Abstract
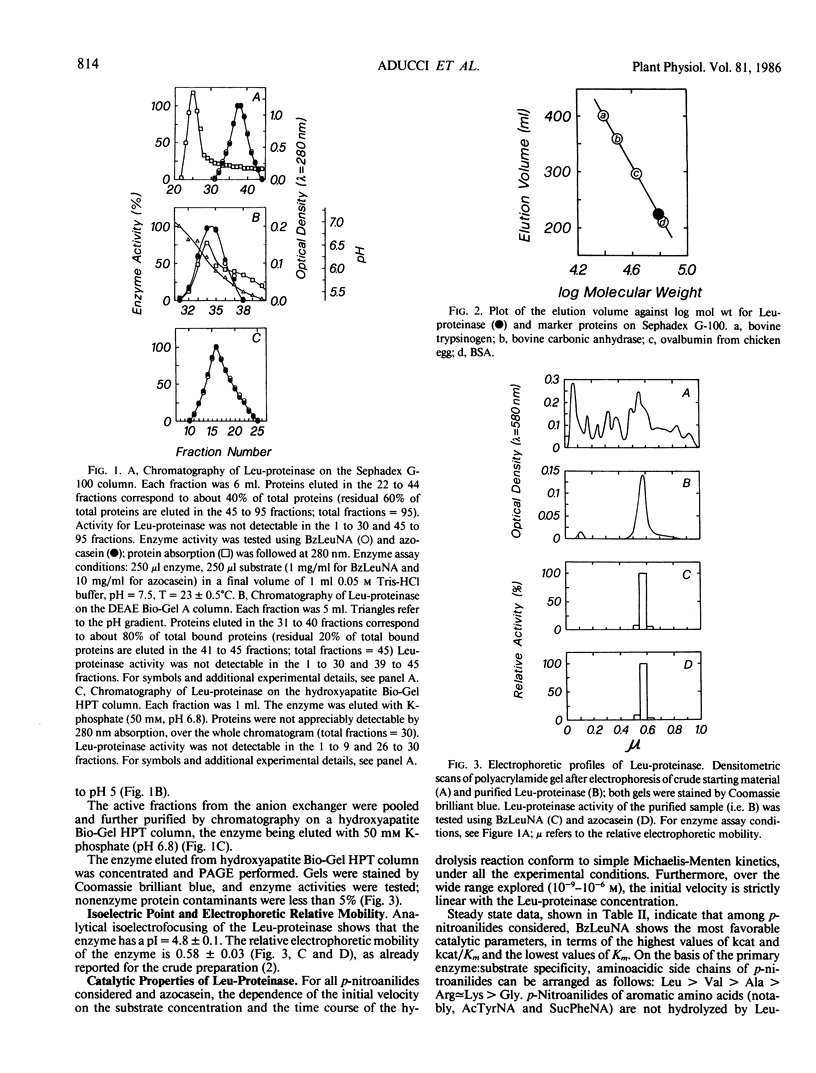
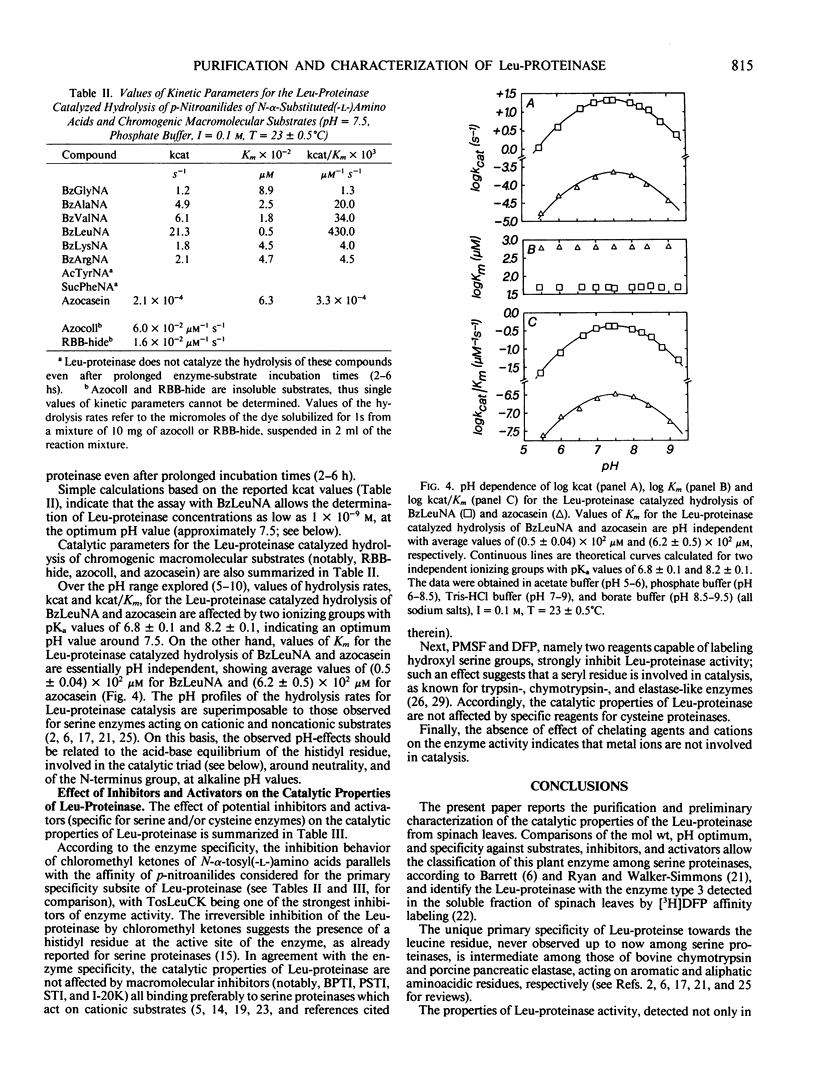
The leucine specific serine proteinase present in the soluble fraction of leaves from Spinacia oleracea L. (called Leu-proteinase) has been purified by acetone precipitation and a combination of gel-filtration, ion exchange, and adsorption chromatography. This enzyme shows a molecular weight of 60,000 ± 3,000 daltons, an isoelectric point of 4.8 ± 0.1, and a relative electrophoretic mobility of 0.58 ± 0.03. The Leu-proteinase catalyzed hydrolysis of p-nitroanilides of N-α-substituted(-l-)amino acids as well as of chromogenic macromolecular substrates has been investigated between pH 5 and 10 at 23 ± 0.5°C and I = 0.1 molar. The enzyme activity is characterized by a bell-shaped profile with an optimum pH value around 7.5, reflecting the acid-base equilibrium of groups with pKa values of 6.8 ± 0.1 and 8.2 ± 0.1 (possibly the histidyl residue present at the active site of the enzyme and the N-terminus group). Among the substrates considered, N-α-benzoyl-l-leucine p-nitroanilide shows the most favorable catalytic parameters and allows to determine an enzyme concentration as low as 1 × 10−9 molar. In agreement with the enzyme specificity, only N-α-tosyl-l-leucine chloromethyl ketone, di-isopropyl fluorophosphate and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, among compounds considered specific for serine enzymes, strongly inhibit the Leu-proteinase. Accordingly, the enzyme activity is insensitive to cations, chelating agents, sulfydryl group reagents, and activators.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonini E., Ascenzi P., Bolognesi M., Gatti G., Guarneri M., Menegatti E. Interaction between serine (pro)enzymes, and Kazal and Kunitz inhibitors. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 15;165(3):543–558. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini E., Ascenzi P. The mechanism of trypsin catalysis at low pH. Proposal for a structural model. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12449–12455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. The many forms and functions of cellular proteinases. Fed Proc. 1980 Jan;39(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borin G., Chessa G., Cavaggion G., Marchiori F., Müller-Esterl W. Synthesis of leupeptins and inhibition of proteinases. I. Inhibition of acrosin and trypsin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Nov;362(11):1435–1445. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.2.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger B. F., Edel F., Cooper A. G. The action of chymotrypsin on two new chromogenic substrates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jul;115(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(66)81058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKLE B. J., SMITH E. L. Crystalline papain; number and reactivity of thiol groups; chromatographic behavior. J Biol Chem. 1958 Feb;230(2):669–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMMEL J. R., SMITH E. L. Crystalline papain. I. Preparation, specificity, and activation. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):515–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C., Shaw E. Inactivation of trypsin-like enzymes with peptides of arginine chloromethyl ketone. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):826–842. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. Serine proteases: structure and mechanism of catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:331–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menegatti E., Bortolotti F., Minchiotti L., De Marco A. Isolation and characterization of a new form of the porcine pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor. Biochemical studies and high-resolution 1H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 22;707(1):50–58. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90395-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluyterman L. A. The activation reaction of papain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 11;139(2):430–438. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Shulman R. G. Crystallographic and NMR studies of the serine proteases. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:419–444. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


