Abstract
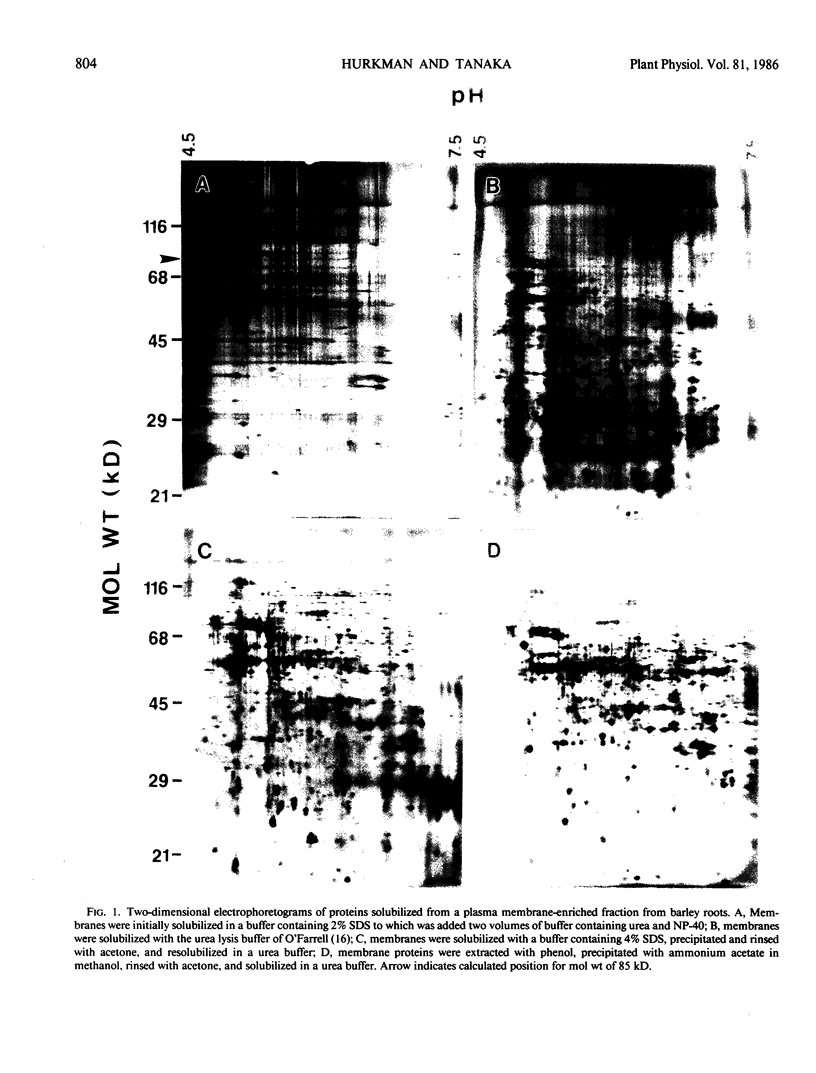
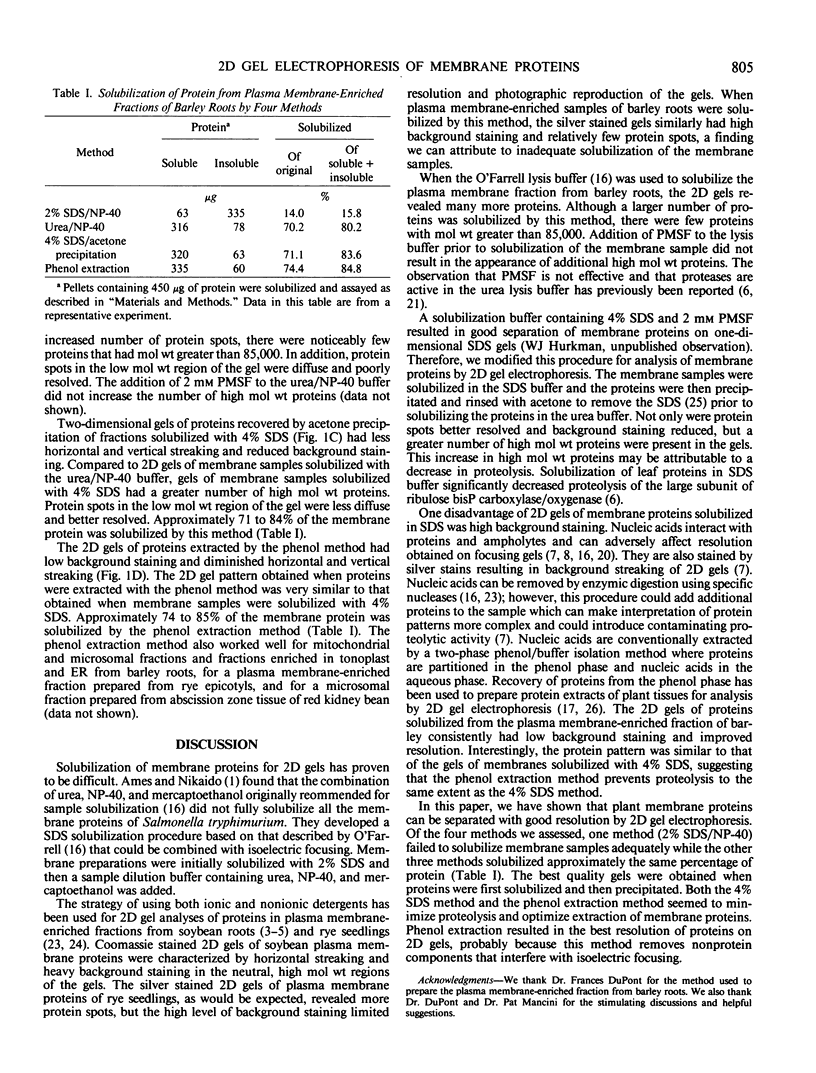
A plasma membrane-enriched fraction prepared from barley roots was analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Four methods of sample solubilization were assessed on silver stained gels. When membranes were solubilized with 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate followed by addition of Nonidet P-40, gels had high background staining and few proteins because of incomplete solubilization. Gels of membranes solubilized in urea and Nonidet P-40 had a greater number of proteins but proteins with molecular weights greater than 85,000 were absent and proteins with low molecular weights were diffuse. High molecular weight proteins were present in gels of membranes solubilized in 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate followed by acetone precipitation but background staining and streaking remained a problem. Gels of the best quality were obtained when membrane proteins were extracted with phenol and precipitated with ammonium acetate in methanol; background staining and streaking were diminished and proteins were clearly resolved. This method makes possible the resolution required for meaningful qualitative and quantitative comparisons of protein patterns on two-dimensional gels of plant membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booz M. L., Travis R. L. Electrophoretic comparison of polypeptides from enriched plasma membrane fractions from developing soybean roots. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1037–1043. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Hurkman W. J. Separation of the Mg-ATPases from the Ca-Phosphatase Activity of Microsomal Membranes Prepared from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):857–862. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer Y., Aspart L., Chartier Y. Auxin-induced regulation of protein synthesis in tobacco mesophyll protoplasts cultivated in vitro: I. Characteristics of auxin-sensitive proteins. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1027–1033. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. Protein contaminants of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A. M., Davies E. Ribonucleic Acid and Protein Metabolism in Pea Epicotyls : II. Response to Wounding in Aged Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):817–821. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A. M., Davies E. Ribonucleic Acid and protein metabolism in pea epicotyls : I. The aging process. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):809–816. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A., Davies E. Ribonucleic Acid and Protein Metabolism in Pea Epicotyls : III. Response to Auxin in Aged Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1983 Nov;73(3):822–827. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theologis A., Ray P. M. Early auxin-regulated polyadenylylated mRNA sequences in pea stem tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):418–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura M., Yoshida S. Involvement of Plasma Membrane Alterations in Cold Acclimation of Winter Rye Seedlings (Secale cereale L. cv Puma). Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):818–826. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert T. J., Dunkle L. D. Alterations in gene expression in sorghum induced by the host-specific toxin from Periconia circinata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6576–6580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurfluh L. L., Guilfoyle T. J. Auxin-induced changes in the patterns of protein synthesis in soybean hypocotyl. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurfluh L. L., Guilfoyle T. J. Auxin-induced changes in the population of translatable messenger RNA in elongating sections of soybean hypocotyl. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):332–337. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- des Francs C. C., Thiellement H., de Vienne D. Analysis of Leaf Proteins by Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis: Protease Action as Exemplified by Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/ Oxygenase Degradation and Procedure to Avoid Proteolysis during Extraction. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):178–182. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]