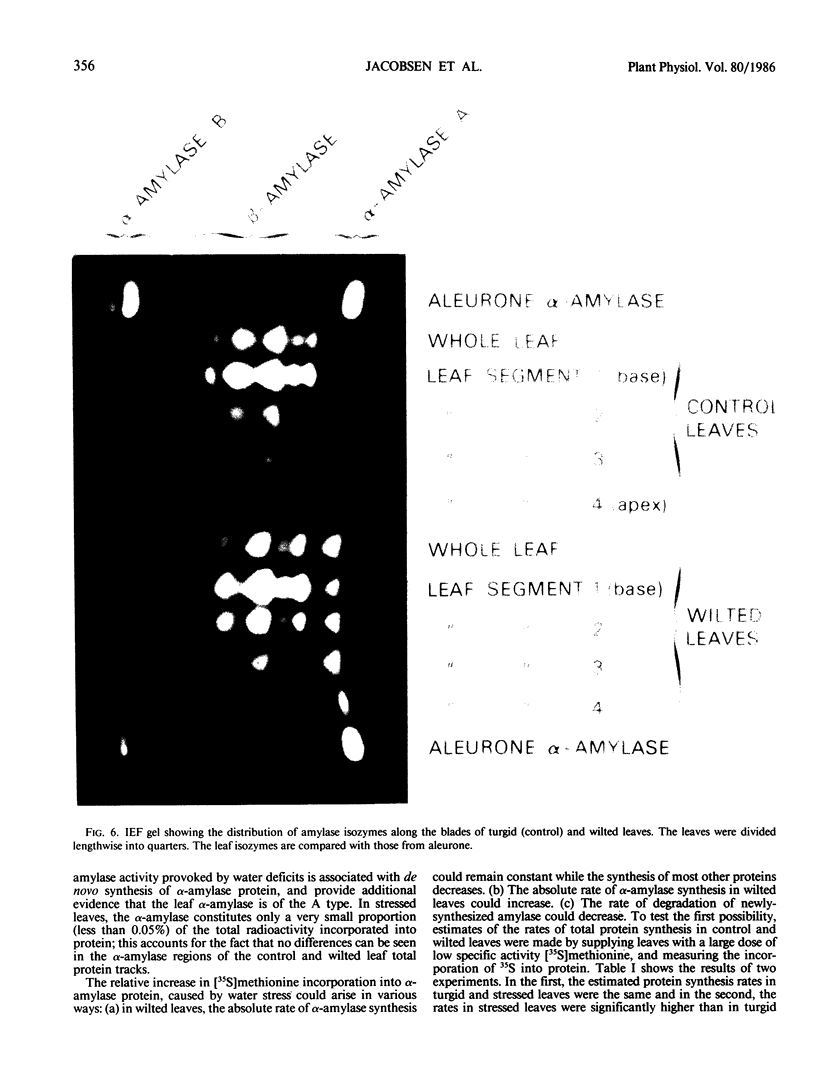
In unwatered seedlings, leaf α-amylase increased as leaf water potential decreased and ABA increased. Water stress had no effect on β-amylase. α-Amylase occurred uniformly along the length of the leaf but β-amylase was concentrated in the basal half of the leaf. Cell fractionation studies indicated that none of the leaf α-amylase occurred inside chloroplasts.
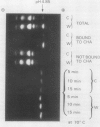
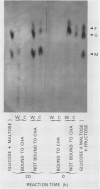
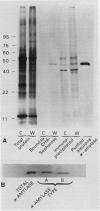
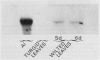
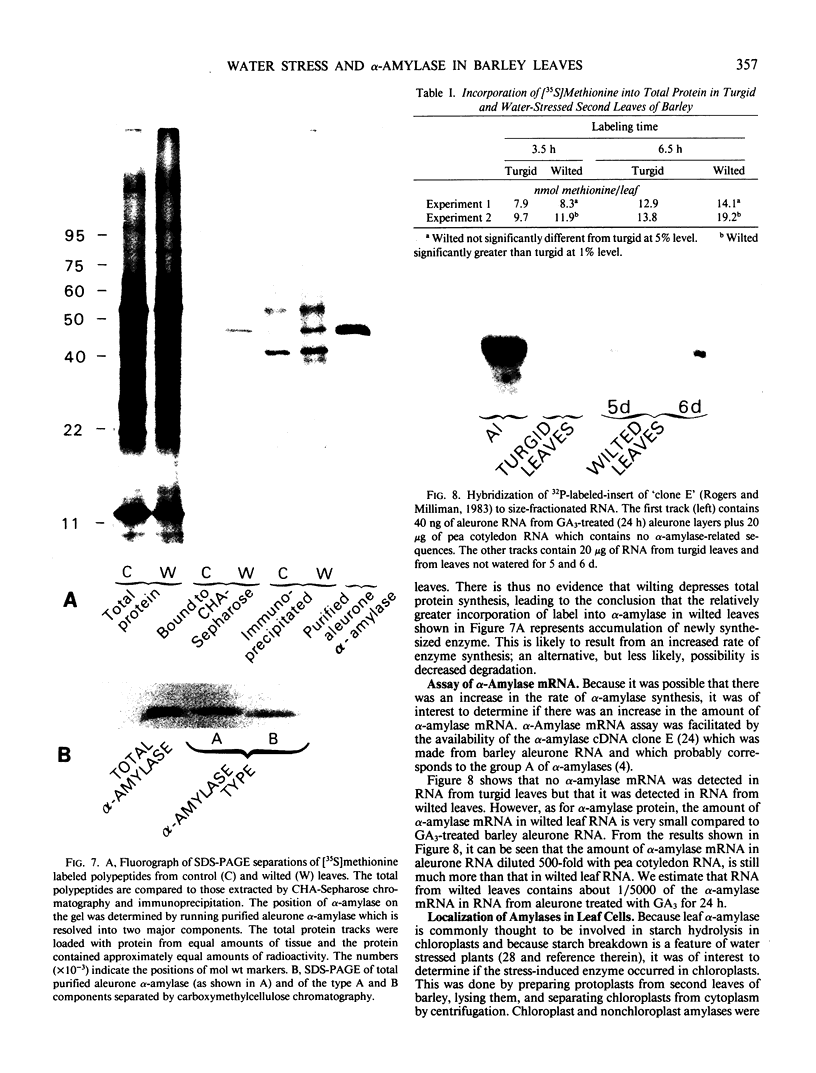
Leaf radiolabeling experiments followed by extraction of α-amylase by affinity chromatography and immunoprecipitation showed that increase of α-amylase activity involved synthesis of the enzyme. However, water stress caused no major change in total protein synthesis. Hybridization of a radiolabeled α-amylase-related cDNA clone to size fractionated RNA showed that water-stressed leaves contained much more α-amylase mRNA than unstressed plants. The results of these and other studies indicate that regulation of gene expression may be a component in water-stress induced metabolic changes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandler P. M., Higgins T. J., Randall P. J., Spencer D. Regulation of Legumin Levels in Developing Pea Seeds under Conditions of Sulfur Deficiency: Rates of Legumin Synthesis and Levels of Legumin mRNA. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):47–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrispeels M. J., Varner J. E. Gibberellic Acid-enhanced synthesis and release of alpha-amylase and ribonuclease by isolated barley and aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):398–406. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhindsa R. S., Cleland R. E. Water stress and protein synthesis: I. Differential inhibition of protein synthesis. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):778–781. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G. E., Robinson S. P., Tyler N. J., Walker D. A. Photosynthesis by isolated protoplasts, protoplast extracts, and chloroplasts of wheat: influence of orthophosphate, pyrophosphate, and adenylates. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):313–319. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Jacobsen J. V., Zwar J. A. Regulated expression of three alcohol dehydrogenase genes in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):573–581. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Scott N. A. Betaine Synthesis from Radioactive Precursors in Attached, Water-stressed Barley Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):342–348. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila J. J., Papp J. E., Schultz G. A., Bewley J. D. Induction of heat shock protein messenger RNA in maize mesocotyls by water stress, abscisic Acid, and wounding. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):270–274. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Higgins T. J. Characterization of the alpha-Amylases Synthesized by Aleurone Layers of Himalaya Barley in Response to Gibberellic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1647–1653. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Scandalios J. G., Varner J. E. Multiple forms of amylase induced by gibberellic acid in isolated barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):367–371. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi C., Gibbs M. Starch Degradation in Synchronously Grown Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Characterization of the Amylase. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):459–463. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen C. E., Safir G. R., Hanson A. D. Water potential in excised leaf tissue: comparison of a commercial dew point hygrometer and a thermocouple psychrometer on soybean, wheat, and barley. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jan;61(1):131–133. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okita T. W., Preiss J. Starch Degradation in Spinach Leaves: ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE AMYLASES AND R-ENZYME OF SPINACH LEAVES. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):870–876. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Measurement and preservation of the in vivo activation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in leaf extracts. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1165–1168. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Isolation and sequence analysis of a barley alpha-amylase cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8169–8174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D., Higgins T. J., Button S. C., Davey R. A. Pulse-labeling Studies on Protein Synthesis in Developing Pea Seeds and Evidence of a Precursor Form of Legumin Small Subunit. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):510–515. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R. Effect of Wilting on Carbohydrates during Incubation of Excised Bean Leaves in the Dark. Plant Physiol. 1971 Dec;48(6):792–794. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.6.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain R. R., Dekker E. E. Seed germination studies. I. Purification and properties of an alpha-amylase from the cotyledons of germinating peas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 6;122(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0926-6593(66)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]